Cochlospermum tinctorium Perr. ex A. Rich. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Cochlospermum tinctorium Perr. ex A. Rich. |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Cochlospermum niloticum Oliv. |
Family |
: |
Bixaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Subshrub up to 80 cm tall with woody subterranean rootstock producing annual shoots. Leaves alternate, palmately (3–)5-lobed; stipules linear, caducous; petiole 3–6 cm long; blade in outline 2–12 cm × 2–16 cm, lobes lanceolate to oblong, basally connate for up to 1/4 of their length, margins entire to serrate, glabrescent to pubescent below. Inflorescence a few-flowered panicle or raceme, usually produced at ground level from the rootstock, sometimes appearing on top of leafy shoots. Flowers bisexual, regular, 5-merous, 6–9 cm in diameter; pedicel 1.5–4 cm long; sepals elliptical-oblong, 1–1.5 cm × 0.5–1 cm, velvety outside; petals obovate, 2.5–4 cm × 2–3 cm, shallowly emarginate, golden-yellow; stamens numerous, free; ovary superior, usually woolly, style simple, slender, stigma small. Fruit a fusiform or obovoid capsule 4–6 cm × 2.5 cm, slightly ridged, brown, grey or black, many-seeded. Seeds reniform, c. 5 mm long, densely covered with long white to yellowish hairs. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antimalarial, antihepatotoxic and tonic (rootstock) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Gallic acid, ellagic acid, ellagitannin, acetogenin, arjunolic acid, cochloxanthin and dihydrocochloxanthin (rootstock) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Gallic acid |
149-91-7 |
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oic acid |
C7H6O5 |
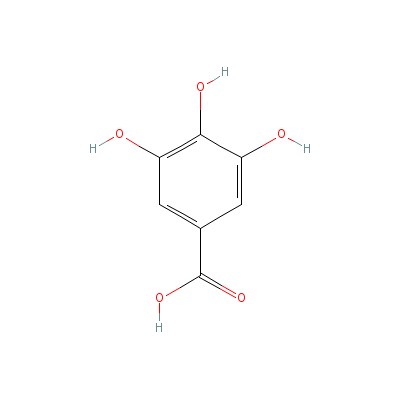
|
| Ellagic acid |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C14H6O8 |
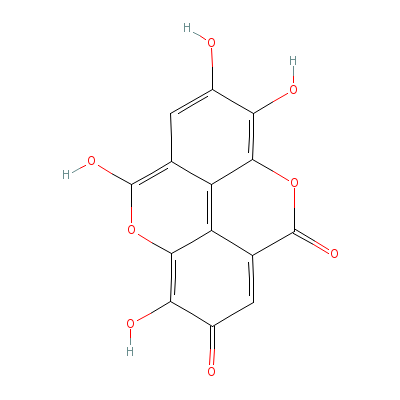
|
| Ellagitannin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
|
| Arjunolic acid |
Not Available |
10,11-dihydroxy-9-(h
ydroxymethyl)-2,2,6a
,6b,9,12a-hexamethyl
-1,3,4,5,6
,6a,7,8,
8a,10,11,12,13,14b-t
etradecahydropicene-
4a-carboxylic acid |
C30H48O5 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The yellow rootstock is one of the most respected medicines for jaundice and liver diseases. It is also applied to cure oedema, urethral discharge, dysmenorrhoea, epilepsy, schistosomiasis, pneumonia, bronchial affections, conjunctivitis, gastric problems, diarrhoea, indigestion, stomach-ache and skin infections. An extract of the rootstock is taken against malaria. A concoction of the fruits with tamarind fruits is drunk to cure snakebites. The pulped leaves are used in a wet dressing to maturate abscesses and furuncles. A decoction of the twigs or rootstock is drunk or used in a bath to treat urino-genital disorders, kidney pain or pain between the ribs. The body is washed with a water extract of the rootstock to cure skin diseases and as prophylaxis. Seed oil is used to treat leprosy. |
Dealers
Products
|
|