Acacia nilotica (L.) WILLD. EX DEL. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Acacia nilotica (L.) WILLD. EX DEL. |
English
Name |
: |
Indian Gum and Indian Gum-Arabic Tree |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Acacia arabica (lamk., ), Mimosa nilotica, L., Mimosa arabica Roxb. |
Family |
: |
Mimosaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A medium to large tree that can reach a height of 10 m, with an average of 4-7 m in height.The leaves are twice compound, i.e. they consist of 5-11 feather-like pairs of pinnae; each pinna is further divided into 7-25 pairs of small, elliptic leaflets that can be bottle to bright green in colour.The flower stalks are hairy. The pods are flat, straight or slightly curved, and fleshy when young with reddish hairs, becoming dark blackish when mature, deeply constricted between each seed and they do not split open, but break up transversely on the ground into single-seeded segments during March to September. Fruit are gray-green, softly hairy flattened pod 6 to 25 cm long, 1 to1.5 cm wide, strongly constricted between each seed; pods slightly sticky internally. Seeds are depressed, subglobular. A deep woody taproot with several branching surface laterals. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antifungal, alleviates spasms, analgesic and lowers blood sugar (stem bark); hemostatic (leaf and bark); expectorant (pod); astringent, demulcent, aphrodisiac and nutritive. Gum extract (Akakia) is styptic, tonic and astringent. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
