| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Vitis vinifera L. |
English
Name |
: |
Grape |
Family |
: |
Vitaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
It is a climbing shrub with simple, lobed, cut or toothed leaves with thyrsoid racemes of greenish flowers, the fruit consisting of watery or fleshy pulp, stones and skin, two-celled, four-seeded. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
The fresh fruit is antilithic, constructive, cooling, diuretic and strengthening. The dried fruit is demulcent, cooling, mildly expectorant, laxative and stomachic. The leaves, especially red leaves, are anti-inflammatory and astringent. The seed is anti-inflammatory and astringent. The sap of young branches is diuretic. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Abscissic acid, acetic acid, alpha-amyrin, alpha-linolenic acid, alpha-terpineol, ascorbic acid, beta-carotene, beta-sitosterol, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, coumarin, ellagic acid, epicatechin, ferulic acid, gallic acid, kaempferol, limonene, luteolin, myricetin, niacin, oleanolic acid, quercetin, quercitrin, resveratrol, rutin, salicyclic acid. |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Acetic acid |
77671-22-8 |
acetic acid |
C2H4O2 |
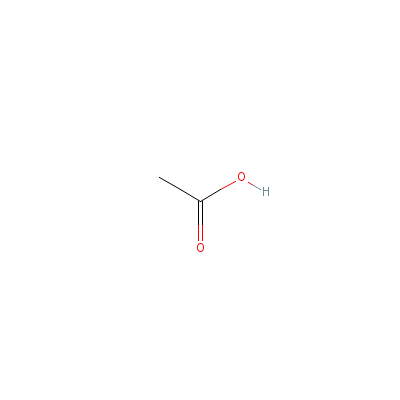
|
| alpha-Amyrin |
638-95-9 |
4,4,6a,6b,8a,11,12,1
4b-octamethyl-2,3,4a
,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,
