| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Rubia cordifolia L. |
English
Name |
: |
Indian Madder |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Rubia manjith Roxb. ex Flem., Rubia munjista Roxb., Rubia tinctorum L. var. cordifolia L. |
Family |
: |
Rubiaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A very variable, prickly creeper or climber. The rootstocks are perennial; the roots, long and cylindric with a thin, red bark; the stems, four angled. The leaves are very variable, cordate-ovate to ovate-lanceolate, 2 to 8 in a whorl, normally 4, sometimes 1 pair is larger. The flowers are small, white or greenish, or in shades of red and yellow, sweet-scented in terminal panicles of cymes; the fruits, globose, or slightly 2-lobed, dark-purplish or black, fleshy with 2 small seeds. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Alterative, anodyne, antiphlogistic, antitussive, diuretic, emmenagogue, expectorant, febrifuge, styptic, tonic, vulnerary, hypoglycemic (EtOH extract of aerial part); cleanses the bowel, antiseptic and astringent (root). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Beta-sitosterol, physcion, purpurin, Munjistin, xanthopurpurin or purpuroxanthin, pseudopurpurin, rubifolic and rubicoumaric acids (plant). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Purpurin |
81-54-9 |
1,2,4-trihydroxyanth
racene-9,10-dione |
C14H8O5 |
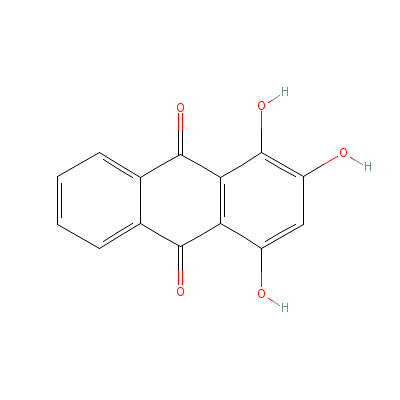
|
| Munjistin |
478-06-8 |
1,3-dihydroxy-9,10-d
ioxo-anthracene-2-ca
rboxylic acid |
C15H8O6 |
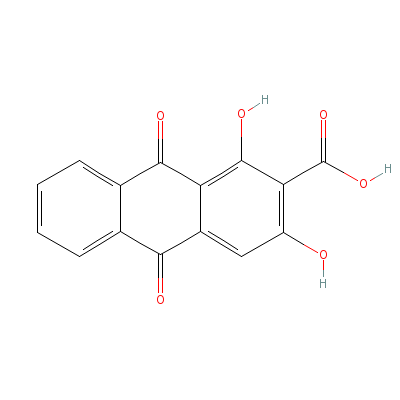
|
| Xanthopurpurin |
518-83-2 |
1,3-dihydroxyanthrac
ene-9,10-dione |
C14H8O4 |
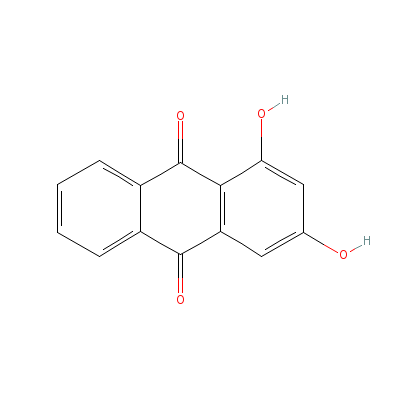
|
| Pseudopurpurin |
476-41-5 |
1,3,4-trihydroxy-9,1
0-dioxo-anthracene-2
-carboxylic acid |
C15H8O7 |
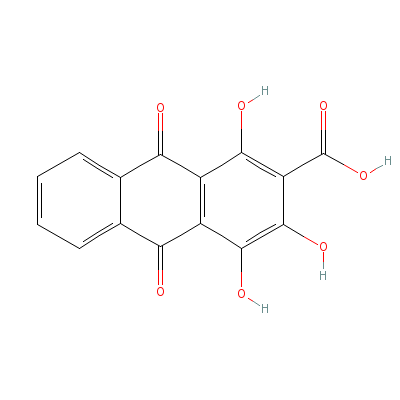
|
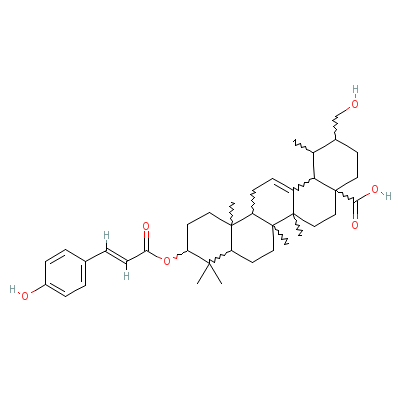
| Rubicoumaric acid |
Not Available |
2-(hydroxymethyl)-10
-[(E)-3-(4-hydroxyph
enyl)prop-2-enoyl]ox
y-1,6a,6b,
9,9,12a-
hexamethyl-2,3,4,5,6
,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,
13,14b-tetradecahydr
o-
1H-picene-4a-car
boxylic acid |
C39H54O6 |
|
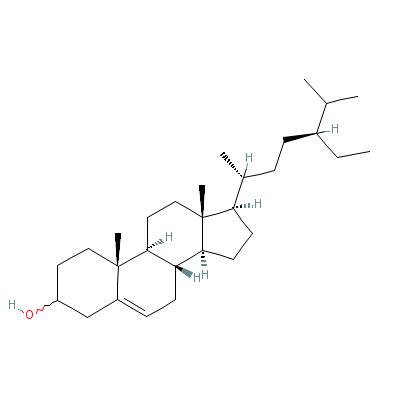
| Beta-sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14, |
C29H50O |
|
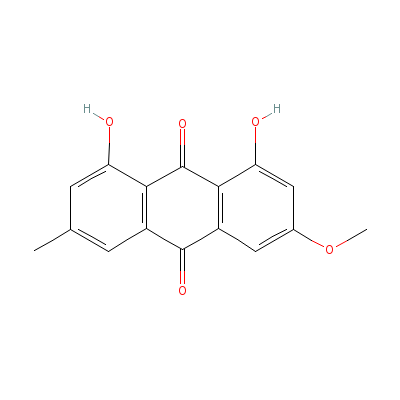
| Physcion |
521-61-9 |
1,8-dihydroxy-3-meth
oxy-6-methyl-anthrac
ene-9,10-dione |
C16H12O5 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
To treat skin diseases, piles, diabetes, fracture, freckles, in rheumatism, leprosy, menorrhagia, abnormal uterine bleeding, internal and external haemorrhage, bronchitis, rheumatism, stones in the kidney, urinary bladder and gall bladder, dysentery etc. (root); antidote for scorpion stings and bites by cobras, in the treatment of blood disorders and spreading fever of kidneys and intestines (stem); spleen enlargement and liver problems (plant). |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
May cause severe chills. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas. |
Dealers
Products
|
|