Sanguisorba officinalis L. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Sanguisorba officinalis L. |
English
Name |
: |
Official burnet, Great burnet, Burnet bloodwort, Salad burnet |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Poterium officinale (L.)A.Gray., Sanguisorba carnea Fisch. ex Link, Sanguisorba polygama F. Nyl. |
Family |
: |
Rosaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Herbs perennial, 30–120 cm tall. Rootstock brown or purple-brown, robust, usually fusiform, rarely terete, cross section yellow-white or purple. Stems erect, angular, glabrous, or base pilose or sparsely glandular hairy. Radical leaves: stipules brown, membranous, glabrous or abaxially sparsely glandular hairy; petiole long, glabrous or sparsely glandular, base sheathing and imbricate, sometimes sparsely glandular hairy; leaf blade with 4–6 pairs of leaflets; leaflets petiolulate, green on both surfaces, ovate, oblong-ovate, fasciated oblong, or fasciated lanceolate, 1–7 × 0.5–3 cm, base cordate to broadly cuneate, margin coarsely obtusely or rarely acutely serrate, both surfaces glabrous or abaxially sparsely pilose. Cauline leaves: stipules large, semiovate, herbaceous, margin acutely serrate; leaflets shortly petiolulate or sessile, oblong to oblong-lanceolate, base subcordate to rounded, apex acute. Inflorescences erect, spicate, ellipsoid, cylindric, or ovoid, usually 1–6 × 0.5–1 cm, flowering from apex to base; rachis glabrous or occasionally sparsely glandular hairy; bracts lanceolate, shorter than or nearly equaling sepals, membranous, abaxially pilose, apex acuminate to caudate; sepals 4, purple, red, pink, or white, elliptic to broadly ovate, abaxially pilose, with faint longitudinal midvein, usually with shortly acute apex; stamens 4; filaments filiform, 0.5–1 × as long as sepals, exserted beyond them or not. Ovary glabrous or puberulous; stigma dilated, discoid, margin fimbriate-papillate. Fruiting hypanthium longitudinally 4-ribbed. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Astringent, refrigerant, styptic and tonic (leaves); anodyne, astringent, diuretic, febrifuge, haemostatic, tonic and vulnerary (root) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
(+)-catechin, (+)-gallocatechin, kaempferol, pomolic acid, quercetin, sanguiin H-2, sanguiin H-6, tannin, ursolic acid (plant); betulinic acid (stem) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| (+)-catechin |
5323-80-8 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)chroman-3,5,7-tri