12a,14,14a
-tetrade
cahydro-1H-picen-3-o
l |
C30H50O |
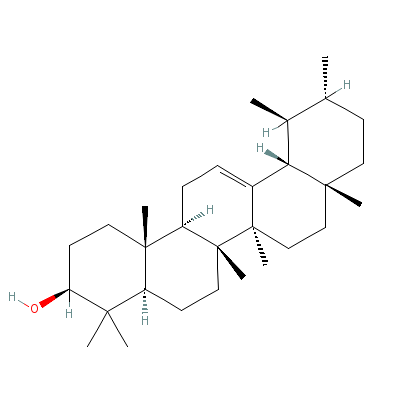
|
| alpha-Linolenic acid |
94138-91-7 |
octadeca-9,12,15-tri
enoic acid |
C18H30O2 |
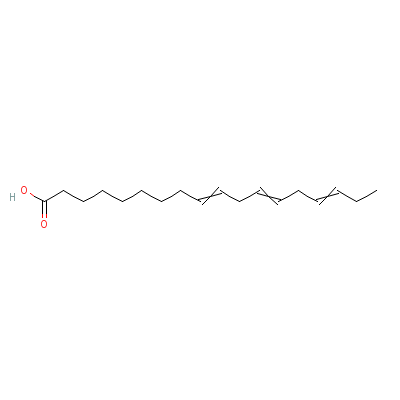
|
| alpha-Terpineol |
10482-56-1 |
2-(4-methyl-1-cycloh
ex-3-enyl)propan-2-o
l |
C10H18O |
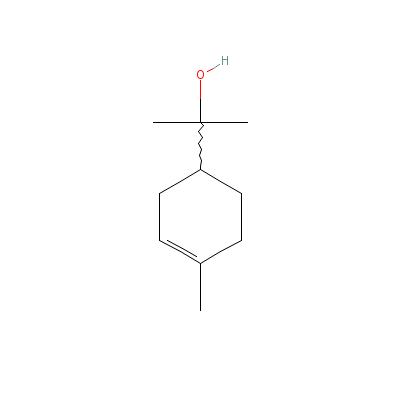
|
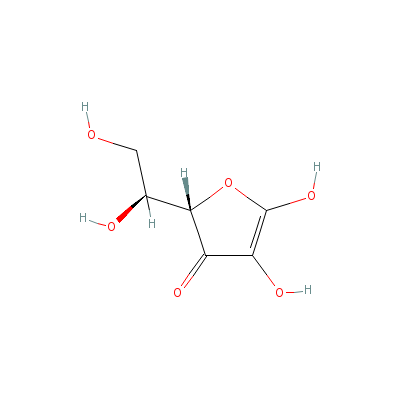
| Ascorbic acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
|
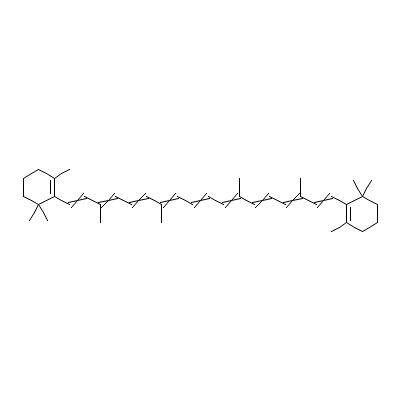
| beta Carotene |
7235-40-7 |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
|
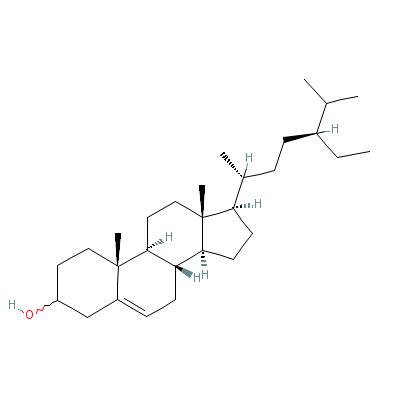
| beta-Sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cycl
openta[a]phenanthren
-3-ol |
C29H50O |
|
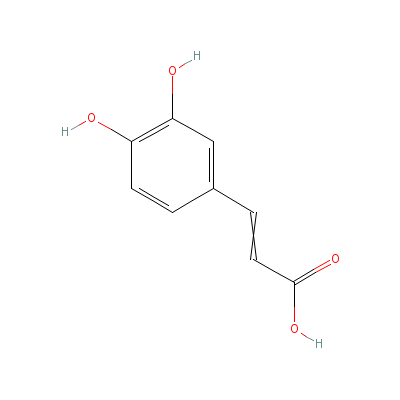
| Caffeic acid |
Not Available |
3-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)prop-2-enoic acid |
C9H8O4 |
|
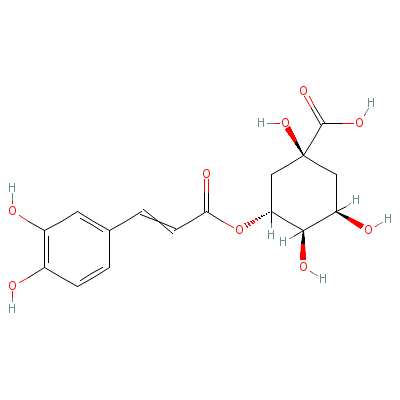
| Chlorogenic acid |
327-97-9 |
3-[3-(3,4-dihydroxyp
henyl)prop-2-enoylox
y]-1,4,5-trihydroxy-
cyclohexan
e-1-carb
oxylic acid |
C16H18O9 |
|
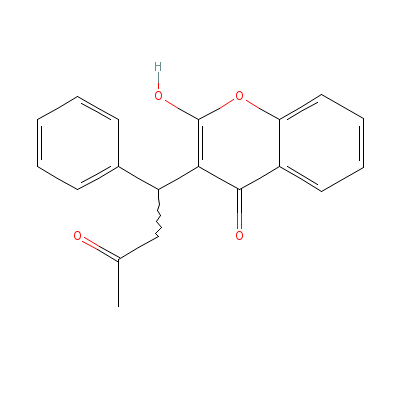
| Coumarin |
60094-90-8 |
6-(1,2-dihydroxy-3-m
ethyl-but-3-enyl)-7-
methoxy-chromen-2-on
e |
C15H16O5 |
|
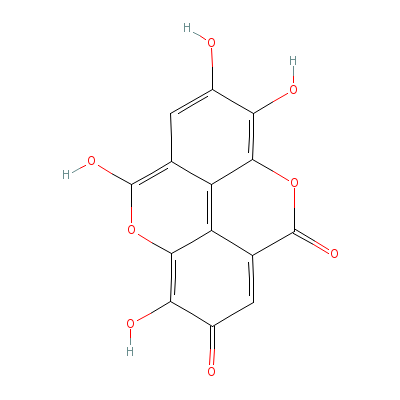
| Ellagic acid |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C14H6O8 |
|
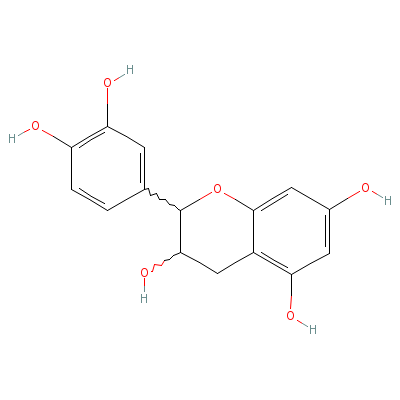
| Epicatechin |
