| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Linum usitatissimum L. |
English
Name |
: |
Linseed and Flax |
Family |
: |
Linaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A stiff, upright annual, about 1 to 2 feet high; stem usually solitary, cylindrical, quite smooth, green, corymbosely branched in the upper part. Leaves alternate sessile, linear-lanceolate, attenuate at each end, entire, smooth, faintly ribbed. Flowers solitary at the ends of the branches. Fruit capsular, surrounded at the base by the persistent sepals, globose, with a sharp-pointed apex, smooth imperfectly 10 celled. Seeds flattened-ovoid, with rounded edges and an abolique blunt beak at the upper end. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
The seed is analgesic, demulcent, emollient, laxative, pectoral and resolvent; increases nerve strength (flower); emollient, expectorant, reduces fever, laxative, aphrodisiac, diuretic and carminative. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Beta-carotene, beta-sitosterol, neolinustatin and linustatin (seed); apigenin, chlorogenic acid and its isomer, luteolin, tocopherol (plant); vitexin (leaf). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Beta-carotene |
Not Available |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
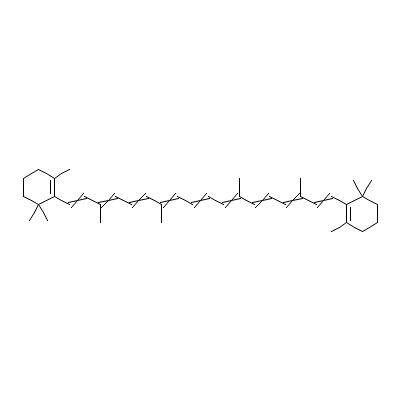
|
| beta-Sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cycl
openta[a]phenanthren
-3-ol |
C29H50O |
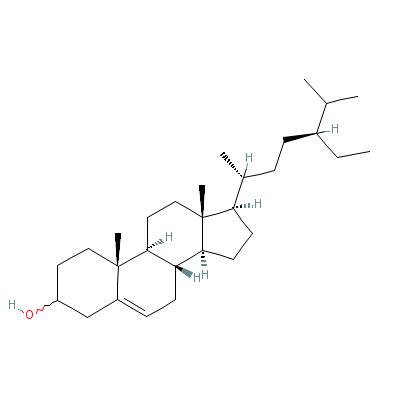
|
| Neolinustatin |
72229-42-6 |
2-methyl-2-[3,4,5-tr
ihydroxy-6-[[3,4,5-t
rihydroxy-6-(hydroxy
methyl)oxa
n-2-yl]o
xymethyl]oxan-2-yl]o
xy-butanenitrile |
C17H29NO11 |
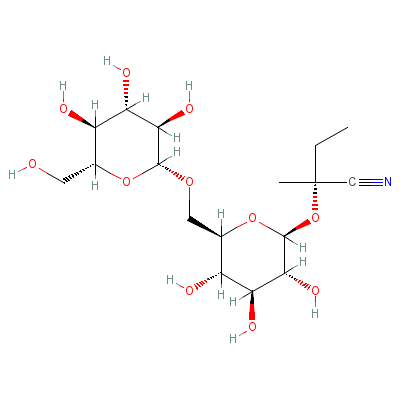
|
| Linustatin |
72229-40-4 |
2-methyl-2-[3,4,5-tr
ihydroxy-6-[[3,4,5-t
rihydroxy-6-(hydroxy
methyl)oxa
n-2-yl]o
xymethyl]oxan-2-yl]o
xy-propanenitrile |
C16H27NO11 |
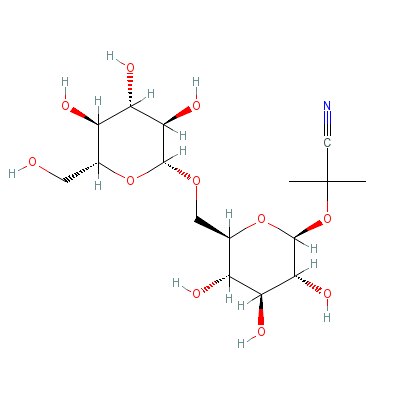
|
