Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) Steud. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) Steud. |
English
Name |
: |
Chinese foxglove |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Rehmannia chinensis Liboschitz. ex Fischer & C.A.Mey., Digitalis glutinosa Gaertner |
Family |
: |
Phrymaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Herbs, 10-30 cm tall, densely villous with glandular and eglandular hairs. Rhizomes to 5.5 cm, fleshy. Stems purple-red. Basal leaves usually rosulate. Stem leaves gradually or abruptly decreasing in size or reduced to bracts upward; leaf blade ovate to narrowly elliptic, 2-13 X 1-6 cm, base tapering, margin irregularly crenate or obtusely serrate to toothed. Flowers axillary or in terminal racemes; pedicel 0.5-3 cm, slender, ascending; bracteoles absent; calyx 1-1.5 cm, 10-veined; lobes 5, oblong-lanceolate, ovate-lanceolate, or subtriangular, 5-6 X 2-3 mm, rarely 2 lower lobes further lobed; corolla 3-4.5 cm, white villous; tube narrow; lobes outside purple-red, inside yellow-purple, 5-7 X 4-10 mm, apex obtuse to emarginate; stamens 4; anther locules oblong, ca. 2.5 mm, base divaricate; ovary 2-loculed when young, 1-loculed with age. Capsule ovoid to narrowly ovoid, 1-1.5 cm. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antibacterial, antiseptic, cardiac, diuretic, febrifuge, haemostatic, hypoglycaemic and tonic (root) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Alanine, aspartic acid, aucubin, beta sitosterol, catalpol, GABA, glutamic acid, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, mannitol, methionine, phosphoric acid, raffinose, threonine, tyrosine, valine, verbascose (root); phenylalanine (plant) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
