Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E. H. Wilson |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E. H. Wilson |
English
Name |
: |
Houpu Magnolia, Silver Magnolia, Whiteleaf Japanese Magnolia |
Family |
: |
Magnoliaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A deciduous tree growing to 20m in height. The bark is thick and brown but does not fissure. The leaves are broad, ovate, 20-40 cm long and 11-20 cm broad. The flowers are fragrant, 10-15 cm wide, with 9-12 (rarely to 17) white tepals, and appear from May to June. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Emmenagogue (flowers); antiseptic, antispasmodic, aphrodisiac, appetizer, diuretic, expectorant, hypotensive, stomachic and tonic (stem bark); bactericidal, digestive and stomachic (plant) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Alpha-pinene, anonaine, beta-pinene, caffeic acid, cyanidin, honokiol, kaempferol, liriodenine, magnocurarine, magnoflorine, quercetin (plant); beta-eudesmol, bornyl acetate, camphene, caryophyllene epoxide (essential oil); magnolol (bark) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| alpha-Pinene |
80-56-8 |
2,7,7-trimethylbicyc
lo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene |
C10H16 |
|
| Anonaine |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C17H15NO2 |

|
| beta-Pinene |
23089-32-9 |
6,6-dimethyl-2-methy
lidene-norpinane |
C10H16 |
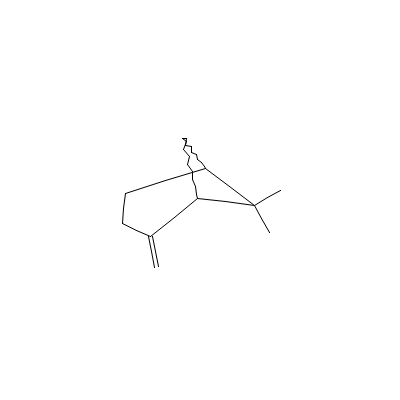
|
| Caffeic acid |
Not Available |
3-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)prop-2-enoic acid |
C9H8O4 |
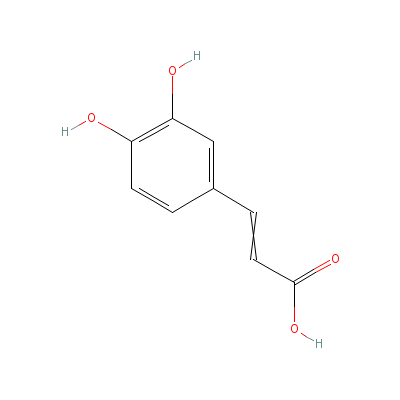
|
| Cyanidin |
87725-42-6 |
[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphe
nyl)-3,7-dihydroxy-c
hromen-5-ylidene]oxo
nium |
C15H11O6+ |
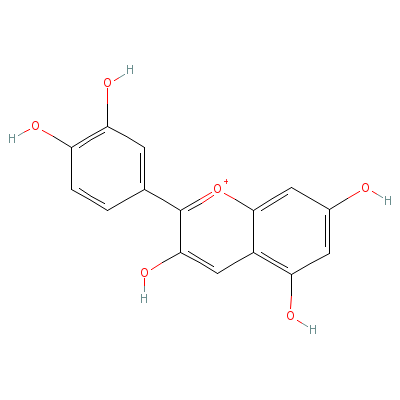
|
| Honokiol |
564-73-8 |
4-(2-hydroxy-5-prop-
2-enyl-phenyl)-2-pro
p-2-enyl-phenol |
C18H18O2 |

