| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Areca catechu L. |
English
Name |
: |
Areca Nut |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Areca faufel Gaertn. |
Family |
: |
Arecaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A tree with a straight smooth stem, the upper portion green, annulate, 12 to 30 m tall. Leaves pinnate, 1.2 to 1.8 m long; leaflets numerous, 30 to 60 cm long; petiole expanded into a broad, tough sheath. Spathe double, compressed, glabrous, spadices much-branched, bearing male and female flowers; male flowers small, numerous sessile; female solitary or in groups of 2 to 3, borne near the base of each ramification of the spadix. Fruit ovoid or oblong, 4 to 5 cm long, smooth, orange or red when fully ripe, single-seeded, orange or red when ripe, single seeded, with a fibrous mesocarp; seed-kernel, 2 to 4 cm in diameter, greyish-brown, ruminate with reddish-brown lines. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Laxative, aphrodisiac, digestive, astringent, diuretic, stimulant, cardiotonic, emmenagogue, antimicrobial and anthelmintic; freshens breath and strengthens gums (paste). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Arecoline, ascorbic acid, beta-sitosterol, choline, diosgenin, gallic acid, lauric acid, linoleic acid, niacin, oleic acid, riboflavin,stearic acid, tannin, thiamin (seed); beta-carotene (plant). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| (+)-catechin |
