Pyrrosia lingua (Thunb.) Farw. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Pyrrosia lingua (Thunb.) Farw. |
English
Name |
: |
Tongue fern, Japanese felt fern |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Acrostichum lingus Thunb., Polypodium tiwannensis Christ, Cyclopholus taiwanensis (Christ), Cyclopholus bodinieri Lev., Cyclopholus lingua (Thunb.) Desv. var. angustifrons Hayata, Nipholus bodmartini Christ, Pyrrosia martini (Christ) Ching, Pyrrosia medogenensis Ching & S. K.Wu. |
Family |
: |
Polypodiaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Plants 10-30 cm. tall. Rhizomes long and creeping, densely covered with scales; the scales lanceolate, longly acuminate at apexes, brownish, margins ciliate. Fronds remote, subdimorphic; stipes and laminae and stipes much varied in sizes fortile fronds much longer and narrower than stelile ones, both fronds slightly longer than stipes, less same lenght, rarely fronds shorter than stipes. Stelile laminae subrounded or obrongly lanceolate, widest at 1/3 of lower parts, attenuated upwards, apexes shortly acuminate, bases cuneater, 1.5-5 x (5-) 10-20 cm. entire, after dry coriaceous, greyish-green and subglabrous on upper surfaces, brownish or brick-red and covered with stellate hairs on under surfaces; fortile frands longer 1/3 than stelile ones, narrower 1/3-2/3 than stelile ones. Main veins slightly raised on undercsides, indisdinctly depresed on upper sides, lateral veins disdinct raised on under sides, clearly visible, veinlets obscure. Sori subelliptic, in regularly multrows between lateral veins and sporeading allover underer surfaces of laminae, or gathered born in most upper half parts of laminae, covered with stellate hairs and brownish when young, brick-red after maturity. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antibacterial, antitussive, expectorant, antiasthmatic, diuretic, hypolipidaemic (leaves) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Beta-sitosterol, mangiferin, isomangiferin, trifolin, kaempferol, diploptene, fumaric acid, boletic acid, caffeic acid, 2-butenedioic acid, chlorogenic acid |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Chlorogenic acid |
327-97-9 |
3-[3-(3,4-dihydroxyp
henyl)prop-2-enoylox
y]-1,4,5-trihydroxy-
cyclohexan
e-1-carb
oxylic acid |
C16H18O9 |
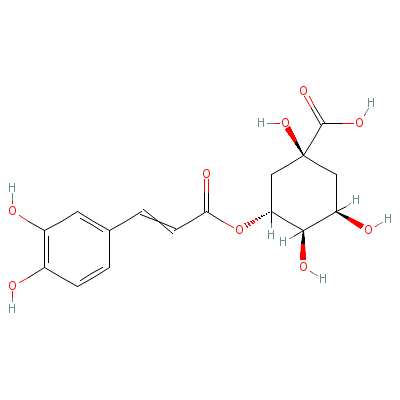
|
| Isomangiferin |
Not Available |
1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy
-4-[(2S,3S,4R,5R,6R)
-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxymethyl)oxan-
2-yl]xanthen-9-one |
C19H18O11 |
|
| Mangiferin |
99331-60-9 |
1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy
-2-[(3S,4R,5R,6R)-3,
4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hy
droxymethy
l)oxan-2
-yl]xanthen-9-one |
C19H18O11 |
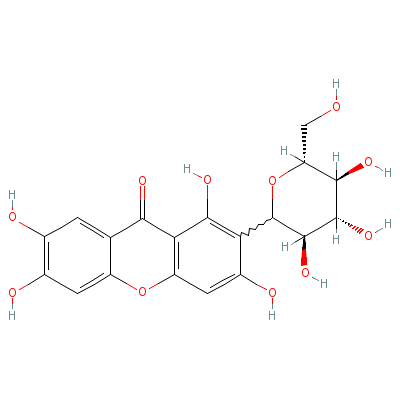
|
| Beta-sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cycl
openta[a]phenanthren
-3-ol |
C29H50O |
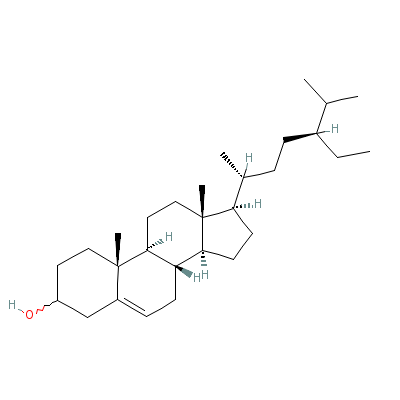
|
| Trifolin |
Not Available |
5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-3-[(2S
,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-
trihydroxy
-6-(hydr
oxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]
oxy-chromen-4-one |
C21H20O11 |

|
| Kaempferol |
80714-53-0 |
3-[3-[4,5-dihydroxy-
6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)oxa
n-2-yl]oxy-oxan-2-yl
]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6
-(hydroxymethyl)oxan
-2
-yl]oxy-4,5-dihy
droxy-2-(4-hydroxyph
enyl)-chromen-7-one |
C33H40O21 |
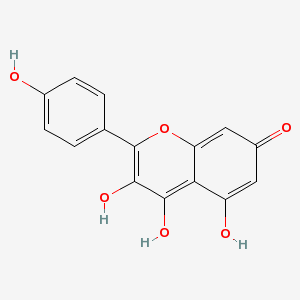
|
| Diploptene |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C30H50 |
|
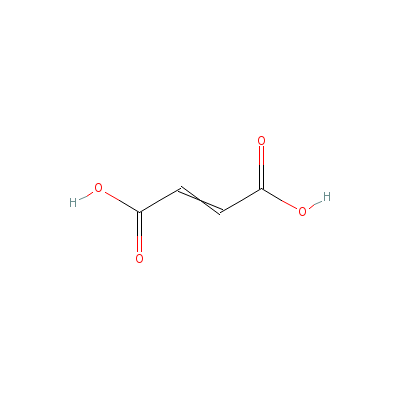
| Fumaric acid |
110-17-8 |
but-2-enedioic acid |
C4H4O4 |
|
| Boletic acid |
Not Available |
(E)-but-2-enedioate |
C4H2O4-2 |
|
| Chlorogenic acid |
327-97-9 |
3-[3-(3,4-dihydroxyp
henyl)prop-2-enoylox
y]-1,4,5-trihydroxy-
cyclohexan
e-1-carb
oxylic acid |
C16H18O9 |

|
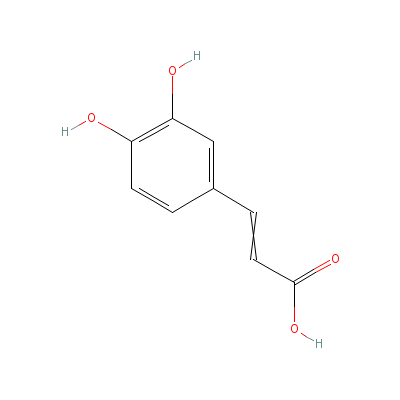
| Caffeic acid |
Not Available |
3-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)prop-2-enoic acid |
C9H8O4 |
|
| 2-Butenedioic acid |
6915-18-0 |
but-2-enedioic acid |
C4H4O4 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Whole plants especially the leaves are used as medicines diuresic for gonorrhea with hematuria, strangury, to clear heat and eliminate wetness for incised wound, burn and scald, diseases due to asthenia of viscera. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 540, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005. Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 540, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|