Albizia odoratissima (L.F.)BENTH |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Albizia odoratissima (L.F.)BENTH |
English
Name |
: |
Black siris, Ceylon rose-wood |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Acacia lomatocarpa DC., Acacia odoratissima Willd., Albizia odoratissima var. millis Benth. ex. Baker, Albizzia micrantha Biovin, Mimosa marginata Lam., Mimosa odoratissima |
Family |
: |
Mimosaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A medium sized to large, erect tree up to 30 m tall with drooping dark green foliate; bark dark grey with numerous horizontal cracks; young branchlets minutely yellowish-brown pubescent, later glabrous. Leaves 10 to 30 cm long; rachis with gland beneath uppermost pairs of pinnae, and a larger oval gland at the base; pinnae 2 to 8 pairs, 5 to 20 cm long; leaflets 6 to 24 pairs, dark green, pubescent, obliquely oblong, obtuse at base. Flowers yellowish-white, fragrant, sessile, arranged in numerous small 10 to 12 flowered, globose heads; peduncles 6 mm long, solitary or 2 to 4 together, arranged in terminal panicles up to 30 cm long; calyx 1.3 mm long, pubescent; corolla 4 mm long, grey-sillky outside, teeth ovate-lanceolate, acute. Fruit (pod) shortly stalked, 10 to 20 cm long and 2.5 to 3.8 cm wide, thin, flexible, glabrous, reticulately veined, purplish-green when immature, reddish-brown when mature; seeds 6 to 12, broadly ovate, flattened, yellow, 8 mm long and 6 mm wide. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Hypoglycemic (seed); coagulates semen and diuretic (seed extract). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Echinocystic acid, rhamnose, arabinose and xylose (seed). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
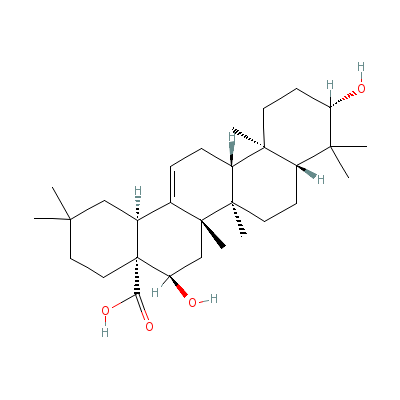
| Echinocystic acid |
510-30-5 |
5,10-dihydroxy-2,2,6
a,6b,9,9,12a-heptame
thyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,
8,8a,10,11
,12,13,1
4b-tetradecahydropic
ene-4a-carboxylic
acid |
C30H48O4 |
|
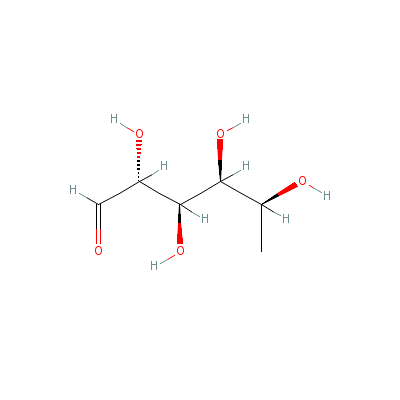
| Rhamnose |
4469-18-5 |
2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy
hexanal |
C6H12O5 |
|
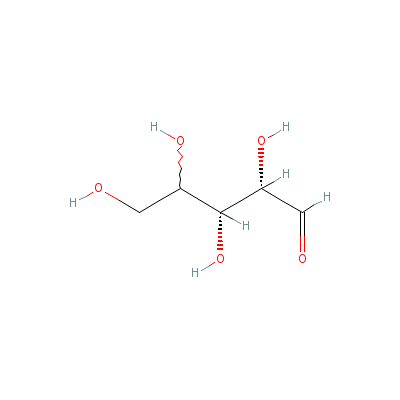
| Arabinose |
20235-19-2 |
2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy
pentanal |
C5H10O5 |
|
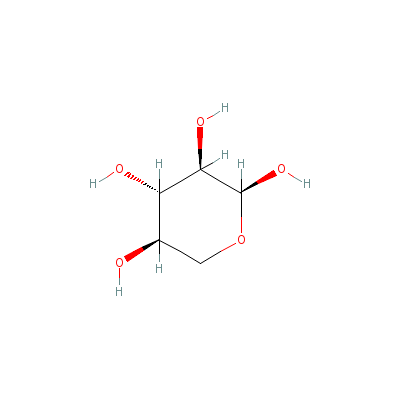
| Xylose |
25990-60-7 |
oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol |
C5H10O5 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
For ulcers and leprosy (bark); in cough (leaf); erysipelas, wounds, dyspnoea, and as an antidote for snake bite and food poisoning. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas. |
Dealers
Products
|
|