| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Sida rhombifolia L. |
English
Name |
: |
Common Bala and Wet Barela |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Sida orientalis Cav. , Sida rhombifolia (L.) var. obovata Wall. ex Masters, Sida rhombifolia (L.) var. rhomboidea (DC) Masters. |
Family |
: |
Malvaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
An annual or perennial herb up to 1.5 m tall. Leaves simple, alternate, 3.5 to 10.0 cm long and 1 to 5 cm wide, variable, apex acute, base cuneate, margins serrate, glabrate above and pubescent beneath. Flowers yellow, solitary or clustered in leaf axils; calyx campanulate, triangular, acuminate; petals 5.5 to 6.0 mm long, emarginate. Fruits mericarps, trigonous, sparsely pubescent, long awned up to 1 mm long. Seeds 1 to 2, subreniform, dark brown or black. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Anthelmintic, antifungal, alleviates spasms, antiinflammatory and antibacterial (plant); depresses the central nervous system and sedative (root). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Various alkaloids (plant); ascorbic acid, beta-carotene, niacin, riboflavin, thiamin (leaf); ephedrine (root) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Ascorbic acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
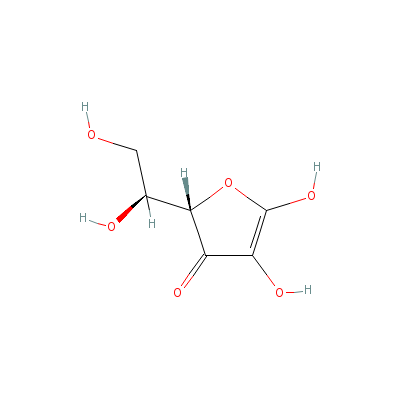
|
| beta-Carotene |
Not Available |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
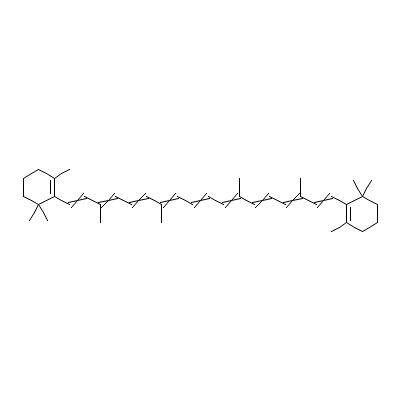
|
| Ephedrine |
6912-63-6 |
2-methylamino-1-phen
yl-propan-1-ol |
C10H15NO |
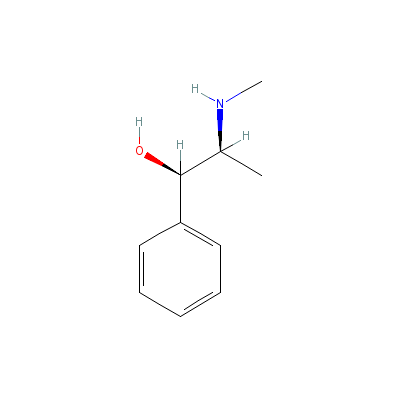
|
| Niacin |
99148-57-9 |
pyridine-3-carboxyli
c acid |
C6H5NO2 |
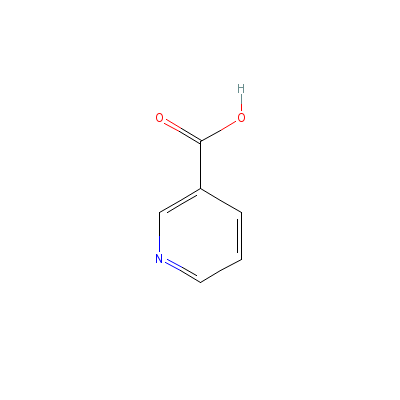
|
| Riboflavin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C17H21N4O9P |
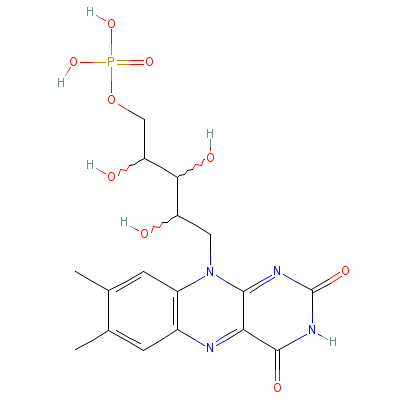
|
| Thiamin |
59-43-8 |
2-[3-[(4-amino-2-met
hyl-pyrimidin-5-yl)m
ethyl]-4-methyl-1-th
ia-3-azoni
acyclope
nta-2,4-dien-5-yl]et
hanol |
C12H17N4OS+ |
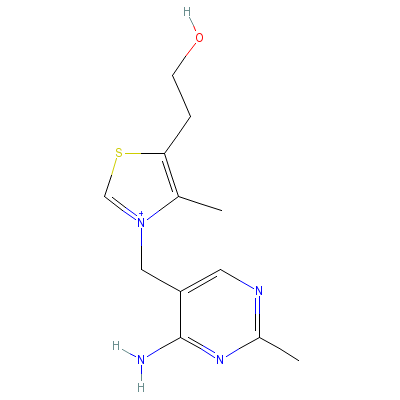
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
It is used for gonorrhoea and ophthalmic disorders in Ayurveda. Unani employs it for piles, gonorrhoea, anti-soud, and as diuretic and aphrodisiac. Root of these herbs are held in great repute in treatment of rheumatism. Stems abound in mucilage and are employed as demulcents and emollients both for external and internal use. The herb is also useful in calculous troubles and as a febrifuge with pepper. Mucilage is used for scorpion sting. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|