| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Vitex negundo L. |
English
Name |
: |
Five-Leaved Chaste Tree, Horseshoe vitex, Negundo chastetree, Chasteberry. |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Nika silvestris Hermann ex Moldenke, Vitex paniculata Lam., Vitex spicata Lour. |
Family |
: |
Verbenaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
This a rounded to spreading large shrub or small tree reaching up to 8 m tall, reputed to be fast-growing and partly shedding off its leaves during water stress. The outside bark surface is slightly rough and peeling off in papery thin flakes and pale-brown color. Leaves are opposite, the leaflet are digitately compound of up to 3 to 5, narrowly elliptic to ovate-lanceolate, minutely hairy or glabrous above, densely finely pubescent beneath, median leaflet about 5 to 15 cm by 1 to 4 cm, depressed veins above, raised underneath, the margin shallowly blunt-toothed; the leaf stalks long, about 4 to7 cm; petioles absent on leaflet towards the petiole or up to 2.5 cm on the median one. The flowers are cymose and arranged in panicles which are terminal and axillary in the axils of upper leaves; the calyx about 102 mm long, shortly 5-toothed; the corolla blue-violet, hairy inside. Fruits are 4-valved , capsule-like, rounded to broadly egg-shaped, 3 to 6 mm long, purple or black when mature. It can be propagated through seeds and cuttings. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Depresses the central nervous system, analgesic, antifungal, antibacterial, antiinflammatory (leaf), anodyne, bitter tonic, expectorant, diuretic, febrifuge, galactagogue, emenagogue, antigastalgic, leaves anti-parasitical, alterative, aromatic, pain reliever. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Chrysophenol D, isoorientin, casticin, D-fructose and luteolin; leucoanthocyanidins and vanillic acid (stem bark); P-hydroxybenzoic acid (seed); beta-sitosterol (seed and stem bark); nishindine and flavonoids (leaf). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Isoorientin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,7-dihydroxy-8-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)tet
rahydropyran-2-yl]-c
hromen-5-one |
C21H20O11 |
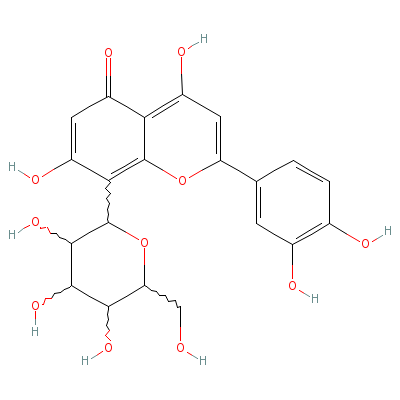
|
| Casticin |
479-91-4 |
4-hydroxy-2-(3-hydro
xy-4-methoxy-phenyl)
-3,6,7-trimethoxy-ch
romen-5-on
e |
C19H18O8 |
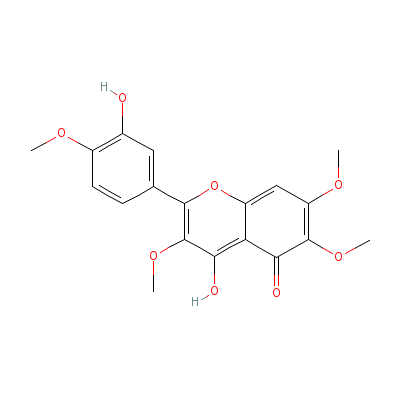
|
| D-fructose |
69-67-0 |
1,3,4,5,6-pentahydro
xyhexan-2-one |
C6H12O6 |
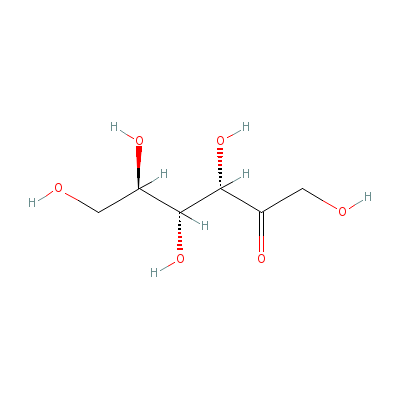
|
| Luteolin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-ch
romen-7-one |
C15H10O6 |
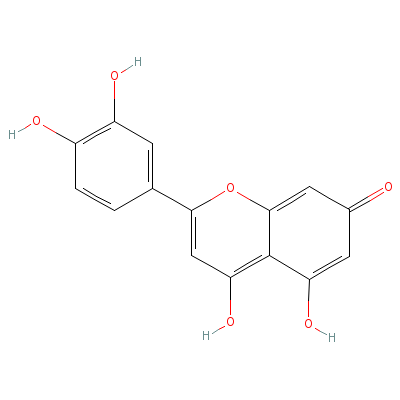
|
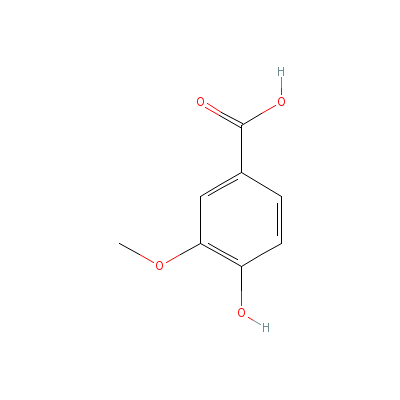
| Vanillic acid |
Not Available |
4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-
benzoic acid |
C8H8O4 |
|
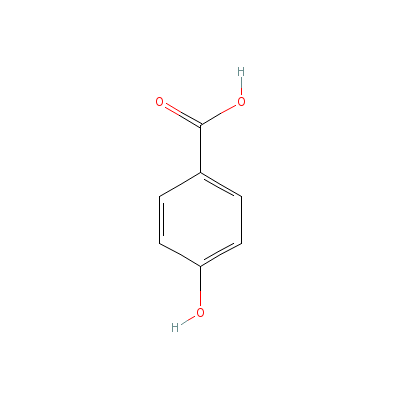
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
99-96-7 |
4-hydroxybenzoic
acid |
C7H6O3 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
As a demulcent (in the sinuses) and on sores (related to scrofula) (oil); in gonorrhea, rheumatism, sprains, fever (related to catarrh) and headache (leaf); aids in the removal of worms and foetid discharges from ulcers (leaf juice), controls acne in teenagers, regulates ovulatory cycle, menopause, menorrhagia (heavy menstruation), menstrual difficulties (secondary amenorrhea), premenstrual syndrome, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea and endometriosis and fibrocystic breast disease among women, relieves pains due to rheumatism, gout, sciatica and the body ache resulted from heavy physical exertion, skin troubles, migraine; with the right proportion it is use for dental care for healthy, disease free teeth, as mouth wash and treatment for toothache. Pillows stuffed with leaves are slept on to remove catarrh and headache. Dried fruit is used to destroy human worm while seeds boiled in water and eaten, or the water is taken internally, to prevent spread of toxins from poisonous bites of animals, also cooling for skin disorders. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Minor gastrointestinal upset and a mild skin rash with itching have been reported in less than 2% of the women monitored while taking vitex. Vitex is not recommended for use during pregnancy. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas.
Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. |
Dealers
Products
|
|