| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Cannabis sativa L. |
English
Name |
: |
Indian Hemp. Hashish and Marijuana |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Cannabis indica, Lam., Cannabis chinensis, Del. |
Family |
: |
Cannabaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
It is a tall annual herb about 1.52 to 4.9 m high with angular stem. Leaves are palmate, alternate or lower one opposite and 5.0 to 20.0 cm long; the lobes of the upper leaves are 1 to 5 and lower 5 to 11, linear lanceolate, sharply toothed, long-popinted and narrowed at base. The flowers are small, greenish and unisexual; males are borne in long dropping panicles and female in short axillary spikes. The achenes are 0.3 cm across, ovate and flat and are enclosed in persistent perianth. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Anodyne, anthelmintic, demulcent, diuretic, emollient, emmenagogue, febrifuge, laxative, narcotic and tonic (seed). It is a pain-killer, sleep-inducer and used to relieve some of the unpleasant side effects suffered by people undergoing chemotherapy. Stimulates the secretion of gastric juices (flower); induces sleep, aphrodisiac, on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems, depresses respiration, analgesic, entheogenic, induces euphoria, hypnotic, intoxicant, narcotic, alleviates spasms. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Cannabinoids and long-chained n-alkanes (essential oil); cannabidiol, "cannabidiolic", cannabigerol and beta-lectin (plant); flavonoid glycosides (leaf); cannabinol, pseudocannabinol, cannabinin and cannin (a resin); ascorbic acid, beta-carotene (seed) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
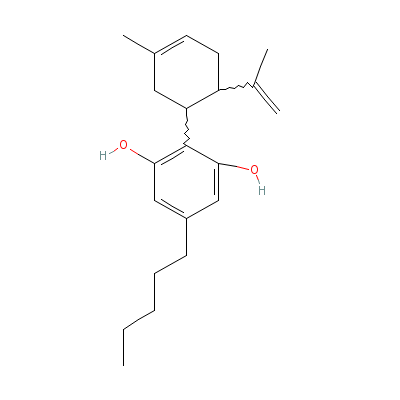
| Cannabidiol |
13956-29-1 |
2-[3-methyl-6-(1-met
hylethenyl)-1-cycloh
ex-3-enyl]-5-pentyl-
benzene-1,
3-diol |
C21H30O2 |
|
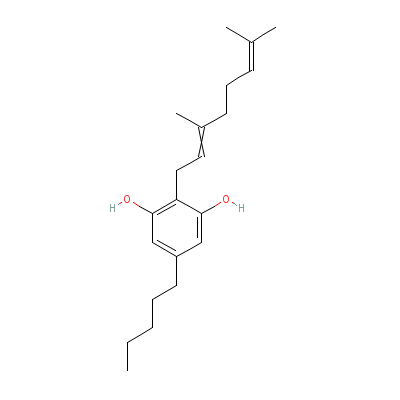
| Cannabigerol |
2808-33-5 |
2-(3,7-dimethylocta-
2,6-dienyl)-5-pentyl
-benzene-1,3-diol |
C21H32O2 |
|
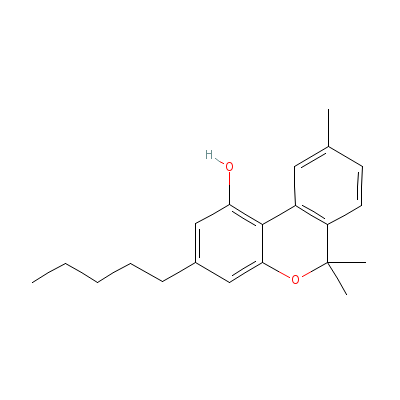
| Cannabinol |
521-35-7 |
Not Available |
C21H26O2 |
|
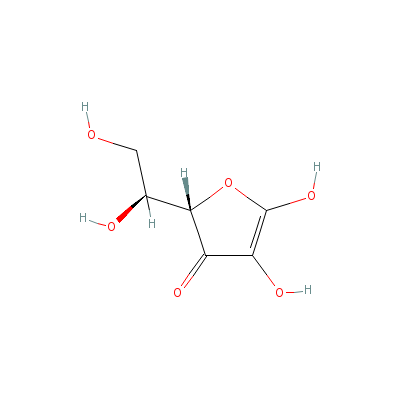
| Ascorbic Acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
|
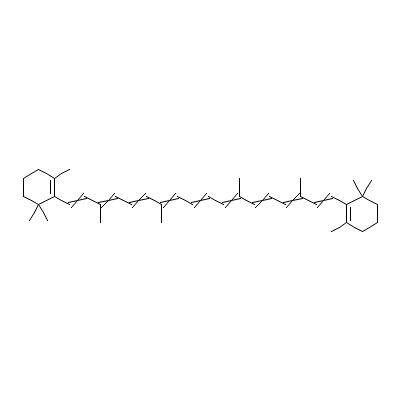
| beta Carotene |
7235-40-7 |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
In hydrocele (bark); anorexia, urinary tract problems (including bladder inflammation), cancer and tumors, common cold, corns, cough, depression and as a psychological aid, glaucoma, gonorrhea, nausea, for sores, varicose veins, gout and rheumatism, in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal, anthrax, asthma, blood poisoning, constipation caused by debility or fluid retention |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
People working with the plant or the fiber may develop dermatitis. In larger doses, hemp drugs may induce catalepsy, followed by coma and DEATH from cardiac failure (C.S.I.R., 1948-1976). |
| Reference |
 |
|
 C.S.I.R. (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research). 1948-1976. The wealth of India 11 vols. New Delhi. C.S.I.R. (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research). 1948-1976. The wealth of India 11 vols. New Delhi.
Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas.
Grieve. M. A Modern Herbal (1931) (www.botanical.com).
Johnson. T. CRC Ethnobotany Reference. |
Dealers
Products
|
|
|
|
|