| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Equisetum hyemale L. |
English
Name |
: |
Common scouring rush, Rough scouring rush, Bottlebrush, Horsetail, Field horsetail, Rough horsetail, Pewterwort, Dutch rush, Shave-grass |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Equisetum prealtum Raf., Equisetum robustum A. Braun., Hippochaete hyemalis (L.) Bruhin |
Family |
: |
Equisetaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A spreading, reed-like perennial plant growing to 3 ft (0.9 m) tall. The evergreen stems are cylindrical, about 1/3 in (0.8 cm) in diameter, jointed, hollow, usually unbranched, and have rough longitudinal ridges. The tiny leaves are joined together around the stem, forming a narrow black-green band or sheath at each joint. Like other Pteridophytes (ferns and their relatives), scouring rush does not produce flowers or seeds. Instead it develops a brown, cone-shaped, spore-producing strobilus at the tip of fertile stems, which are shorter than the infertile stems. The spores themselves are microscopic. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Abortifacient, astringent, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, diaphoretic, diuretic, expectorant, febrifuge, haemostatic, hypotensive and styptic (whole plant) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Aconitic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid (plant) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Aconitic acid |
499-12-7 |
prop-1-ene-1,2,3-tri
carboxylic acid |
C6H6O6 |

|
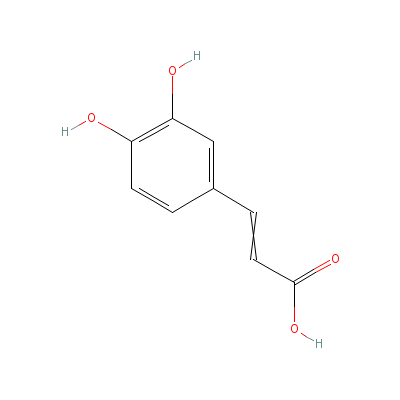
| Caffeic acid |
Not Available |
3-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)prop-2-enoic acid |
C9H8O4 |
|
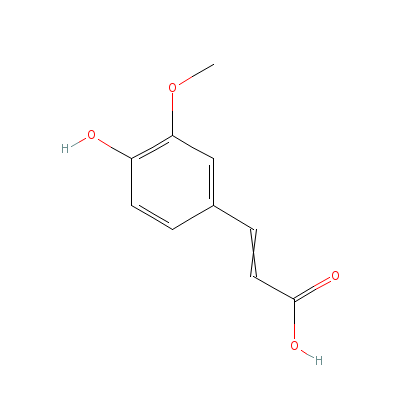
| Ferulic acid |
24276-84-4 |
3-(4-hydroxy-3-metho
xy-phenyl)prop-2-eno
ic acid |
C10H10O4 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The whole plant has an appetite-stimulating effect. The plant is a useful diuretic when taken internally and is used in the treatment of kidney and bladder problems. A decoction applied externally will stop the bleeding of wounds and promote healing. It has also been used for treating adenopathy, backache, cataract, cholecystosis, colds, conjunctivosis, constipation, cystosis, dermatosis, diarrhea, dysentery, dysmenorrhea, dysuria, embolism, enuresis, fever, fistulas, gonorrhea, hemorrhoid, incontinence, ophthalmia, prostatosis, sores, syphilis, tuberculosis and water
retention. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 James A Duke and Maryl Fulton. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs - 2nd Edition, P: 666, CRC Press July 2002. James A Duke and Maryl Fulton. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs - 2nd Edition, P: 666, CRC Press July 2002.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|