| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Rheum officinale Baill. |
English
Name |
: |
Chinese rhubarb |
Family |
: |
Polygonaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Herbs large, 1.5-2 m tall. Rhizomes and roots stout. Stem stout, hollow, finely sulcate, with white hairs, especially above and at nodes. Petiole of basal leaf terete, ca. as long as blade or slightly shorter, pubescent; leaf blade orbicular, rarely broadly ovate, large, 30-50 cm in diam., or longer than wide, abaxially pubescent, adaxially glabrous, rarely pubescent along veins, basal veins 5-7, base subcordate; palmatilobate, apex subacute; stem leaves smaller upward; ocrea large, to 15 cm, broad, outside with dense hairs. Panicles large; branches spreading. Pedicel 3-3.5 mm, slender, jointed below middle. Flowers 4- or 5-fascicled; tepals 6, green to yellow-white, elliptic or narrowly elliptic, 2-2.5 × 1.2-1.5 mm; stamens shorter than perianth. Style deflexed; stigma inflated. Fruit oblong-ellipsoid, 8-10 × 7-9 mm; wings ca. 3 mm wide, with longitudinal veins near margin. Seeds broadly ovoid. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Anticholesterolemic, antiseptic, antispasmodic, antitumor, aperient, astringent, cholagogue, demulcent, diuretic, laxative, purgative, stomachic and tonic (root) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Aloe-emodin, anthraquinone, caffeic acid, calcium oxalate, cinnamic acid, emodin, ferulic acid, gallic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid, pectin, rhein, rutin (root) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Aloe-emodin |
481-72-1 |
1,8-dihydroxy-3-(hyd
roxymethyl)anthracen
e-9,10-dione |
C15H10O5 |
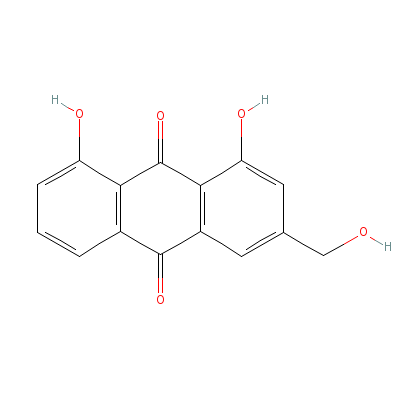
|
| Anthraquinone |
84-65-1 |
Anthracene-9,10-dion
e |
C14H8O2 |
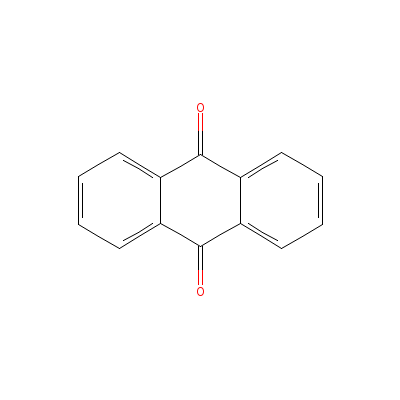
|
| Caffeic acid |
Not Available |
3-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)prop-2-enoic acid |
C9H8O4 |
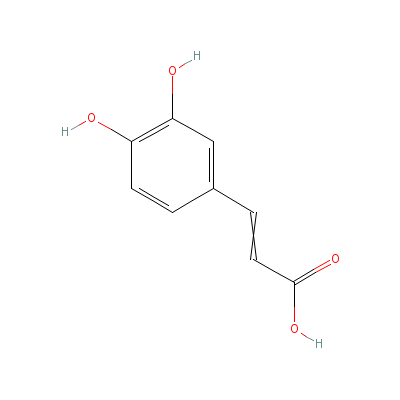
|
| Calcium oxalate |
5794-28-5 |
calcium oxalate |
C2CaO4 |
|
| Cinnamic acid |
63938-16-9 |
3-phenylprop-2-enoic
acid |
C9H8O2 |
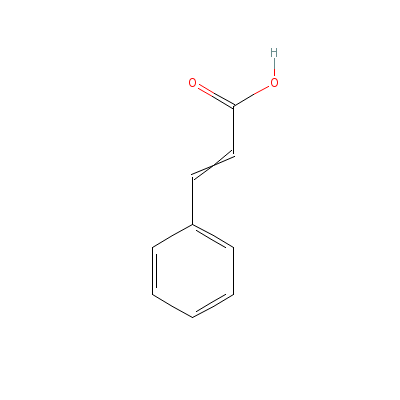
