| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Boerhavia diffusa L. |
English
Name |
: |
Hog Weed, Horse Purslane, Red Spiderling |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Boerhavia coccinea (P.Mill.), Boerhavia procumbens |
Family |
: |
Nyctaginaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A very variable, diffusely branched, pubescent or glabrous, prostrate herb with a stout, woody rootstock; stems creeping, often purplish, swollen at the nodes up to 1.2 m long. Leaves long-petioled, ovate or oblong-cordate, entire or sinuate, usually whitish and smooth beneath an rough green on upper surface. Flowers red, pink or white, borne in small umbels arranged in axillary and terminal panicles. Fruit ovate, oblong, 1.3 cm long, five-ribbed, pubescent, viscid, glandular. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antidote, diuretic, emetic, expectorant, laxative, stomachic. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
B-Sitosterol, a-2-sitosterol, palmitic acid, ester of b-sitosterol, tetracosanoic, hexacosonoic, stearic, arachidic acid, urosilic acid, Hentriacontane, b-Ecdysone, triacontanol; triacontanol hentriacontane, ß-sitosterol, ursolic acid, 5,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethyoxy-6,8-dimethyl flavone, the rotenoid boeravinones AI, BI, C2 , D, E and F, dihydroisofurenoxanthin, borhavine, punarnavoside, liriodendrin and syringaresinol mono-D-glucoside (roots). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Palmitic acid |
66321-94-6 |
Hexadecanoic acid |
C16H32O2 |
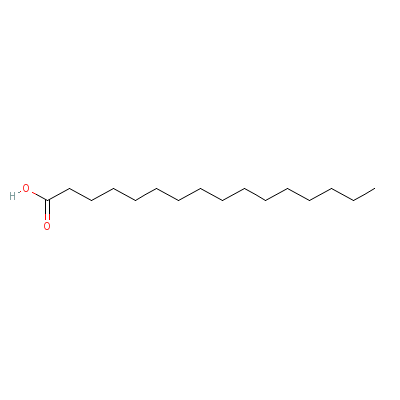
|
| Tetracosanoic acid |
66502-42-9 |
Tetracosanoic acid |
C24H48O2 |
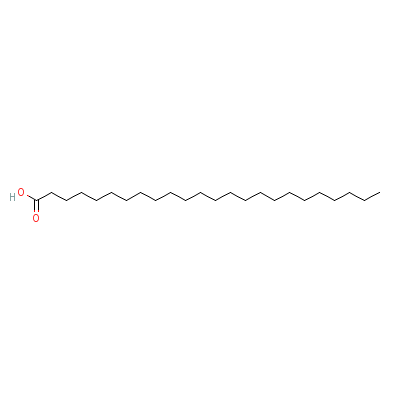
|
| Hentriacontane |
630-04-6 |
Hentriacontane |
C31H64 |
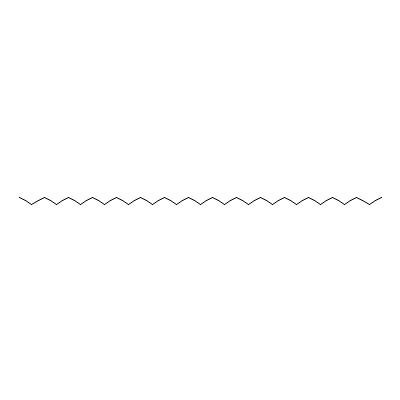
|
| Liriodendrin |
Not Available |
2-[4-[8-[3,5-dimetho
xy-4-[3,4,5-trihydro
xy-6-(hydroxymethyl)
tetrahydro
pyran-2-
yl]oxy-phenyl]-3,7-d
