Pueraria tuberosa (ROXB. EX. WILLD.) DC. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Pueraria tuberosa (ROXB. EX. WILLD.) DC. |
English
Name |
: |
Indian Kudze |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Hedysarum tuberosum Roxb. |
Family |
: |
Fabaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A large perennial climber with a woody, tubercled stem up to 12 cm in diameter and very large tuberous roots. Leaves trifoliate; rachis 10 to 15 cm long; stipules 4 mm long, ovate-oblong, cordate; leaflets subcoriaceous, ovate, 13 to 20 cm long and nearly as wide, apex acuminate, base cuneate or truncate, glabrescent above, pubescent beneath, lateral leaflets unequal-sided; petiolules 4.5 to 6 mm long. Flowers bluish-white to purplish blue, borne in lax, leafless racemes 15 to 30 cm long; pedicels 2 to 3 mm long, silky-pubescent, fascicled along the rachis. Fruits (pods) membranous, flat, linear, 5 to 7.5 cm long, constricted between seeds, densely covered with long, silky, bristly brown hairs; seeds 3 to 6. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Emetic, demulcent, antirheumatic, stimulates the secretion and/or flow of milk (root); lowers blood sugar and antiimplantation (tuber). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Puerarin, tuberosin, stigmasterol, beta-sitosterol and daidzin (root and tuber). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Puerarin |
Not Available |
7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydro
xyphenyl)-8-[(2S,3S,
4R,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trih
ydroxy-6-(
hydroxym
ethyl)oxan-2-yl]chro
men-4-one |
C21H20O9 |

|
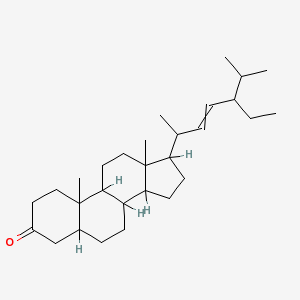
| Stigmasterol |
4736-55-4 |
17-(4-ethyl-1,5-dime
thyl-hex-2-enyl)-10,
13-dimethyl-1,2,4,5,
6,7,8,9,10
,11,12,1
3,14,15,16,17-hexade
cahydrocyclopenta[a]
phenanthren-3-one |
C29H48O |
|
| Tuberosin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C20H18O5 |

|
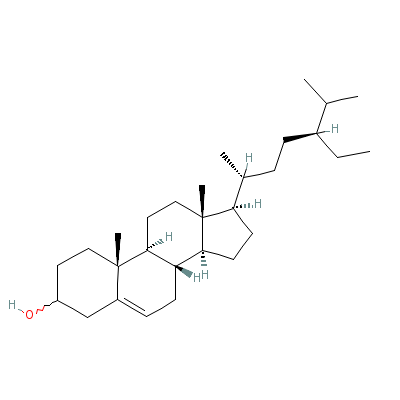
| Beta-Sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17-dodecahydro
-1H-cyclopenta[a]phe
nanthren-3-ol |
C29H50O |
|
| Daidzin |
Not Available |
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-
7-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-
3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(
hydroxymet
hyl)oxan
-2-yl]oxy-chromen-4-
one |
C21H20O9 |

|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The root is used as a demulcent and in the treatment of fevers. It is peeled and bruised into a cataplasm for swelling of joints. It is crushed and rubbed externally in the treatment of fevers, headaches and rheumatism. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas.
Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. |
Dealers
Products
|
|