| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Mentha piperita STOKES |
English
Name |
: |
Peppermint |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Mentha officinalis, Mentha hircina, Hull., Mentha viridi-aquatica, F. Schultz. |
Family |
: |
Lamiaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
The leaves of this kind of mint are shortly but distinctly stalked, 2 inches or more in length, and 3/4 to 1 1/2 inches broad, their margins finely toothed, their surfaces smooth, both above and beneath, or only very slightly, hardly visibly, hairy on the principal veins and mid-rib on the underside. The stems, 2 to 4 feet high, are quadrangular, often purplish. The whorled clusters of little reddish-violet flowers are in the axils of the upper leaves, forming loose, interrupted spikes, and rarely bear seeds. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Peppermint and menthol possess carminative, antispasmodic, and choleretic properties, and are also used as an external analgesic and nasal decongestant. antiseptic, relieves flatulence, soothes the stomach stimulant and promotes the flow of bile (plant); alleviates spasms (leaf); antifungal (essential oil); diuretic and expectorant. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Menthol, menthone, menthy acetate, phellandrene, pinene, L-limonene, cadinene, terpinene, cineole, acetic acid, amyl alcohol, acetaldehyde, isovaleric acid, isovaleric aldehyde and a lactone (essential oil). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Menthol |
2216-51-5 |
5-methyl-2-propan-2-
yl-cyclohexan-1-ol |
C10H20O |
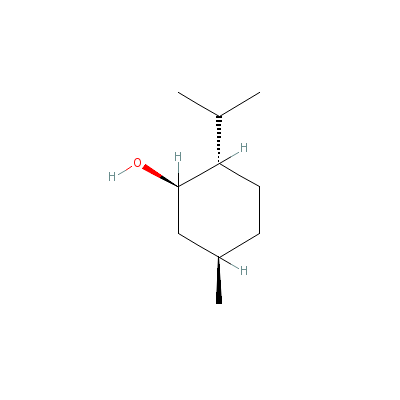
|
| Menthone |
89-80-5 |
5-methyl-2-propan-2-
yl-cyclohexan-1-one |
C10H18O |
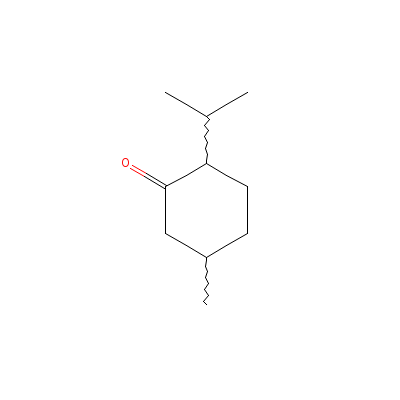
|
| l-Limonene |
7721-11-1 |
1-methyl-4-prop-1-en
-2-yl-cyclohexene |
C10H16 |
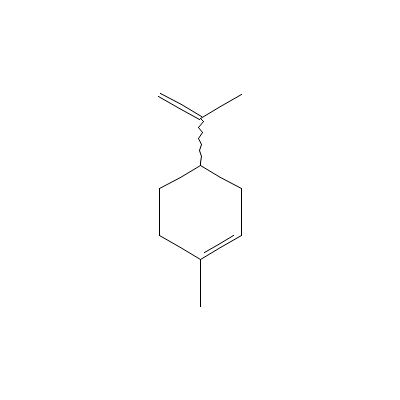
|
| Cadinene |
29350-73-0 |
1,6-dimethyl-4-propa
n-2-yl-1,2,3,4,4a,5,
6,8a-octahydronaphth
alene |
C15H26 |
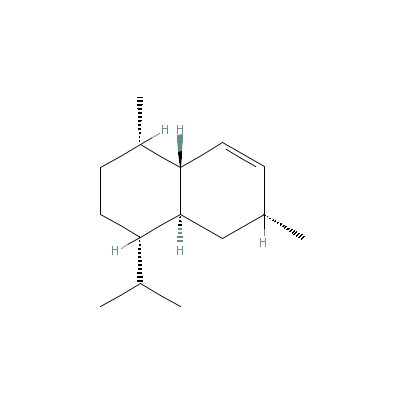
|