|
| Kaempferol |
80714-53-0 |
3-[3-[4,5-dihydroxy-
6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)oxa
n-2-yl]oxy-oxan-2-yl
]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6
-(hydroxymethyl)oxan
-2
-yl]oxy-4,5-dihy
droxy-2-(4-hydroxyph
enyl)-chromen-7-one |
C33H40O21 |
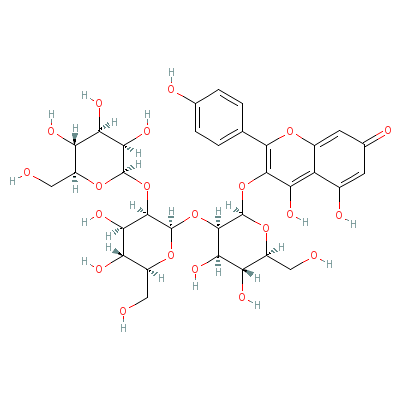
|
| Liriodenine |
475-75-2 |
Not Available |
C17H9NO3 |
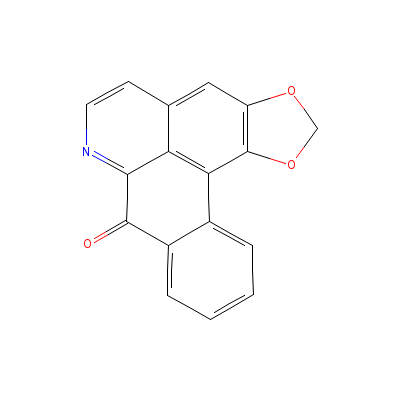
|
| Magnocurarine |
6801-40-7 |
(1R)-1-[(4-hydroxyph
enyl)methyl]-6-metho
xy-2,2-dimethyl-3,4-
dihydro-1H
-isoquin
olin-7-ol |
C19H24NO3+ |
|
| Magnoflorine |
6681-18-1 |
Not Available |
C20H24NO4+ |
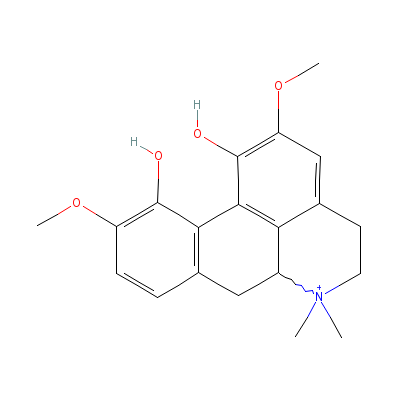
|
| Quercetin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-3,4,5-trihydroxy
-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O7 |
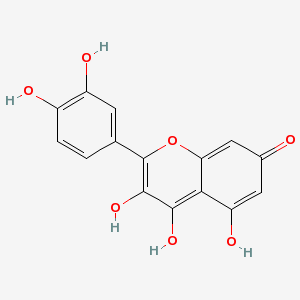
|
| beta-Eudesmol |
473-15-4 |
2-(4a-methyl-8-methy
lidene-decalin-2-yl)
propan-2-ol |
C15H26O |
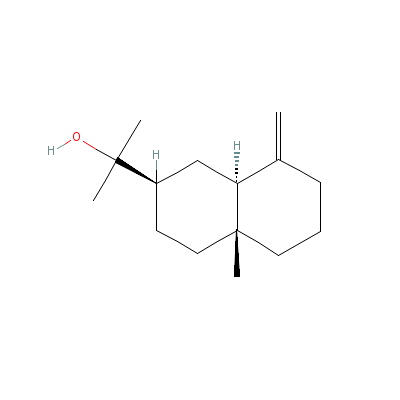
|
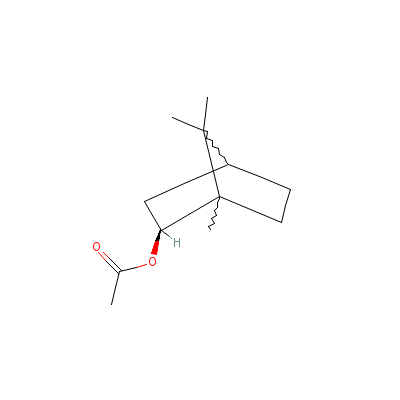
| Bornyl acetate |
20347-65-3 |
(1,7,7-trimethylnorb
ornan-2-yl) acetate |
C12H20O2 |
|
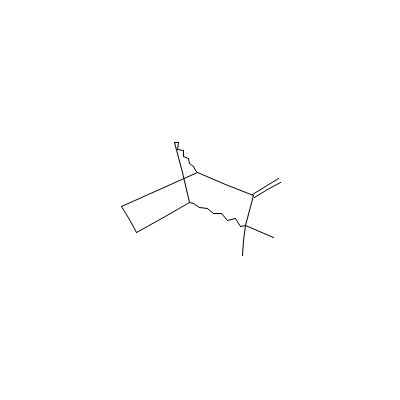
| Camphene |
5794-04-7 |
2,2-dimethyl-3-methy
lidene-norbornane |
C10H16 |
|
| Caryophyllene epoxide |
32095-03-7 |
Not Available |
C15H24O |
|
| Magnolol |
Not Available |
2-(2-hydroxy-5-prop-
2-enyl-phenyl)-4-pro
p-2-enyl-phenol |
C18H18O2 |

|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The flowers are used in the treatment of abdominal distension, shortness of breath etc. The bark is used internally in the treatment of abdominal distension, loss of appetite, gastro-enteritis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, amenorrhea, menstrual cramps, asthma and coughs with acute phlegm. It has also been indicated for Alzheimer's disease and is currently getting much press as a "cortisol", a stress hormone-lowering supplement. Cortisol has also been associated with weight gain (particularly fat in the abdominal area), sugar control problems, memory problems, and a host of other stress induced disorders. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Contraindicated for pregnant women. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 416, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005. Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 416, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|