(+)-Catechin, ascorbic acid, beta-carotene, chlorogenic acid, digitonin, epigallocatechin, isoquercitrin, lignin, malic acid, oleic acid, oxalic acid, pyrogallol, quercetin, quercitrin, riboflavin, thiamin (plant); beta-amyrin, octacosanol (root); ellagic acid, tannin, gallic acid (bark); polyphenols (pod and bark); phospholipids (seed); betulin (plant, root bark); protocatechuic acid (fruit). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Tannin |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
C27H22O18 |
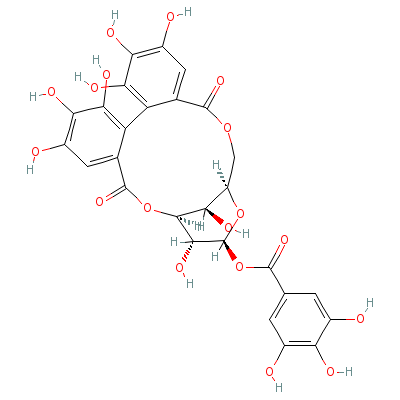
|
| Gallic acid |
149-91-7 |
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oic acid |
C7H6O5 |
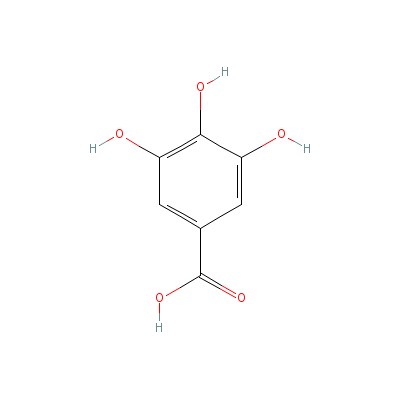
|
| (+)-Catechin |
5323-80-8 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)chroman-3,5,7-tri
ol |
C15H14O6 |
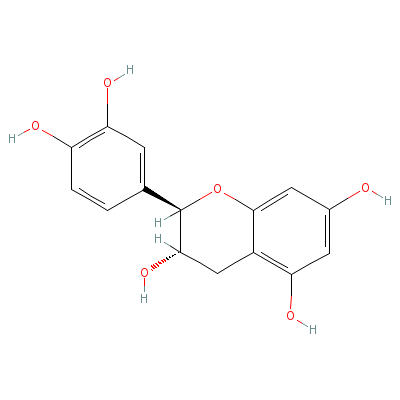
|
| Ascorbic Acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
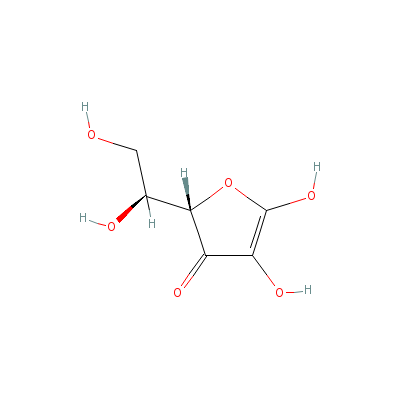
|
| beta-Carotene |
Not Available |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
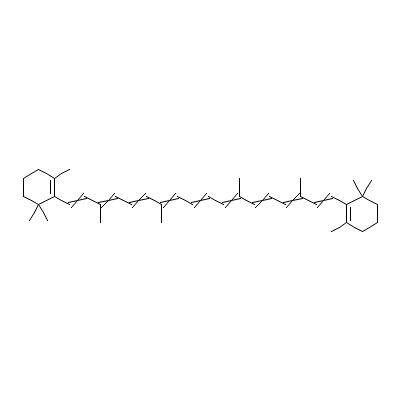
|
| Chlorogenic acid |
327-97-9 |
3-[3-(3,4-dihydroxyp
henyl)prop-2-enoylox
y]-1,4,5-trihydroxy-
cyclohexan
e-1-carb
oxylic acid |
C16H18O9 |
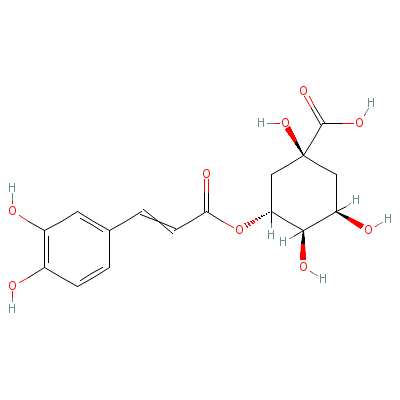
|
| Digitonin |
52781-76-7 |
Not Available |
C56H92O29 |
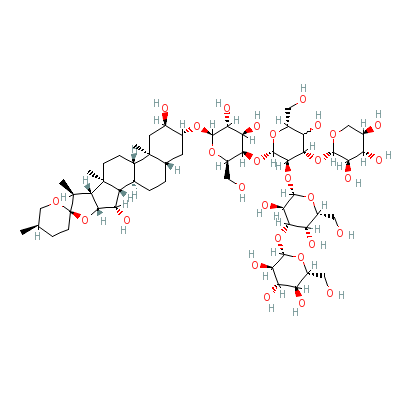
|
| Epigallocatechin |
970-74-1 |
