| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Gloriosa superba L. |
English
Name |
: |
Climbing Lily |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Methonica superba Lamk., Gloriosa simplex Don. |
Family |
: |
Liliaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Herbaceous tendril climber; rootstock tuberous, naked; stem 3 to 6 m long, sparingly branched; leaves sessile or nearly so, opposite or 3-nately whorled, tip tendrillar; flowers axillary, solitary, nearly 10 cm, at first greenish, becoming yellow and finally scarlet or red; capsules nearly 5 cm long. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Ayurveda uses its roots as abortifacient, acrid, alexiteric, anthelmintic, antipyretic, bitter, depurative, digestive, emetic, expectorant, gastrointestinal irritant, purgative, rejuvenative, stomachic, thermogenic, tonic, in dealing debility, dyspepsia, flatulence, haemorrhoids, helminthiasis, inflammations, in promoting labour pain and expulsion of the placenta; stimulates uterine contractions (fresh plant juice and rhizome); antimalarial and laxative (tuber). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Benzoic acid, choline, chrysophanic acid, colchicine, glucose, salicylic acid, stigmasterol (bulb); demethylcolchicine, N-formyldeaceatylcolchicine. |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
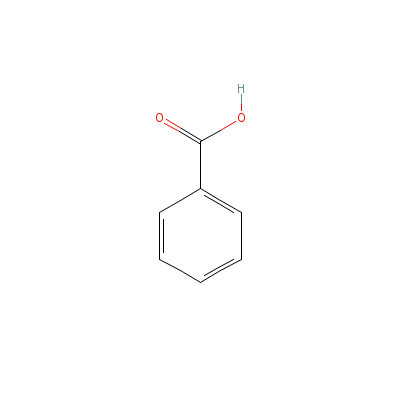
| Benzoic acid |
8013-63-6 |
benzoic acid |
C7H6O2 |
|
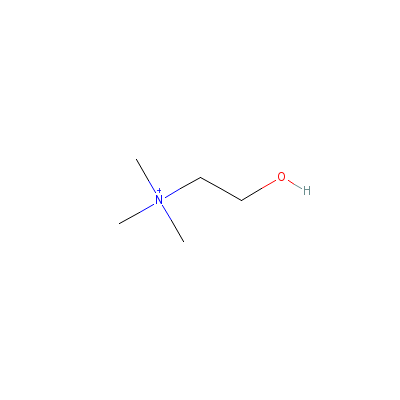
| Choline |
67-48-1 |
2-hydroxyethyl-trime
thyl-ammonium |
C5H14NO+ |
|
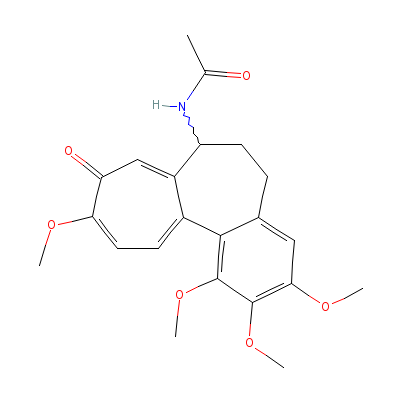
| Colchicine |
54192-66-4 |
Not Available |
C22H25NO6 |
|
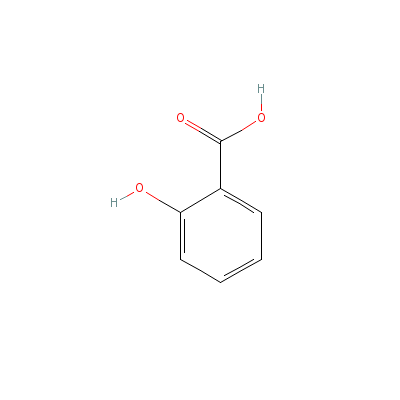
| Salicylic acid |
8052-31-1 |
2-hydroxybenzoic
acid |
C7H6O3 |
|
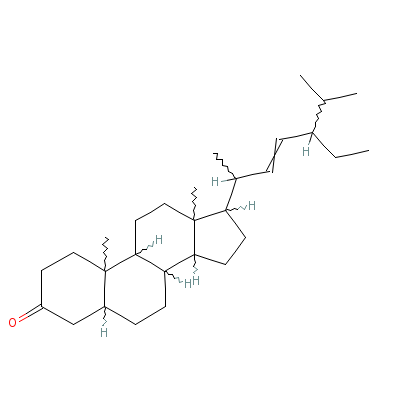
| Stigmasterol |
4736-55-4 |
17-(4-ethyl-1,5-dime
thyl-hex-2-enyl)-10,
13-dimethyl-1,2,4,5,
6,7,8,9,10
,11,12,1
3,14,15,16,17-hexade
cahydrocyclopenta[a]
phenanthren-3-one |
C29H48O |
|
| Chrysophanic acid |
Not Available |
1,8-dihydroxy-3-meth
yl-anthracene-9,10-d
ione |
C15H10O4 |

|
| Salicylic acid |
8052-31-1 |
2-hydroxybenzoic
acid |
C7H6O3 |

|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Antimalarial, increasing the secretion of gastric juices, laxative and as a tonic (tuber); leprosy and anthelmintic (root); to treat arthritis , piles, boils, for extraction of foreign body, for easy delivery, baldness, scrofula and ear diseases (root powder); effective against paralysis, rheumatism, snake bite, insect bites and leaf-juice effective against lice (root-paste). Various ethnic medical practices across India employ this plant for gout, stomachache,intermittent fevers, wounds, spleen complaints, syphilis, tumours, asthma, cholera, gonorrhoea, leprosy, piles, dropsy, labour pain and for acute spasmodic pain. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas.
Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. |
Dealers
Products
|
|