5323-80-8 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)chroman-3,5,7-tri
ol |
C15H14O6 |
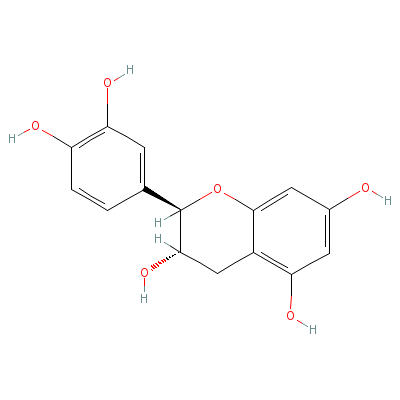
|
| Arecoline |
300-08-3 |
methyl
1-methyl-5,6-dihydro
-2H-pyridine-3-carbo
xylate |
C8H13NO2 |
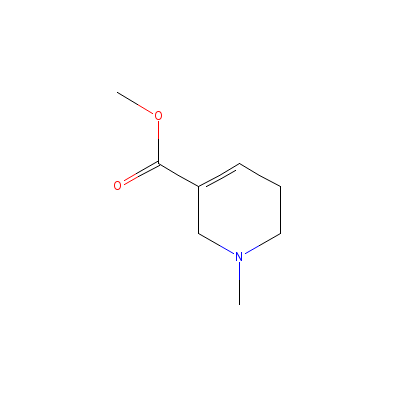
|
| Ascorbic Acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
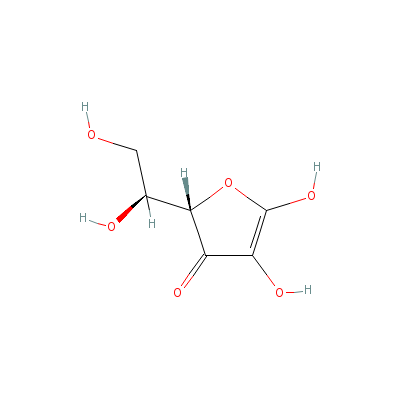
|
| Beta-sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cycl
openta[a]phenanthren
-3-ol |
C29H50O |
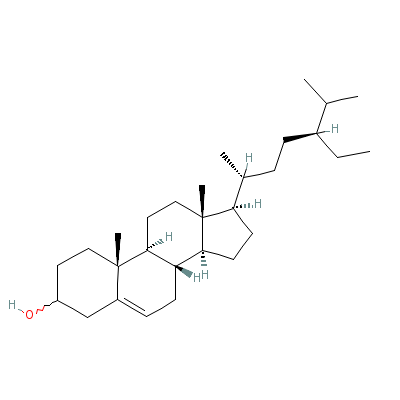
|
| Choline |
67-48-1 |
2-hydroxyethyl-trime
thyl-ammonium |
C5H14NO+ |
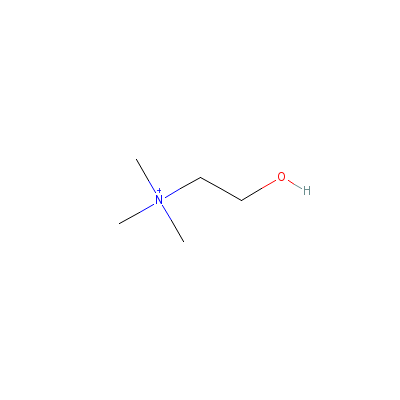
|
| Diosgenin |
512-04-9 |
Not Available |
C27H42O3 |
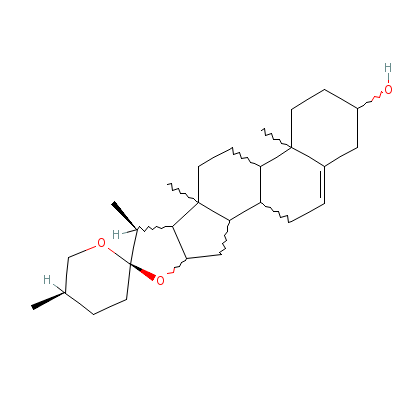
|
| Gallic acid |
149-91-7 |
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oic acid |
C7H6O5 |
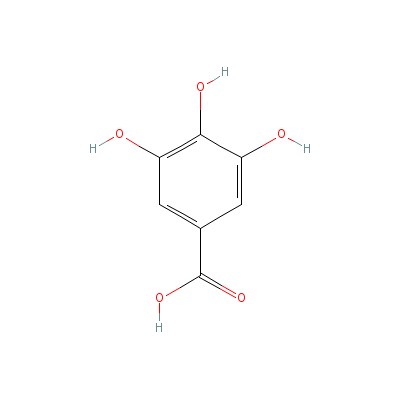
|
| Lauric acid |
8045-27-0 |
Dodecanoic acid |
C12H24O2 |
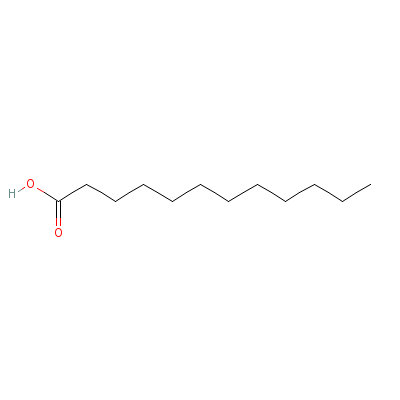
|
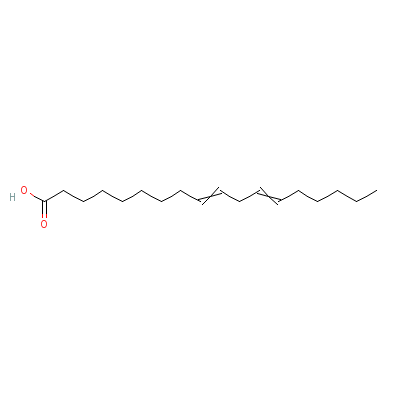
| Linoleic acid |
8024-22-4 |
Octadeca-9,12-dienoi
c acid |
C18H32O2 |
|
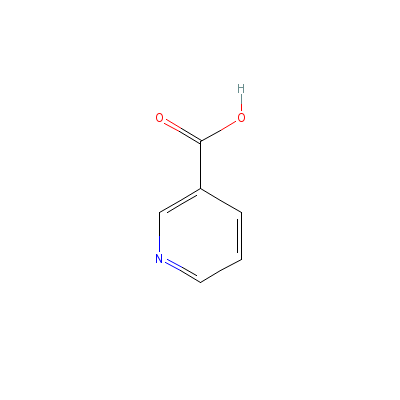
| Niacin |
99148-57-9 |
pyridine-3-carboxyli
c acid |
C6H5NO2 |
|
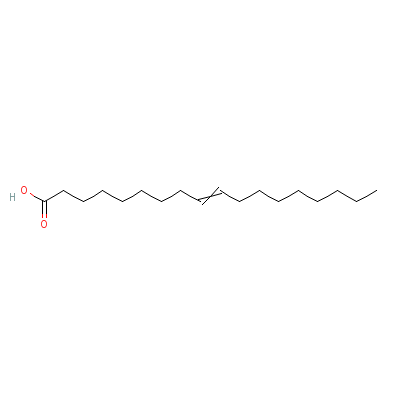
| Oleic acid |
8046-01-3 |
octadec-9-enoic acid |
C18H34O2 |
|
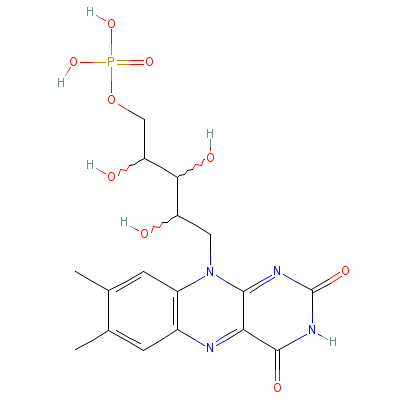
| Riboflavin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C17H21N4O9P |
|
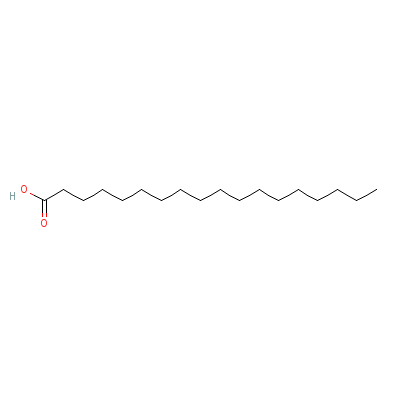
| Stearic acid |
82497-27-6 |
octadecanoic acid |