(2R,3R)-2-(3,4,5-tri
hydroxyphenyl)chroma
n-3,5,7-triol |
C15H14O7 |
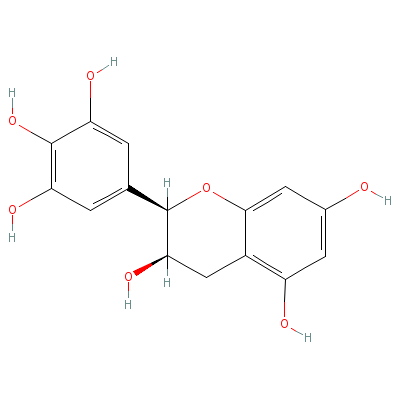
|
| Isoquercitrin |
21637-25-2 |
3-[5-(1,2-dihydroxye
thyl)-3,4-dihydroxy-
oxolan-2-yl]oxy-2-(3
,4-dihydro
xyphenyl
)-4,5-dihydroxy-chro
men-7-one |
C21H20O12 |
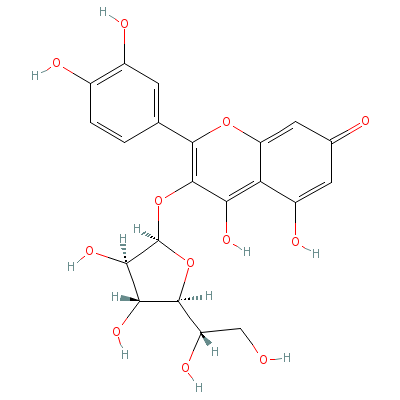
|
| Malic acid |
Not Available |
2-hydroxybutanedioic
acid |
C4H6O5 |
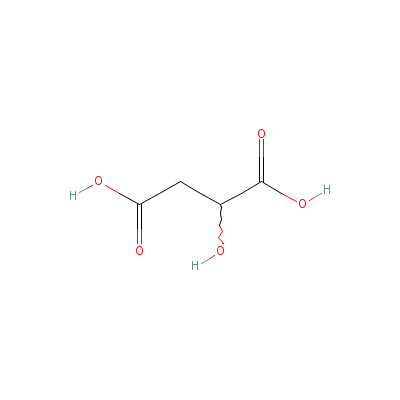
|
| Oleic acid |
8046-01-3 |
octadec-9-enoic acid |
C18H34O2 |
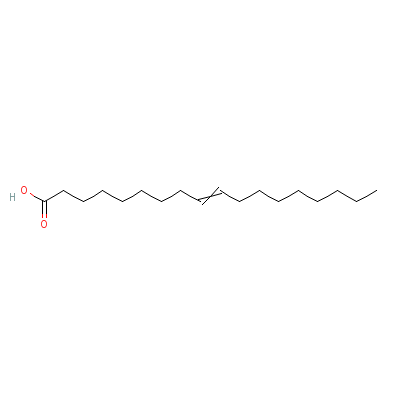
|
| Oxalic acid |
553-91-3 |
Oxalic acid |
C2H2O4 |
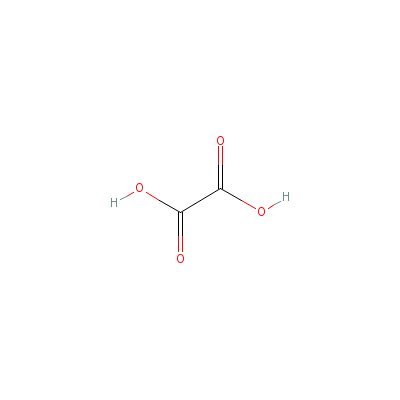
|
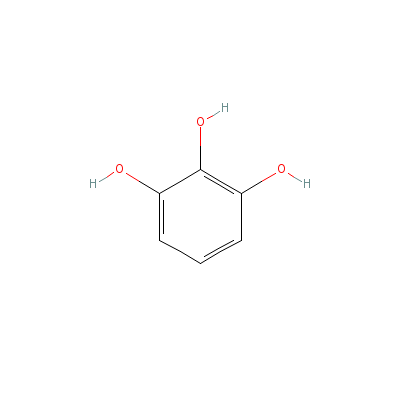
| Pyrogallol |
Not Available |
benzene-1,2,3-triol |
C6H6O3 |
|
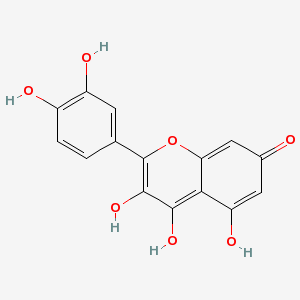
| Quercetin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-3,4,5-trihydroxy
-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O7 |
|
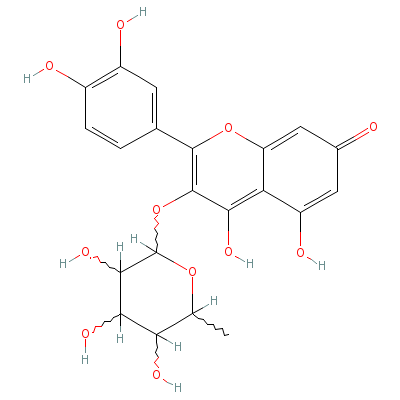
| Quercitrin |
6151-25-3 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-
(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
methyl-oxa
n-2-yl)o
xy-chromen-7-one |
C21H20O11 |
|
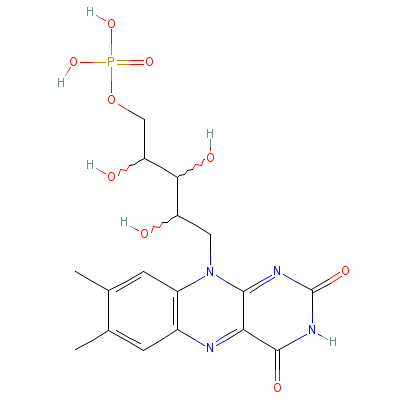
| Riboflavin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C17H21N4O9P |
|
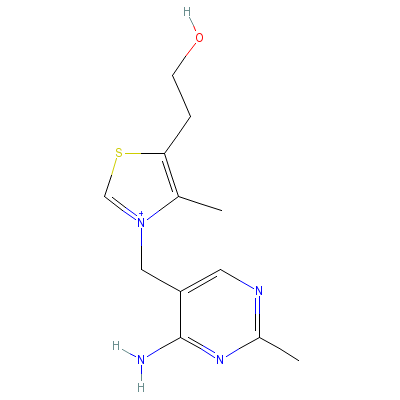
| Thiamin |
59-43-8 |
2-[3-[(4-amino-2-met
hyl-pyrimidin-5-yl)m
ethyl]-4-methyl-1-th
ia-3-azoni
acyclope
nta-2,4-dien-5-yl]et
hanol |
C12H17N4OS+ |
|
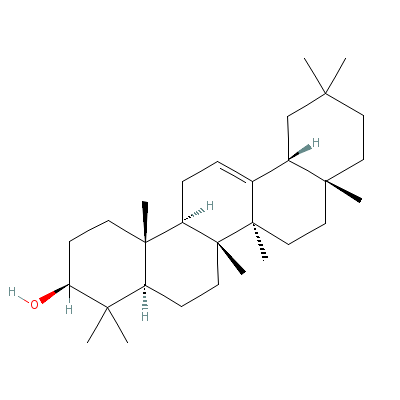
| Beta-Amyrin |