490-46-0 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)chroman-3,5,7-tri
ol |
C15H14O6 |
|
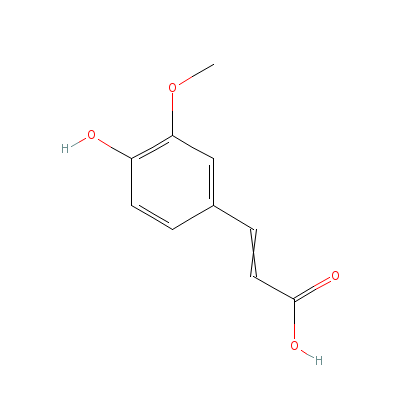
| Feruclic acid |
24276-84-4 |
3-(4-hydroxy-3-metho
xy-phenyl)prop-2-eno
ic acid |
C10H10O4 |
|
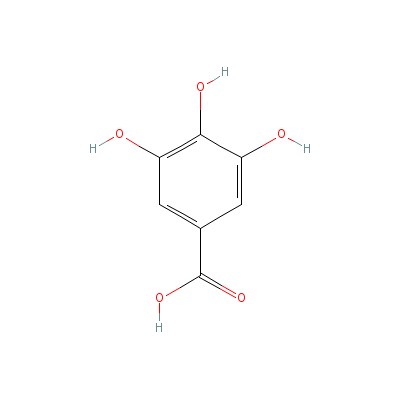
| Gallic acid |
149-91-7 |
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oic acid |
C7H6O5 |
|
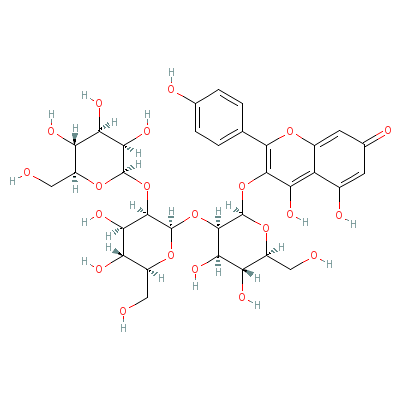
| Kaempferol |
80714-53-0 |
3-[3-[4,5-dihydroxy-
6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)oxa
n-2-yl]oxy-oxan-2-yl
]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6
-(hydroxymethyl)oxan
-2
-yl]oxy-4,5-dihy
droxy-2-(4-hydroxyph
enyl)-chromen-7-one |
C33H40O21 |
|
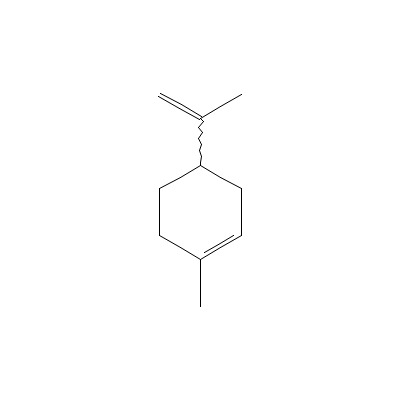
| Limonene |
9003-73-0 |
1-methyl-4-prop-1-en
-2-yl-cyclohexene |
C10H16 |
|
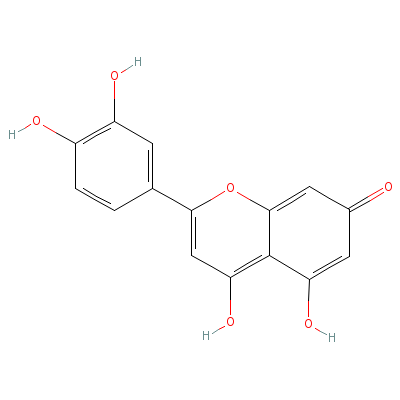
| Luteolin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-ch
romen-7-one |
C15H10O6 |
|
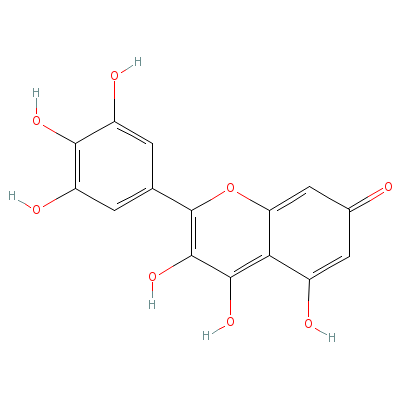
| Myricetin |
529-44-2 |
3,4,5-trihydroxy-2-(
3,4,5-trihydroxyphen
yl)-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O8 |
|
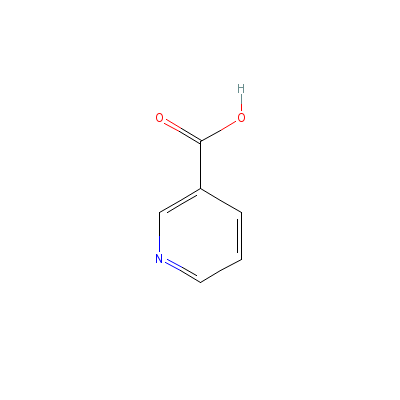
| Niacin |
99148-57-9 |
pyridine-3-carboxyli
c acid |
C6H5NO2 |
|
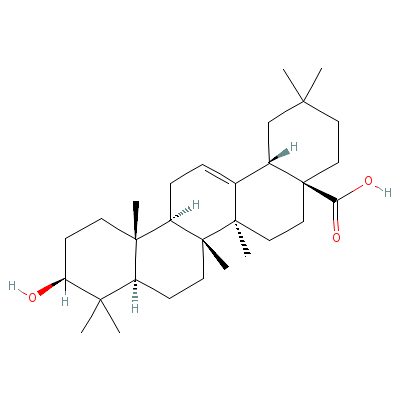
| Oleanolic acid |
508-02-1 |
10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b
,9,9,12a-heptamethyl
-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a