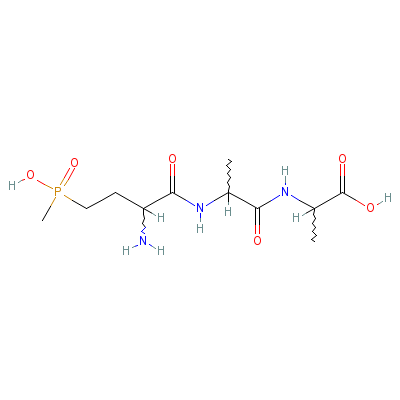
| Alanine |
35597-43-4 |
2-[2-[2-amino-4-(hyd
roxy-methyl-phosphor
yl)-butanoyl]aminopr
opanoylami
no]propa
noic acid |
C11H22N3O6P |
|
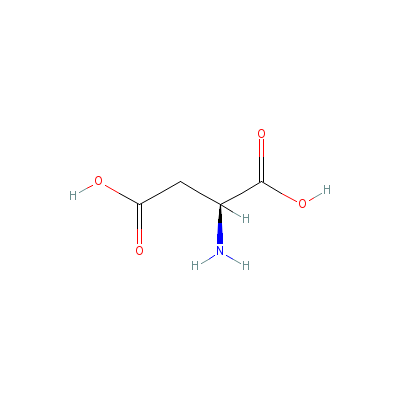
| Aspartic acid |
6899-03-2 |
2-aminobutanedioic
acid |
C4H7NO4 |
|
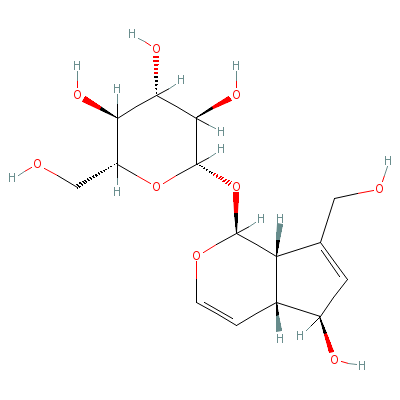
| Aucubin |
479-98-1 |
2-[[9-hydroxy-7-(hyd
roxymethyl)-4-oxabic
yclo[4.3.0]nona-2,7-
dien-5-yl]
oxy]-6-(
hydroxymethyl)oxane-
3,4,5-triol |
C15H22O9 |
|
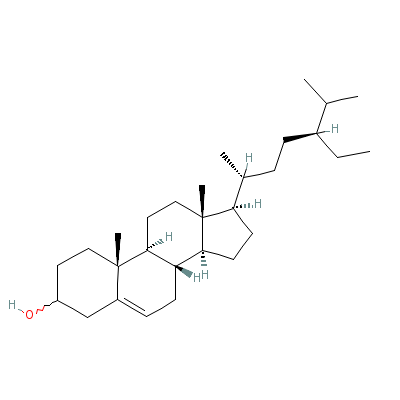
| Beta-sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cycl
openta[a]phenanthren
-3-ol |
C29H50O |
|
| Catalpol |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C15H22O10 |
|
| GABA |
70582-09-1 |
4-aminobutanoic acid |
C4H9NO2 |
|
| Glutamic acid |
Not Available |
2-aminopentanedioic
acid |
C5H9NO4 |
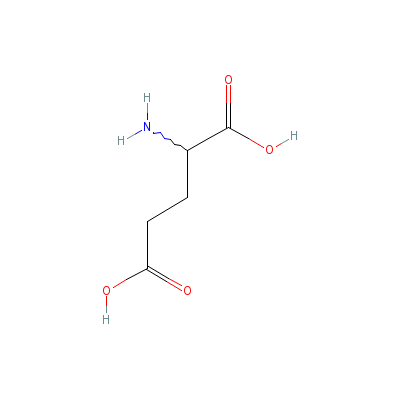
|
| Glycine |
87867-94-5 |
2-aminoacetic acid |
C2H5NO2 |
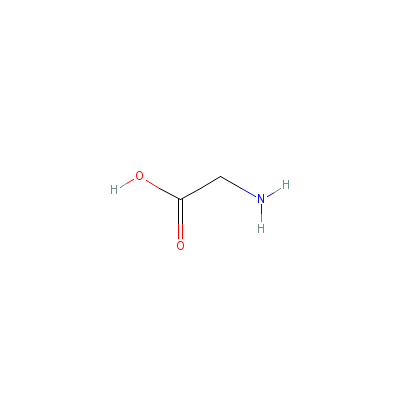
|
| Histidine |
6027-02-7 |
2-amino-3-(3H-imidaz
ol-4-yl)propanoic
acid |
C6H9N3O2 |
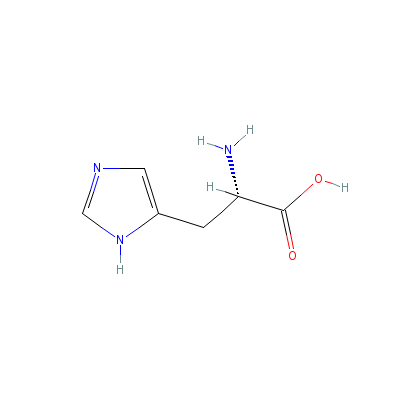
|
| Isoleucine |
319-78-8 |
2-amino-3-methyl-pen
tanoic acid |
C6H13NO2 |
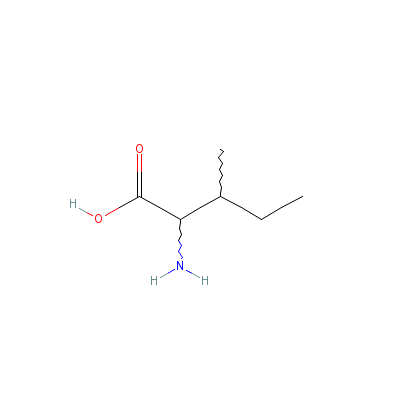
|
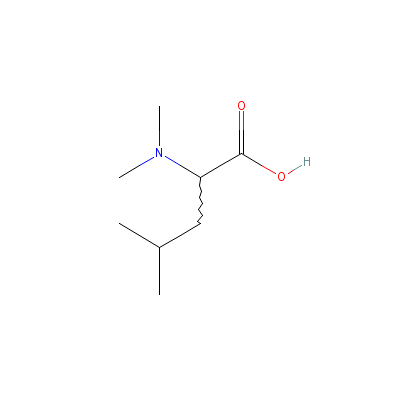
| Leucine |
2439-37-4 |
2-dimethylamino-4-me
thyl-pentanoic acid |
C8H17NO2 |
|
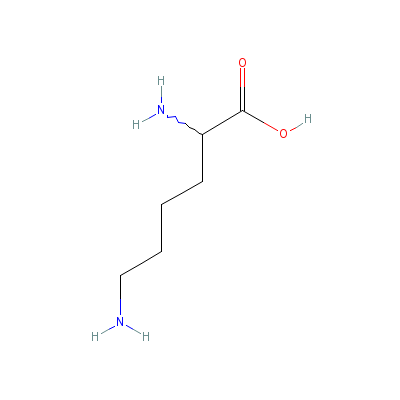
| Lysine |
923-27-3 |
2,6-diaminohexanoic
acid |
C6H14N2O2 |
|