559-70-6 |
4,4,6a,6b,8a,11,11,1
4b-octamethyl-1,2,3,
4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,1
2a,14,14a-
tetradec
ahydropicen-3-ol |
C30H50O |
|
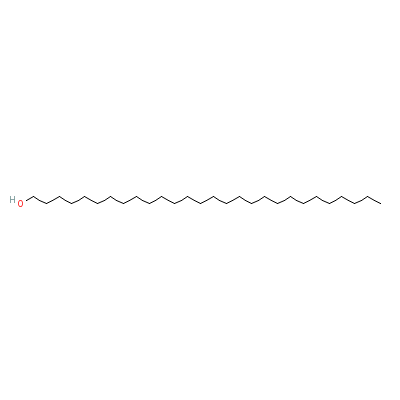
| Octacosanol |
67905-27-5 |
Octacosan-1-ol |
C28H58O |
|
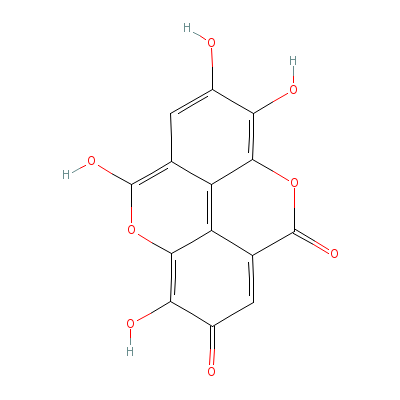
| Ellagic acid |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C14H6O8 |
|
| Tannin |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
C27H22O18 |

|
| Betulin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C30H50O2 |
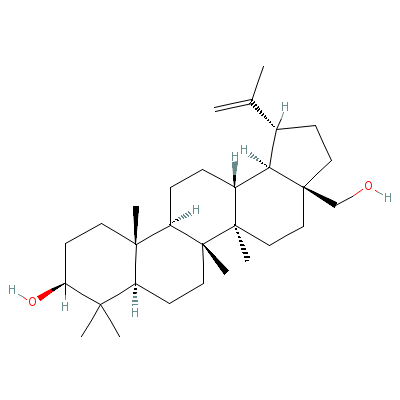
|
| Protocatechuic acid |
5417-95-8 |
N,N-diethyl-N'-(2,4,
8,9-tetrazabicyclo[4
.3.0]nona-2,4,7,10-t
etraen-5-y
l)propan
e-1,3-diamine |
C12H20N6 |
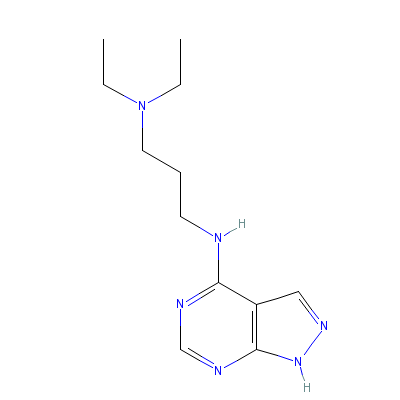
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
In asthma (gum, bark and leaf); ophthalmia (and other eye problems) and “sexual weakness” (leaf decoction); diabetes, dysentery and diarrhea, bronchitis and skin maladies (bark); headache, urinary problems, sore throat and gonorrhea (leaf); as a toothbrush; Tender growing tops rubbed into a paste with sugar and water act as demulcent in coughs. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
No Records |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
The Himalaya Drug Company.
Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
Grieve M. A Modern Herbal 1931 (www.botanical.com).
Johnson T. CRC Ethnobotany Desk.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|