Diospyros malabarica (Desr.) Kostel. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Diospyros malabarica (Desr.) Kostel. |
English
Name |
: |
Indian persimon, Gaub persimmon, Wild Mangosteen |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Diospyros embryopteris Pers., Diospyros glutinosa Koening, Diospyros siamensis Ridl. [non Hoch.] |
Family |
: |
Ebenaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
An evergreen timber tree that grows to a height of 37m with a girth of 2m. The bole is straight and the wood is hard and dense. The bark is black, smooth. The leaves are simple and exstipulate. The flowers are bell-shaped; Male flowers are formed in 3–5 flowered cymes axillary; Female flowers are solitary, 4-merous, with four styles, and an 8-celled ovary. The fruits are globose, up to 3.5cm in diameter, green, tinted red in colour and seated on a persistent calyx. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antidote and demulcent(fruits); astringent (seeds); hypoglycemic, antiviral and antiprotozoal (bark); antifertility agent and emmenagogue (plant) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Beta-sitosterol,betulin, betulinic acid, oleanolic acid, lupeol and gallic acid (leaf and bark) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Betulinic Acid |
4481-62-3 |
Not Available |
C30H46O3 |
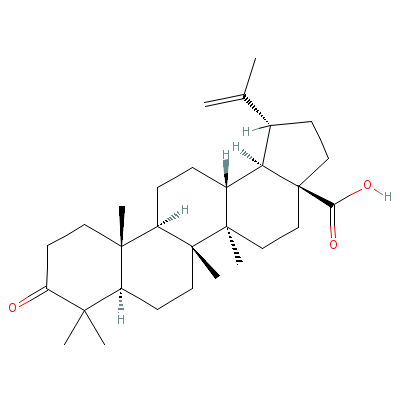
|
| Betulin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C30H50O2 |
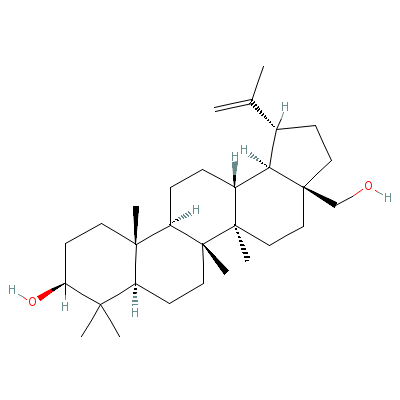
|
| Beta-sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14, |
C29H50O |
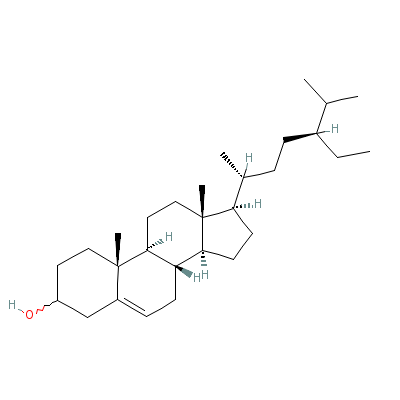
|
| Oleanolic acid |
508-02-1 |
10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b
,9,9,12a-heptamethyl
-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a
,10,11,12,
13,14b-t
etradecahydropicene-
4a-carboxylic acid |
C30H48O3 |
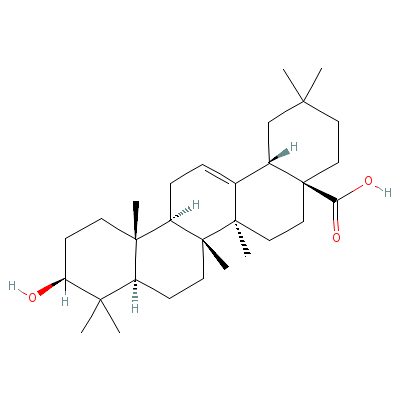
|
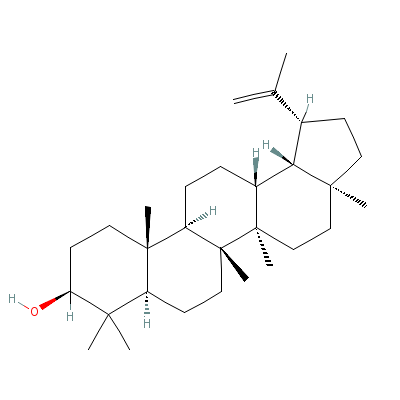
| Lupeol |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C30H50O |
|
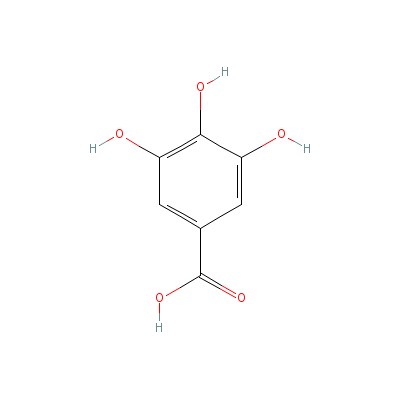
| Gallic acid |
149-91-7 |
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oic acid |
C7H6O5 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
To treat diarrhea, dysentery and fever, and as an antidote for snake poisoning (fruits); in blood diseases, gonorrhea and leprosy (ripe fruits); as a vaginal injection in gonorrhea (extract of the fruit); used to heal sores and wounds (juice of fruits); as a good application to boils and tumors (bark); useful in bilious fever (juice of bark); in diarrhea (seeds) |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Christophe Wiart. Medicinal Plants of Asia and the Pacific, P:75-76, CRC Press, June 2006. Christophe Wiart. Medicinal Plants of Asia and the Pacific, P:75-76, CRC Press, June 2006.
Mondal,S.K., Chakraborty,G., Gupta,M.,and Mazumder,U.K. 2005. Hepatoprotective Activity of Diospyros malabarica Bark in. Carbon tetrachloride Intoxicated Rats. European Bulletin of Drug Research, 13(1). |
Dealers
Products
|
|