| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Eclipta prostrata Linn |
English
Name |
: |
Thistles, Trailing Eclipta and Common Sand-Aster |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Eclipta alba (Linn.) Hassk. Cotula alba L., Verbesina alba L., Verbesina pseudoacmilla L., Eclipta erecta L. |
Family |
: |
Asteraceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
An erect or prostrate, much branched, roughly hairy, annual, rooting at the nodes; and grows as high as approximately 30 cm; the leaves are opposite, sessile and lanceolate; the flower-heads are white. Its seeds are small and black and resemble mustard seeds. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Kills nematodes, antihepatotoxic, depurative, antiinflammatory, antiviral, absorbent, relieves pain, ovicidal, stimulates the cardiovascular system, alleviates spasms (plant); laxative and emetic (root). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Wedelolactone, demethyl wedelolactone, stigmasterol, hentriacontanol, heptacosanol and terthienylmethanol (root); luteolin-7-O-glucosides and beta-amyrin (aerial part); ecliptine, nicotine and resin. |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Wedelolactone |
524-12-9 |
Not Available |
C16H10O7 |
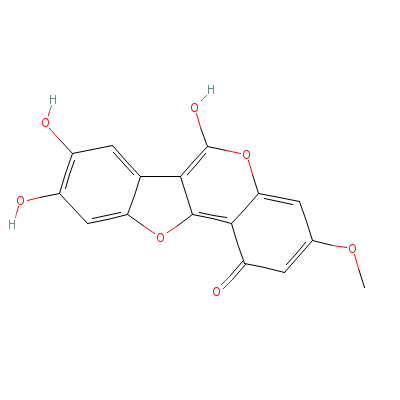
|
| Stigmasterol |
4736-55-4 |
17-(4-ethyl-1,5-dime
thyl-hex-2-enyl)-10,
13-dimethyl-1,2,4,5,
6,7,8,9,10
,11,12,1
3,14,15,16,17-hexade
cahydrocyclopenta[a]
phenanthren-3-one |
C29H48O |
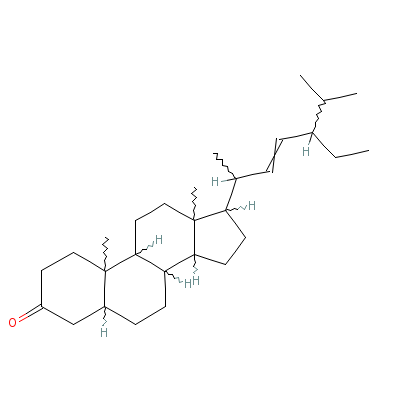
|
| Heptacosanol |
2004-39-9 |
Heptacosan-1-ol |
C27H56O |
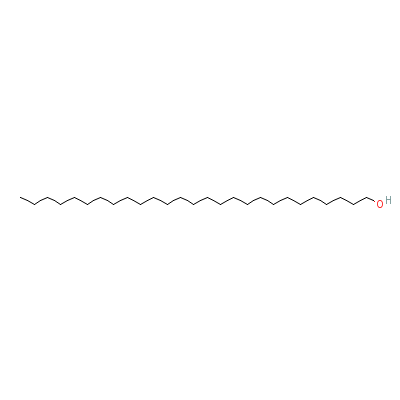
|
| Luteolin-7-O-glucoside |
26811-41-6 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4-hydroxy-7-[3,4
,5-trihydroxy-6-(hyd
roxymethyl
)oxan-2-
yl]oxy-chromen-5-one |
C21H20O11 |
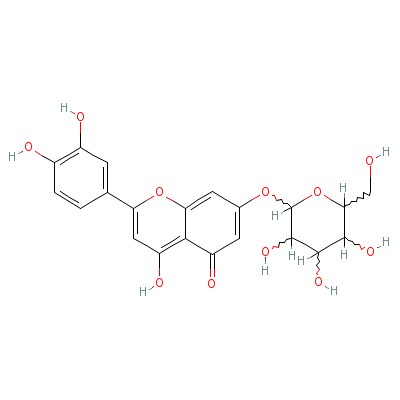
|
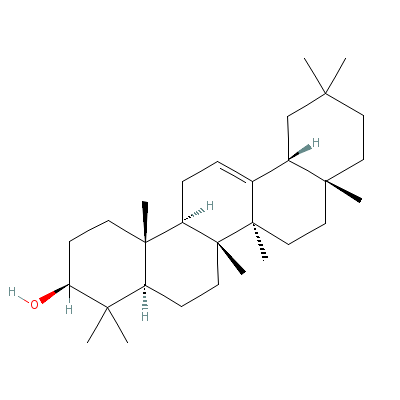
| Beta-Amyrin |
559-70-6 |
4,4,6a,6b,8a,11,11,1
4b-octamethyl-1,2,3,
4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,1
2a,14,14a-
tetradec
ahydropicen-3-ol |
C30H50O |
|
| Nicotine |
65-31-6 |
3-(1-methylpyrrolidi
n-2-yl)pyridine |
C10H14N2 |
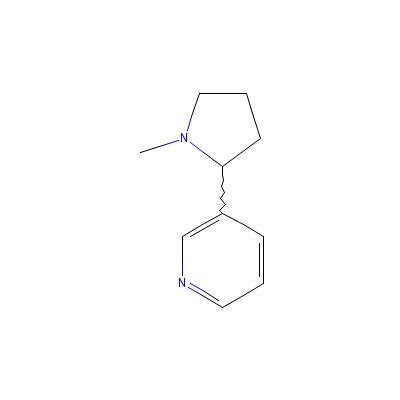
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Tetanus, baldness, long-term skin diseases, in enlargements of the liver and spleen (as a tonic and deobstruent) (plant); in catarrhal jaundice (plant juice and "aromatics"); as an antiseptic in cattle wounds etc. and in syphilis (root), removes worms, cough and indigestion, good remedy for dental disorders. Various local traditions and Ayurveda employ its parts for elephantiasis, migraine, pyorrhoea, chronic dysentery, oedema, nervous weakness, anorexia, gum troubles and to remove intestinal worms.This plant invigorates sex and consumed for fertility. It is an antidote for poisons. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Can cause chills. Safety in young children, or pregnant or nursing women is not known. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Grieve M. A Modern Herbal 1931 (www.botanical.com).
Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas. |
Dealers
Products
|
|
|
|
|