,10,11,12,
13,14b-t
etradecahydropicene-
4a-carboxylic acid |
C30H48O3 |
|
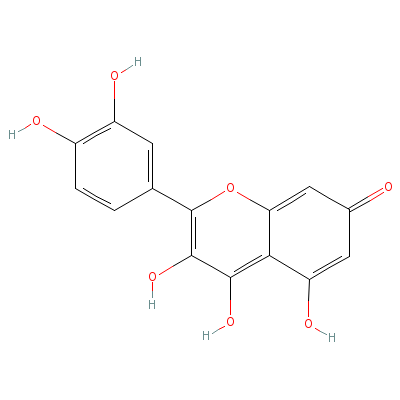
| Quercetin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-3,4,5-trihydroxy
-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O7 |
|
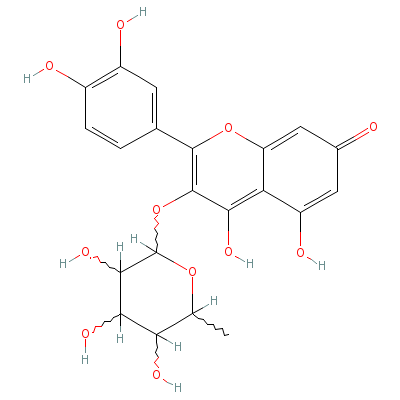
| Quercitrin |
6151-25-3 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-
(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
methyl-oxa
n-2-yl)o
xy-chromen-7-one |
C21H20O11 |
|
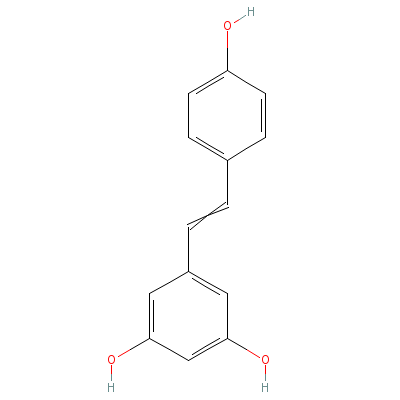
| Resveratrol |
Not Available |
5-[2-(4-hydroxypheny
l)ethenyl]benzene-1,
3-diol |
C14H12O3 |
|
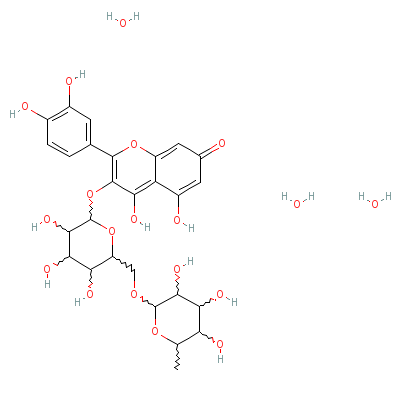
| Rutin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
[(3,4,5-tr
ihydroxy
-6-methyl-tetrahydro
pyran-2-yl)oxymethyl
]tetrahydropyran-2-y
l]
oxy-chromen-7-on
e trihydrate |
C27H36O19 |
|
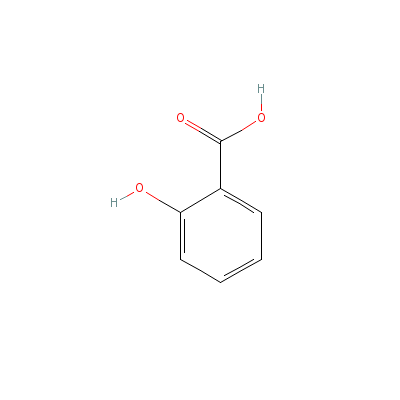
| Salicylic acid |
8052-31-1 |
2-hydroxybenzoic
acid |
C7H6O3 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Grapes are a nourishing and slightly laxative fruit that support the body through illness, especially of the gastro-intestinal tract and liver. Because the nutrient content of grapes is close to that of blood plasma, grape fasts are recommended for detoxification. A period of time on a diet based entirely on the fruit is especially recommended in the treatment of torpid liver or sluggish biliary function. The fruit is also helpful in the treatment of varicose veins, haemorrhoids and capillary fragility. It has a slight effect in easing coughs.A decoction is used in the treatment of threatened abortion, internal and external bleeding, cholera, dropsy, diarrhoea and nausea. It is also used as a wash for mouth ulcers and as douche for treating vaginal discharge. Red grape leaves are also helpful in the treatment of varicose veins, haemorrhoids and capillary fragility. It is used as a remedy for skin diseases and is also an excellent lotion for the eyes. The tendrils are astringent and a decoction is used in the treatment of diarrhoea. The seeds and leaves are astringent, the leaves being formerly used to stop haemorrhages and bleeding. It is used dried and powdered as a cure for dysentery in cattle. The sap, termed a tear or lachryma, forms an excellent lotion for weak eyes and specks on the cornea. Ripe grapes in quantity influence the kidneys producing a free flow of urine and are apt to cause palpitation in excitable and full-blooded people. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Hypersensitivity to grape seed.Relative contraindication with anticoagulant therapy, pregnancy and lactation. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Sharma PV. Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. Sharma PV. Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
|
|
|