|
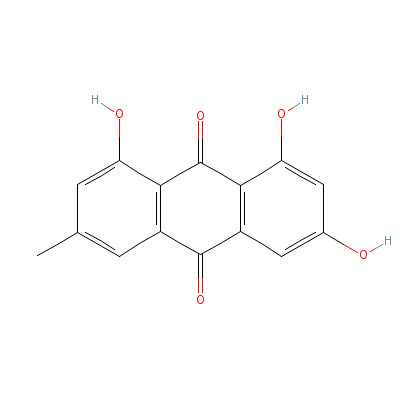
| Emodin |
Not Available |
1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-m
ethyl-anthracene-9,1
0-dione |
C15H10O5 |
|
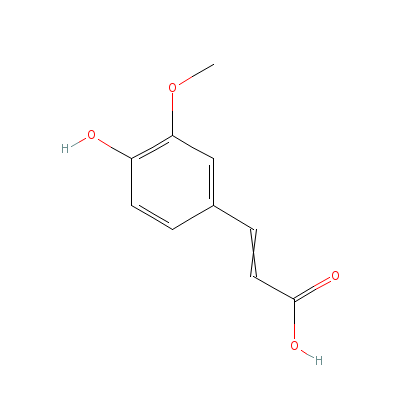
| Ferulic acid |
24276-84-4 |
3-(4-hydroxy-3-metho
xy-phenyl)prop-2-eno
ic acid |
C10H10O4 |
|
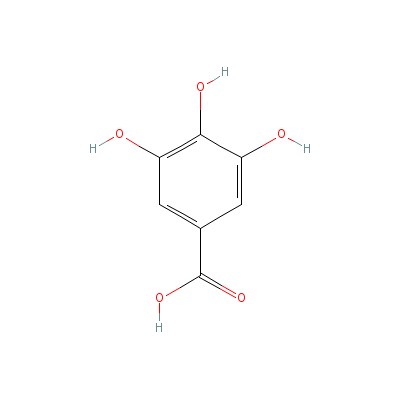
| Gallic acid |
149-91-7 |
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oic acid |
C7H6O5 |
|
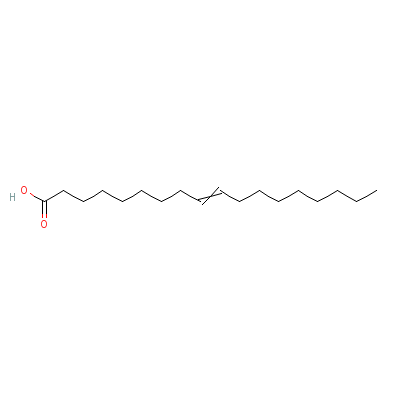
| Oleic acid |
8046-01-3 |
octadec-9-enoic acid |
C18H34O2 |
|
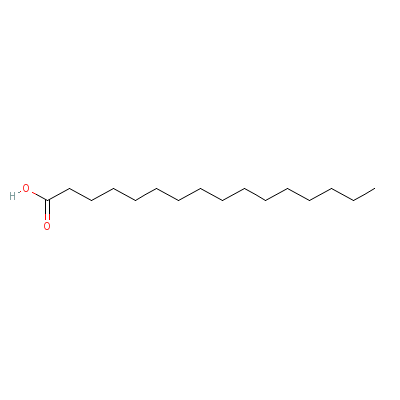
| Palmitic acid |
66321-94-6 |
Hexadecanoic acid |
C16H32O2 |
|
| Pectin |
9047-18-1 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
|
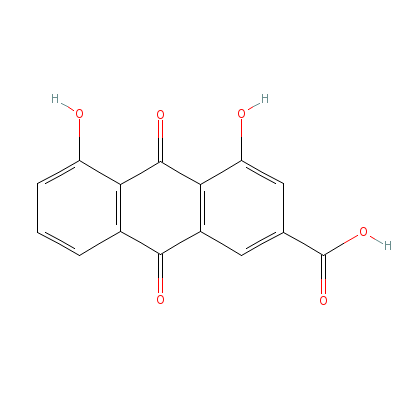
| Rhein |
Not Available |
4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-d
ioxo-anthracene-2-ca
rboxylic acid |
C15H8O6 |
|
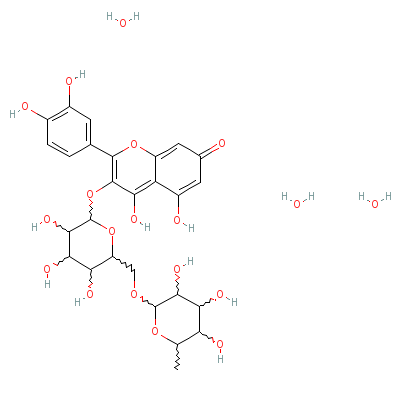
| Rutin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
[(3,4,5-tr
ihydroxy
-6-methyl-tetrahydro
pyran-2-yl)oxymethyl
]tetrahydropyran-2-y
l]
oxy-chromen-7-on
e trihydrate |
C27H36O19 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The root is taken internally in the treatment of chronic constipation, diarrhoea, liver and gall bladder complaints, haemorrhoids, hepatitis, menstrual problems and skin eruptions due to an accumulation of toxins. Externally, the root is used in the treatment of burns. A homeopathic remedy prepared from the dried root is used especially in the treatment of diarrhoea in teething children. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
1. Not prescribed for pregnant or lactating women, nor for patients with intestinal obstruction.
2. People with a tendency to rheumatism, arthritis, gout, kidney stones or hyperacidity should take especial caution if including this plant in their diet since it can aggravate their condition |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 552, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005. Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 552, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|