| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Silybum marianum Gaertn. |
English
Name |
: |
Holy or Milk Thistle |
Family |
: |
Asteraceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Annual or biennial erect robust spinous herb, 30-120 cm tall. Stem grooved; leaves large, mottled with white, strongly spinescent; the fruit is an egg-shaped achene with an elongated downy structure protruding out. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antihemorrhagic, pungent, demulcent, antispasmodic and antihepatotoxic (seed); sudorific, aperient, diaphoretic and gentle laxative (leaf); astringent, bitter, cholagogue, diaphoretic, diuretic, emetic, emmenagogue, hepatic, stimulant, stomachic and tonic (plant) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Apigenin, naringenin (fruit), beta-carotene (plant), kaempferol, quercetin (seed) Silymarin (fruit and seed); apigenin and beta-sitosterol (aerial part) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Apigenin |
520-36-5 |
4,5-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-chrome
n-7-one |
C15H10O5 |
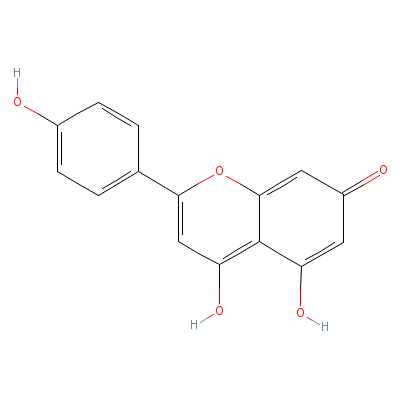
|
| Naringenin |
Not Available |
5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-chroma
n-4-one |
C15H12O5 |
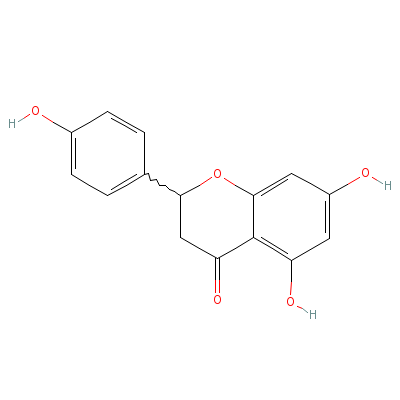
|
| beta-Carotene |
Not Available |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
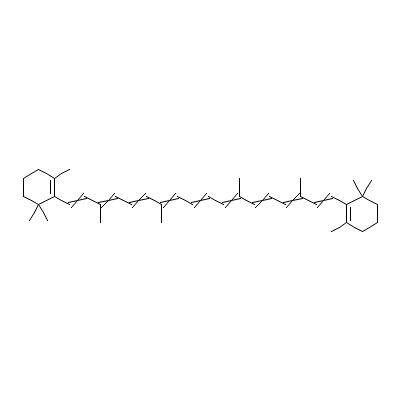
|
| Kaempferol |
80714-53-0 |
3-[3-[4,5-dihydroxy-
6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)oxa
n-2-yl]oxy-oxan-2-yl
]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6
-(hydroxymethyl)oxan
-2
-yl]oxy-4,5-dihy
droxy-2-(4-hydroxyph
enyl)-chromen-7-one |
C33H40O21 |
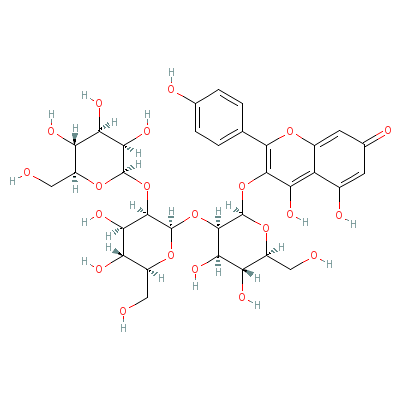
|
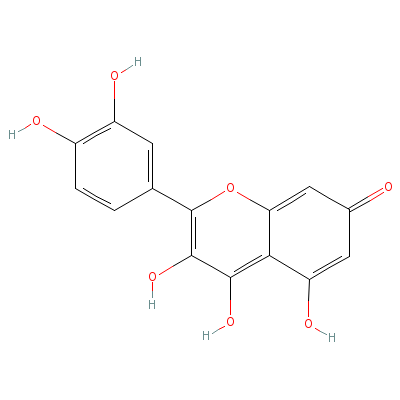
| Quercetin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-3,4,5-trihydroxy
-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O7 |
|
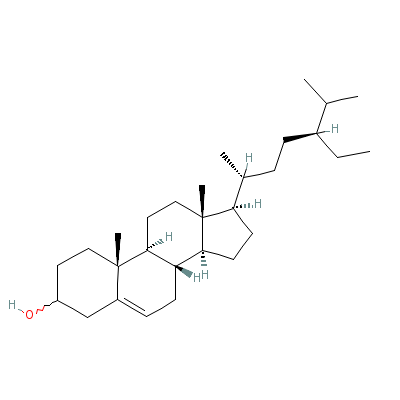
| Beta-Sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17-dodecahydro
-1H-cyclopenta[a]phe
nanthren-3-ol |
C29H50O |
|
| Silymarin |
Not Available |
(2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihyd
roxy-2-[(8R,9R)-9-(4
-hydroxy-3-methoxy-p
henyl)-8-(
hydroxym
ethyl)-7,10-dioxabic
yclo[4.4.0]deca-2,4,
11-trien-3-yl]chroma
n-
4-one |
C25H22O10 |

|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
For arresting bleeding and as a demulcent (seed); as a diaphoretic and gentle laxative (leaf); liver problems such as hepatitis, jaundice and cirrhosis and due to eating fungi containing phalloidine or amantine; in gallstones, for intermittent fevers, dropsy and as emmenagogue (whole plant). |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Dehmlow C. Erhard J. de Groot H. Inhibition of Kupffer cell functions as an explanation for the hepatoprotective properties of silibinin. Hepatology1996 Apr;23(4):749-54. |
|
|