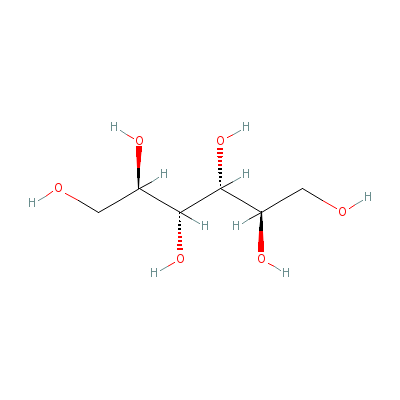
| Mannitol |
85085-15-0 |
hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-h
exaol |
C6H14O6 |
|
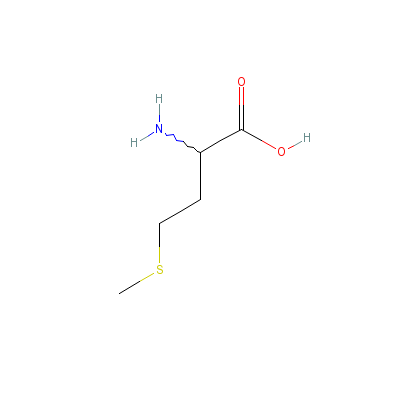
| Methionine |
348-67-4 |
2-amino-4-methylsulf
anyl-butanoic acid |
C5H11NO2S |
|
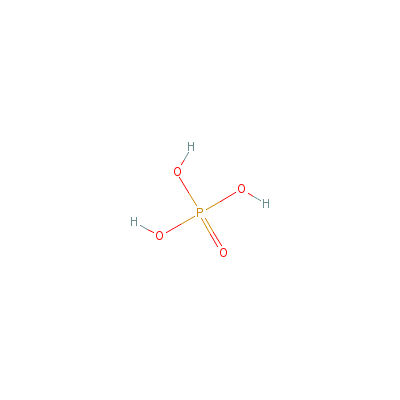
| Phosphoric acid |
7664-38-2 |
phosphoric acid |
H3O4P |
|
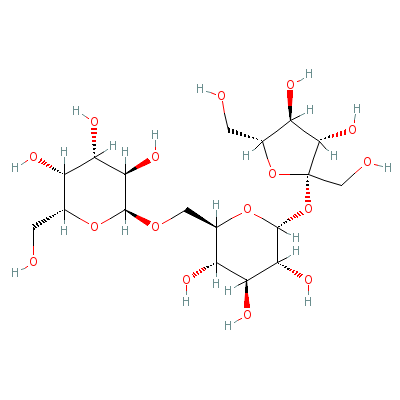
| Raffinose |
Not Available |
(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[
[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-6-
[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-3,4-d
ihydroxy-2
,5-bis(h
ydroxymethyl)oxolan-
2-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihy
droxy-oxan-2-yl]meth
ox
y]-6-(hydroxymet
hyl)oxane-3,4,5-trio
l |
C18H32O16 |
|
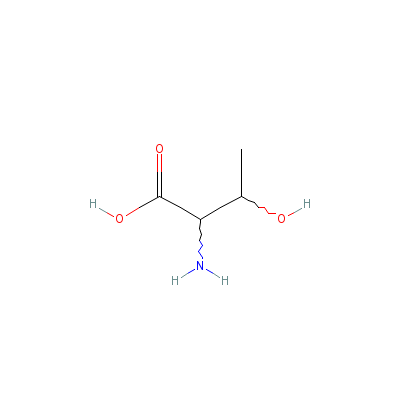
| Threonine |
632-20-2 |
2-amino-3-hydroxy-bu
tanoic acid |
C4H9NO3 |
|
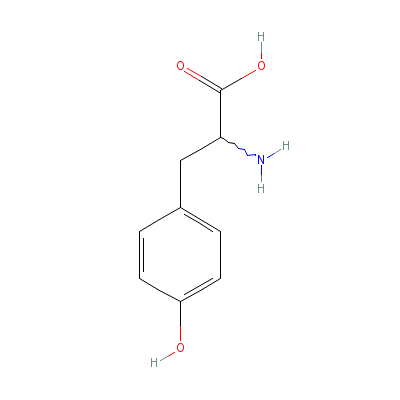
| Tyrosine |
556-02-5 |
2-amino-3-(4-hydroxy
phenyl)-propanoic
acid |
C9H11NO3 |
|
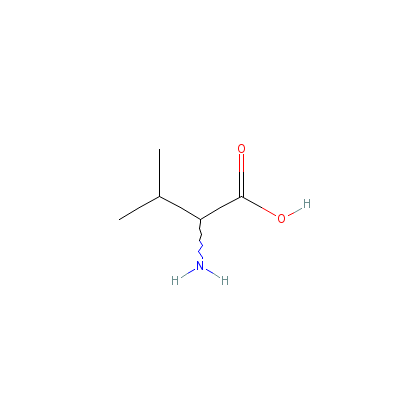
| Valine |
7004-03-7 |
2-amino-3-methyl-but
anoic acid |
C5H11NO2 |
|
| Verbascose |
Not Available |
(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[
[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-
[[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6
-[(2S,3S,4R,5S)-3,4-
dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hy
droxymethyl)oxolan-2
-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihyd
roxy-oxan-2-yl]metho
xy]-3,4,5-trihydroxy
-oxan-2-yl]methoxy]-
6-[[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)
