| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Solanum melongena L. |
English
Name |
: |
Egg Plant |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Solanum cumingii Dunal, Solanum pressum Dunal, Solanum undatum Poiret sensu Ochse |
Family |
: |
Solanaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
An erect or suffrutescent, herbaceous perennial. Leaves simple, large, entire, lobed. Flowers blue, in clusters of 2 to 5. Fruit berry, large, yellow or dark purple, different shaped caps with persistent calyx. Seed many, yellow or cream, discoid. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Stimulant and lowers blood cholesterol (seed); analgesic, narcotic (leaf); antihaemorrhoidal and hypotensive (fruit). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Melongosides-A. B. E. F and H (steroidal saponins of seed); alkaloids (leaf); ascorbic acid, beta-carotene, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, choline, (fruit); ferulic acid (root) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Ascorbic acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
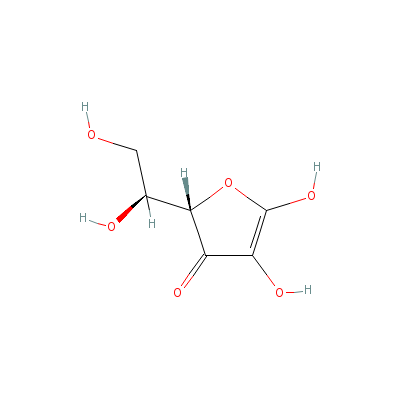
|
| beta-Carotene |
Not Available |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
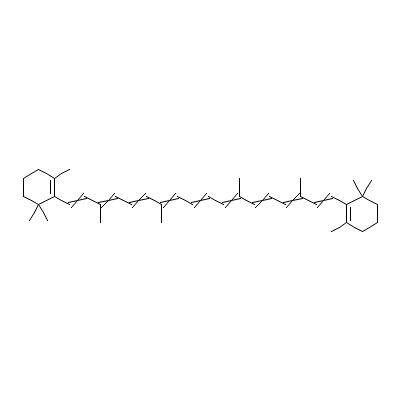
|
| Caffeic acid |
Not Available |
3-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)prop-2-enoic acid |
C9H8O4 |
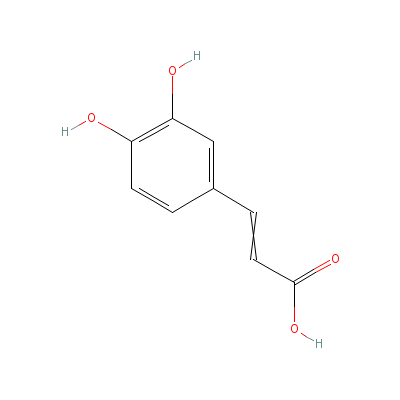
|
| Chlorogenic acid |
327-97-9 |
3-[3-(3,4-dihydroxyp
henyl)prop-2-enoylox
y]-1,4,5-trihydroxy-
cyclohexan
e-1-carb
oxylic acid |
C16H18O9 |
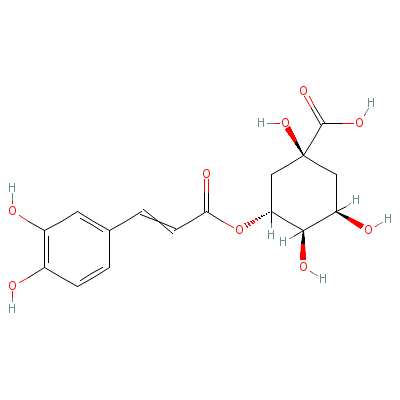
|
| Choline |
67-48-1 |
2-hydroxyethyl-trime
thyl-ammonium |
C5H14NO+ |
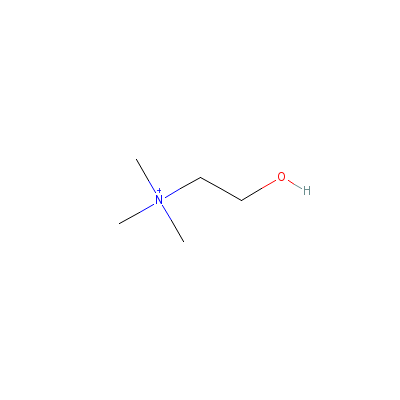
|
| Ferulic acid |
24276-84-4 |
3-(4-hydroxy-3-metho
xy-phenyl)prop-2-eno
ic acid |
C10H10O4 |
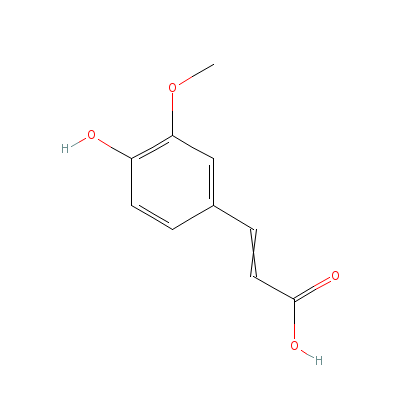
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Hemorrhoids, as a stimulant and lowering blood cholesterol (seed). It is also used as an antidote to poisonous mushrooms. It is bruised with vinegar and used as a poultice for cracked nipples, abscesses and haemorrhoids. A decoction is applied to discharging sores and internal haemorrhages. A soothing and emollient poultice for the treatment of burns, abscesses, cold sores and similar conditions can be made from the leaves. Aubergine leaves are toxic and should only be used externally. The ashes of the peduncle are used in the treatment of intestinal haemorrhages, piles and toothache. A decoction of the root is astringent. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|