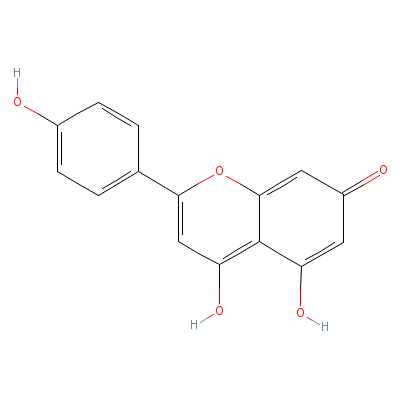
| Apigenin |
520-36-5 |
4,5-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-chrome
n-7-one |
C15H10O5 |
|
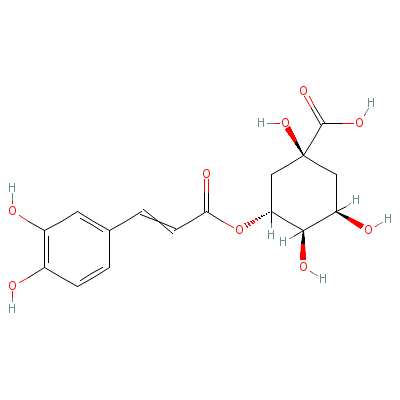
| Chlorogenic acid |
327-97-9 |
3-[3-(3,4-dihydroxyp
henyl)prop-2-enoylox
y]-1,4,5-trihydroxy-
cyclohexan
e-1-carb
oxylic acid |
C16H18O9 |
|
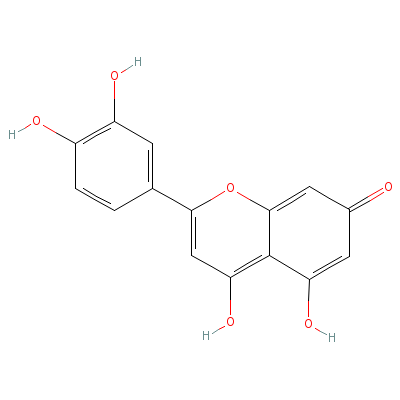
| Luteolin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-ch
romen-7-one |
C15H10O6 |
|
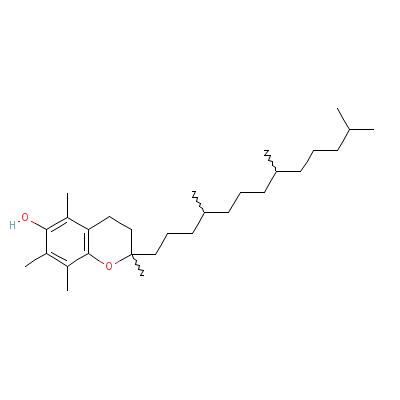
| Tocopherol |
59-02-9 |
2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-
2-(4,8,12-trimethylt
ridecyl)chroman-6-ol |
C29H50O2 |
|
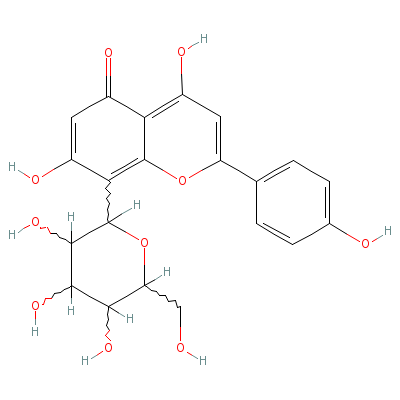
| Vitexin |
521-33-5 |
4,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-8-[3,4
,5-trihydroxy-6-(hyd
roxymethyl
)oxan-2-
yl]-chromen-5-one |
C21H20O10 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
For increasing nerve strength and as a cardiac tonic (flower); gout and rheumatism (seed oil); cancer, colds, constipation, corns, cough, intoxication, pulmonary disorders, sclerosis, spasms, tumors, gallstones, urogenital diseases and as a poultice, soothes irritated tissues, controls coughing and relieves pain. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Animal research suggests that large amounts of flaxseed or lignans consumed during pregnancy might adversely affect the development of the reproductive system (Tou et al., 1998). No studies have attempted to investigate whether this could be a problem in humans.
Allergic reactions to flaxseed have occasionally been reported, but are considered very uncommon. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas.
Bentley and Trimen, Medicinal Plants.
Tou JC, Chen J, Thompson LU. Flaxseed and its lignan precursor, secoisolariciresinol diglycoside, affect pregnancy outcome and reproductive development in rats. J Nutr 1998;128:1861–8. |
Dealers
Products
|
|