ioxabicyclo[3.3.0]oc
t-4-yl]-2,6-dimethox
y-
phenoxy]-6-(hydr
oxymethyl)tetrahydro
pyran-3,4,5-triol |
C34H46O18 |
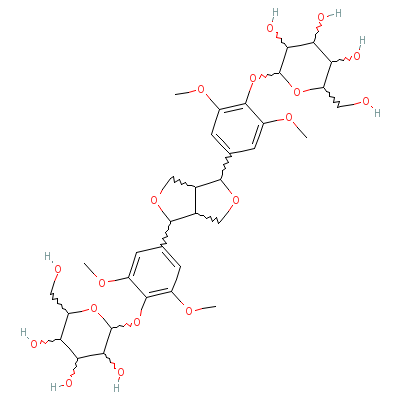
|
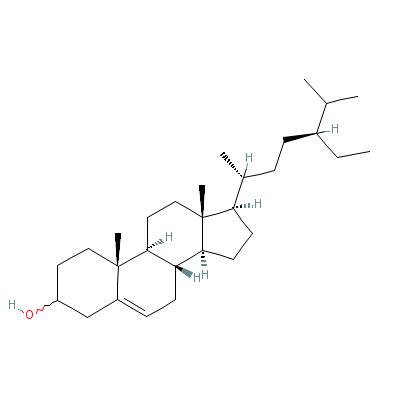
| Beta-Sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cycl
openta[a]phenanthren
-3-ol |
C29H50O |
|
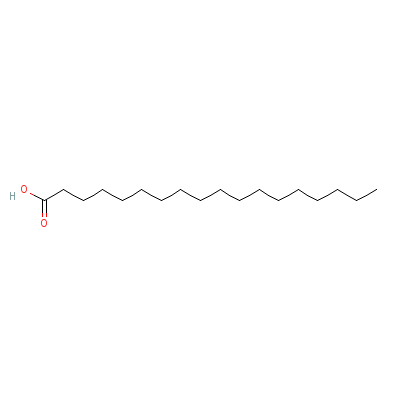
| Stearic acid |
82497-27-6 |
octadecanoic acid |
C18H36O2 |
|
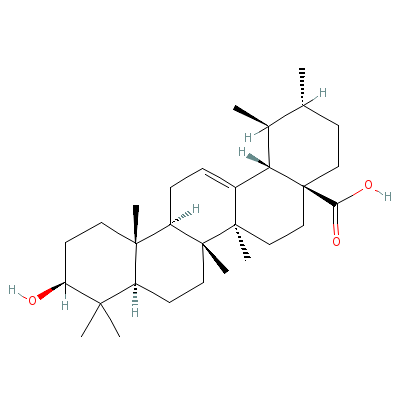
| Ursolic acid |
77-52-1 |
10-hydroxy-1,2,6a,6b
,9,9,12a-heptamethyl
-2,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a
,10,11,12,
13,14b-t
etradecahydro-1H-pic
ene-4a-carboxylic
acid |
C30H48O3 |
|
| Liriodendrin |
Not Available |
2-[4-[8-[3,5-dimetho
xy-4-[3,4,5-trihydro
xy-6-(hydroxymethyl)
tetrahydro
pyran-2-
yl]oxy-phenyl]-3,7-d
ioxabicyclo[3.3.0]oc
t-4-yl]-2,6-dimethox
y-
phenoxy]-6-(hydr
oxymethyl)tetrahydro
pyran-3,4,5-triol |
C34H46O18 |

|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
To treat anaemia, oedema, internal abscess, calculi, eye diseases, oedema during pregnancy, haemoptysis, for inducing sleep, fever, rheumatic ailments, difficult labour, vaginal pain, rejuvinative, asthma, oedema, anaemia, jaundice, ascites, anasarca, scanty urine and internal inflammation. It is also an antidote to snake poisoning. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
There are no known safety issues or interactions associated with Punarnava when taken in the recommended doses; however, exceeding the recommended doses can cause vomiting. Safety in young children, pregnant or nursing women, or those with severe liver or kidney disease is not known. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Sharma PV. Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. Sharma PV. Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas.
Chandan BK, Sharma AK. Anand KK. Boerhaavia diffusa: a study of its hepatoprotective activity.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|