ol |
C15H14O6 |
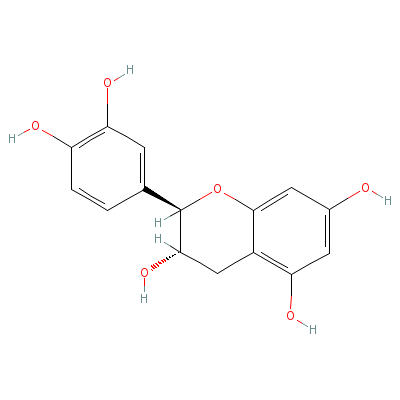
|
| (+)-gallocatechin |
970-73-0 |
2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyp
henyl)chroman-3,5,7-
triol |
C15H14O7 |
|
| Kaempferol |
80714-53-0 |
3-[3-[4,5-dihydroxy-
6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)oxa
n-2-yl]oxy-oxan-2-yl
]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6
-(hydroxymethyl)oxan
-2
-yl]oxy-4,5-dihy
droxy-2-(4-hydroxyph
enyl)-chromen-7-one |
C33H40O21 |
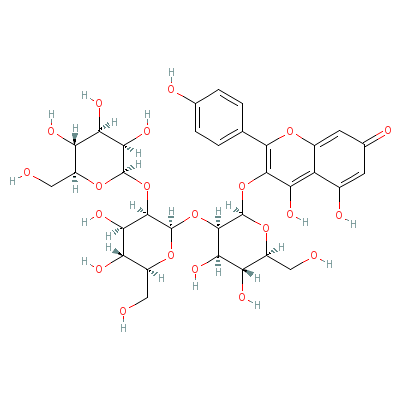
|
| Pomolic acid |
13849-91-7 |
(1R,2R,4aS,6aS,6aS,6
bR,8aS,10S,12aS,14bR
)-1,10-dihydroxy-1,2
,6a,6b,9,9
,12a-hep
tamethyl-2,3,4,5,6,6
a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13
,14b-tetradecahydrop
ic
ene-4a-carboxyli
c acid |
C30H48O4 |
|
| Quercetin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-3,4,5-trihydroxy
-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O7 |
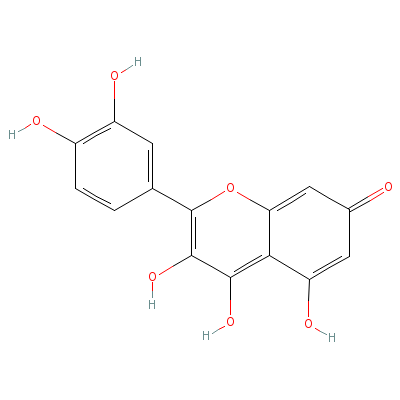
|
| Sanguiin H-2 |
82200-04-2 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
|
| Sanguiin H-6 |
82978-00-5 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
|
| Tannin |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
C27H22O18 |
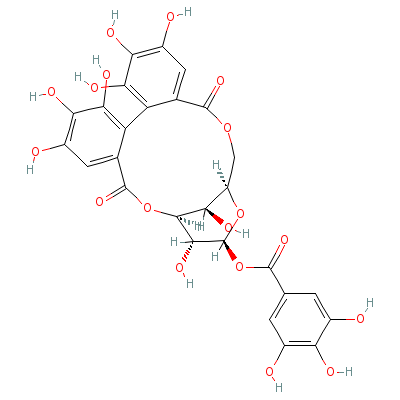
|
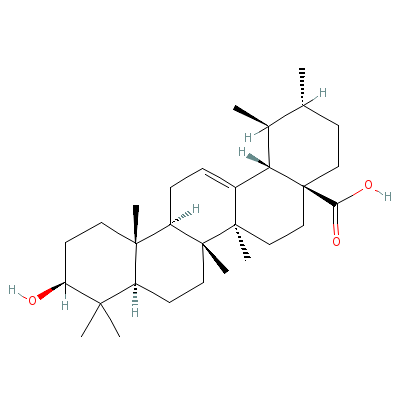
| Ursolic acid |
77-52-1 |
10-hydroxy-1,2,6a,6b
,9,9,12a-heptamethyl
-2,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a
,10,11,12, |
C30H48O3 |
|
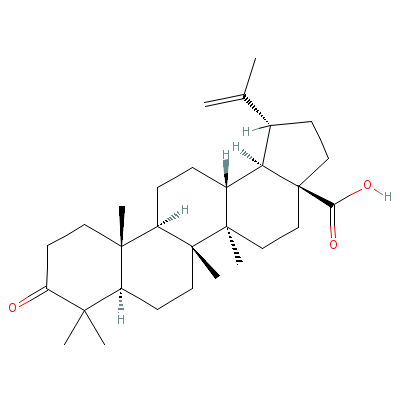
| Betulinic acid |
4481-62-3 |
Not Available |
C30H46O3 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The leaves are used in the treatment of fevers and bleeding. The roots are used in the treatment of peptic ulcers, haematuria, menorrhagia, nosebleeds, bloody stool, dysentery, diarrhoea, haemorrhoids and burns. The whole plant especially the roots are useful for the internal treatment for all sorts of abnormal discharges including diarrhoea, dysentery and leucorrhoea. It is used externally in the treatment of burns, scalds, sores, eczema, skin ulcerations and other skin diseases. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Not to be used topically on large areas of burns as the hydrolytic tannins in the root (Di Yu) can be absorbed by the skin, resulting in liver inflammation. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 566, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005. Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 566, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|