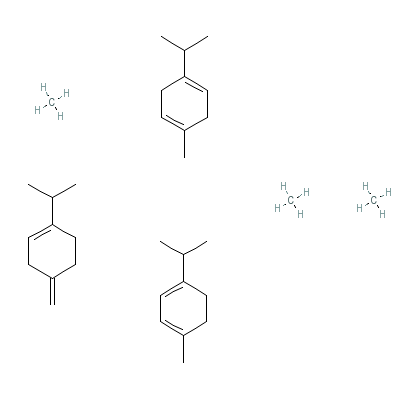
| Terpinene |
8013-00-1 |
methane;
4-methylidene-1-prop
an-2-yl-cyclohexene;
1-methyl-4-propan-2-
yl-cyclohexa-1,3-d
iene;
1-methyl-4-propan-2-
yl-cyclohexa-1,4-die
ne |
C33H60 |
|
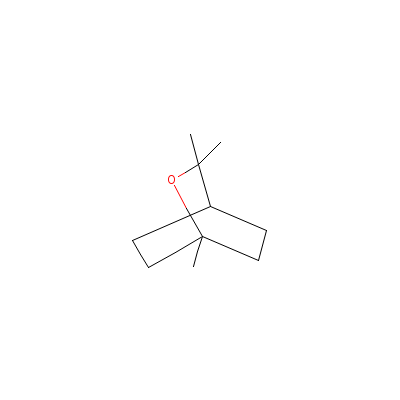
| Cineole |
8024-53-1 |
2,2,4-trimethyl-3-ox
abicyclo[2.2.2]octan
e |
C10H18O |
|
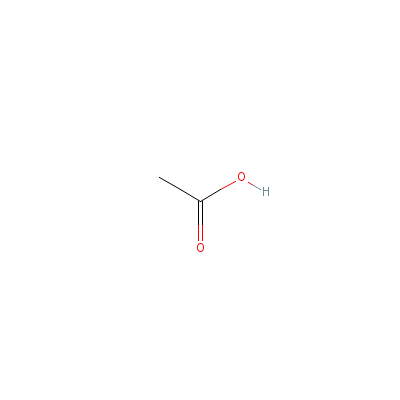
| Acetic acid |
77671-22-8 |
acetic acid |
C2H4O2 |
|
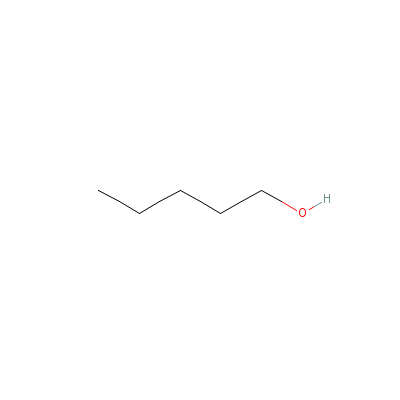
| Amyl alcohol |
71-41-0 |
pentan-1-ol |
C5H12O |
|
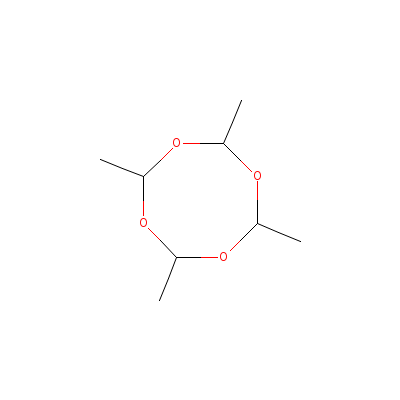
| Acetaldehyde |
108-62-3 |
2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-
1,3,5,7-tetraoxocane |
C8H16O4 |
|
| Isovaleric acid |
503-74-2 |
3-methylbutanoic
acid |
C5H10O2 |
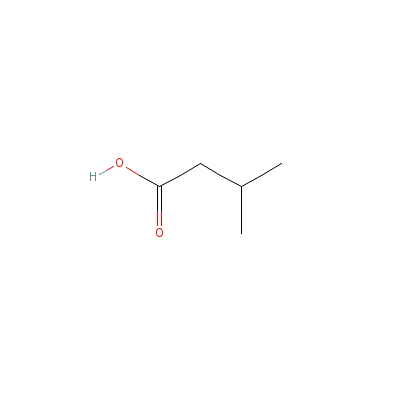
|
| Isovaleric aldehyde |
590-86-3 |
3-methylbutanal |
C5H10O |
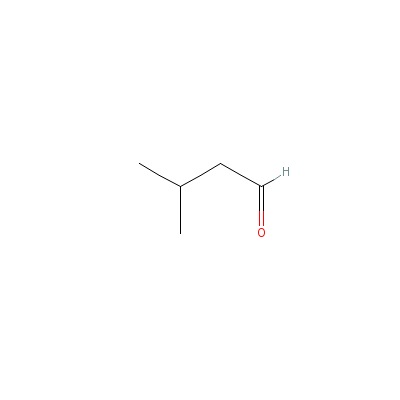
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Stomach problems (including colic), gall bladder pains, nausea and as a stimulant (plant); headache and local aches (leaf); diuretic, alleviating spasms and as an expectorant (during colds). The anti-spasmodic quality relieves pain arising in the alimentary canal. Due to its stimulating, stomachic and carminative properties, it is effective in treating certain forms of dyspepsia, flatulence and colic. Peppermint tea is used also for palpitation of the heart. In cases of hysteria and nervous disorders, an infusion of Peppermint is administered. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Peppermint is contraindicated for hiatus hernia because of its relaxing effect of the esophageal sphincter (Brinker and Francis, 1997) |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Stary, Medicinal Herbs and Plants. Stary, Medicinal Herbs and Plants.
Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
The Himalaya Drug Company.
Bentley and Trimen, Medicinal Plants.
Brinker, Francis N.D. Herb Contraindications and Drug Interactions. Eclectic Institute, Inc., Oregon. 1997. 72. |
Dealers
Products
|
|