-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxymethyl)oxan-
2-yl]oxymethyl]oxane
-3,4,5-triol |
C30H52O26 |
|
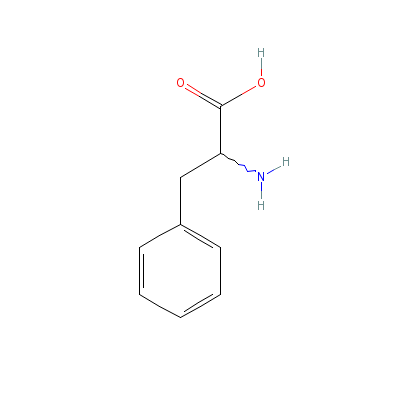
| Phenylalanine |
3617-44-5 |
2-amino-3-phenyl-pro
panoic acid |
C9H11NO2 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The roots are used in the treatment of a wide range of ailments, including anaemia, cancer, bleeding, constipation, coughs, fever, hematemesis, epistaxis, hematuria, metrorrhagia, metrostasis and premature ejaculation. The charcoaled root is used to stop bleeding and tonify the spleen and stomach. The fresh root is used to treat thirst, the rash of infectious diseases and bleeding due to pathological heat. The dried root is used to treat bleeding due to blood deficiency and to nourish the vital essence. The prepared root is used to treat dizziness and palpitations due to anaemia or blood deficiency, chronic tidal fever, night sweats, dry mouth, lumbago, nocturnal emissions, diabetes, sallow complexion, dizziness, palpitation, insomnia, irregular menstruation, and metrorrhagia. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
1. Contraindicated in patients with Spleen Deficiency or Damp Heat of the Spleen with abdominal distension and loose stools.
2. Contraindicated in patients with copious sputum due to Qi Stagnation, gastric and abdominal distension, poor appetite, and loose stools. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 546-549, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005. Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 546-549, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005.
|
|
|