C18H36O2 |
|
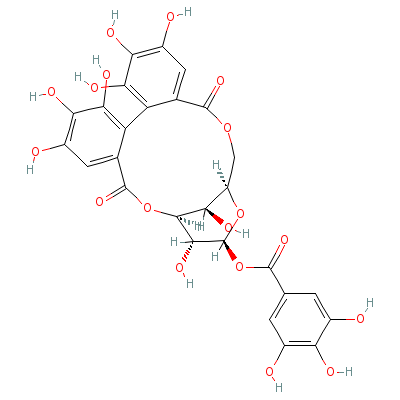
| Tannin |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
C27H22O18 |
|
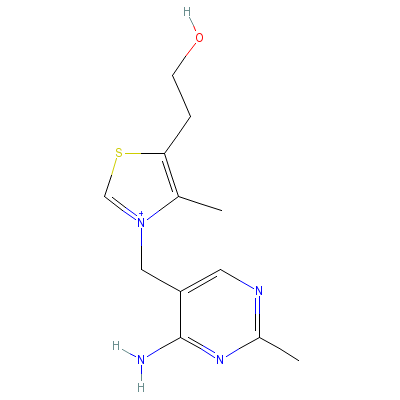
| Thiamin |
59-43-8 |
2-[3-[(4-amino-2-met
hyl-pyrimidin-5-yl)m
ethyl]-4-methyl-1-th
ia-3-azoni
acyclope
nta-2,4-dien-5-yl]et
hanol |
C12H17N4OS+ |
|
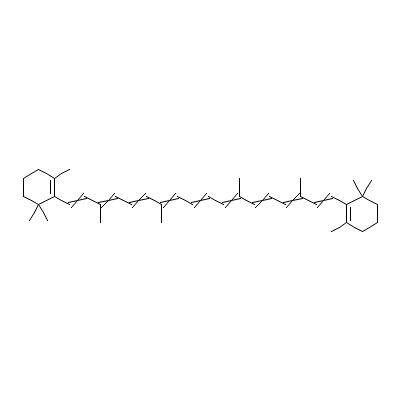
| beta Carotene |
7235-40-7 |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
To treat inflammation of the eyes, giddiness and gleet, in urinary maladies and diarrhea (powdered); skin disorders and external ulcers, for cleaning teeth, in the removal of tapeworms and other intestinal parasites, to treat liver disorders (root decoction). |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Sri Lankans have reported that the unripe fruits (used as a laxative) can alter eyesight. Chewing betel nuts can also cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, chest pain, irregular heartbeats, high or low blood pressure, and irregular heart beats. A heart attack occurred in a man immediately after chewing betel nut. It is not clear if betel was the cause. There may be a higher risk of cancers of the liver, mouth, stomach, prostate, cervix, and lung with regular betel use. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. Sharma, Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
The Himalaya Drug Company.
Johnson T. CRC Ethnobotany Desk Reference (www.herbweb.com/herbage). |
Dealers
Products
|
|