Alocasia indica (Lour.) Spach |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Alocasia indica (Lour.) Spach |
English
Name |
: |
Giant Taro |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Alocasia macrorrhiza (Linn.) G. Don, |
Family |
: |
Araceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A robust perennial herb up to 5 m in height found wild and cultivated all over India. Aerial stems stout, 2 m or more long, leaf blades 60 cm-1 m long, erect or spreading, ovate, sagittate with 1.35 m long, sheathing petioles; flowers fragrant, spadix and spathe 23 cm long on a 30 cm long peduncle, berries 0.75-1 cm in diam. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Diurectic; styptic and astringent (leaves) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Campesterol, ß-sitosterol, cholesterol and phytosterol-like compound (tubers) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
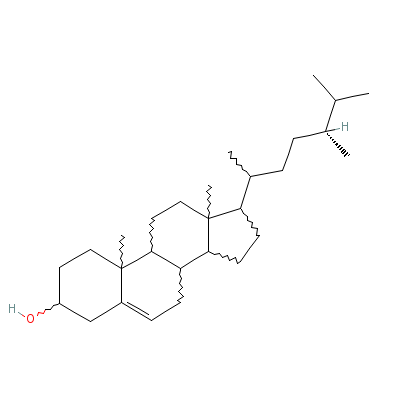
| Campesterol |
474-62-4 |
17-(5,6-dimethylhept
an-2-yl)-10,13-dimet
hyl-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,1
2,14,15,16
,17-dode
cahydro-1H-cyclopent
a[a]phenanthren-3-ol |
C28H48O |
|
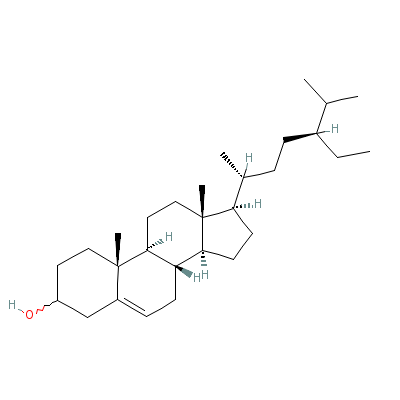
| Beta-sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14, |
C29H50O |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Useful in inflammation and diseases of the abdomen and spleen (rootstock); to stings of giant nettle. The juice of the petiole is dropped into the ears of children for otorrhoea. For stomach ache (rhizome). |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
The leaves, stalks, tubers and roots contains high concentration of soluble oxalates, and prolonged use of these in diet may lead to calcium deficiency and oxaluria. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Sharma PV. Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. Sharma PV. Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
Kamboj SS. Shangary S. Singh J. Kamboj KK. Sandhu RS. New lymphocyte stimulating monocot lectins from family Araceae. Immunol Invest1995 Aug;24(5):845-55. |
Dealers
Products
|
|