| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Thuja occidentalis L. |
English
Name |
: |
Arbor vitae, Tree of life, White cedar, Yellow cedar, American cedar, Hackmatack |
Family |
: |
Cupressaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A small to medium sized tree shaped like an arrowhead - a pyramid with a broad base and a small, round top, often with several main trunks. Bark fibrous, red-brown, weathering to gray; diamond-shaped patterns are usually apparent. Twigs: new growth is green and scale-like, turning brown, occurring in very flattened foliar sprays. Leaves evergreen, scale-like, on main shoots, 1/4 inch long with long points. Lateral shoots are flattened, 1/8 inch long with short points. Flowers monoecious; solitary, females green with 4 to 6 scales; males are green tipped with brown and globose. Fruit cone, 1/2 inch long, oblong, borne upright on the branches, scales are leathery, red-brown and rounded, with a small spine on the tip. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antiviral, diuretic, abortifacient (plant); Alterative, anthelmintic, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, aromatic, astringent, diaphoretic, diuretic and emmenagogue (recently dried leafy young twigs); antiseptic, expectorant and rubefacient (leaf esssential oil) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
(+)-catechin, acetic acid, ascorbic acid, beta-sitosterol, borneol, bornyl acetate, camphene, camphor, formic acid, inositol, isovaleric acid, kaempferol 3-rhamnoside, limonene, myricetin-3-rhamnoside, oleic acid, pinitol, quercitrin, sabinene, tannin, terpineol, valerianic acid (branches); alpha-thujaplicin, beta-eudesmol (wood); |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| (+)-catechin |
5323-80-8 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)chroman-3,5,7-tri
ol |
C15H14O6 |
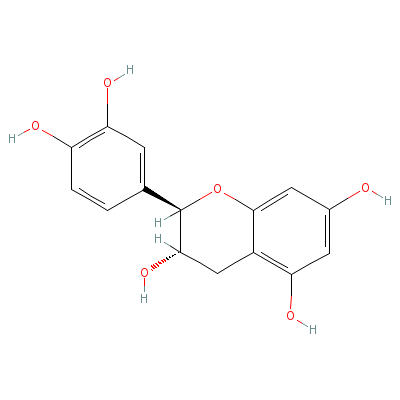
|
| Acetic acid |
77671-22-8 |
acetic acid |
C2H4O2 |
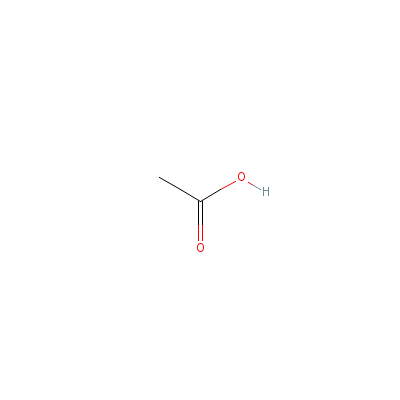
|
| Ascorbic acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
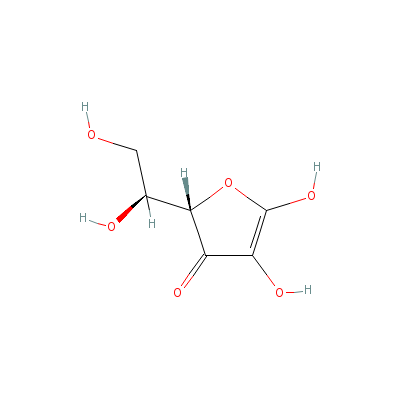
|
| Beta-sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14, |
C29H50O |
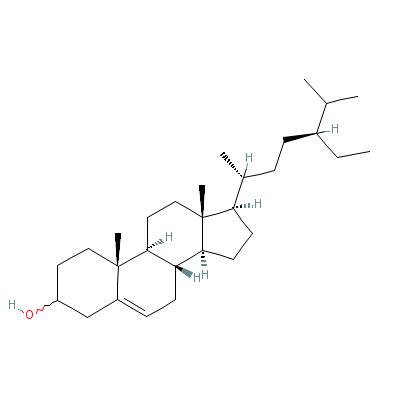
|
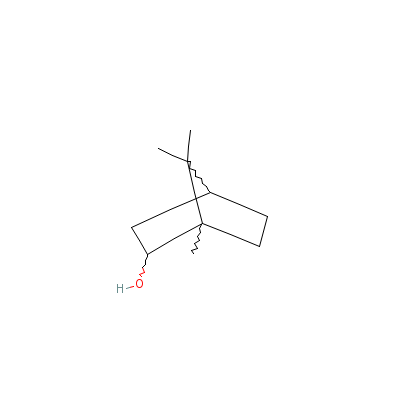
| Borneol |
10385-78-1 |
1,7,7-trimethylnorbo
rnan-2-ol |
C10H18O |
|
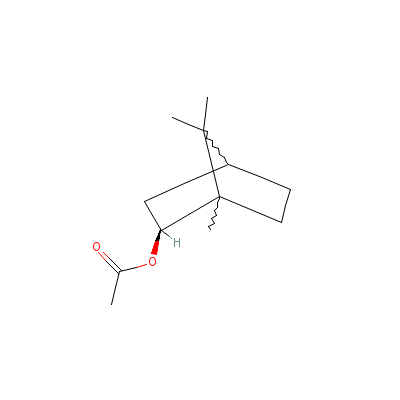
| Bornyl acetate |
20347-65-3 |
(1,7,7-trimethylnorb
ornan-2-yl) acetate |
C12H20O2 |
|
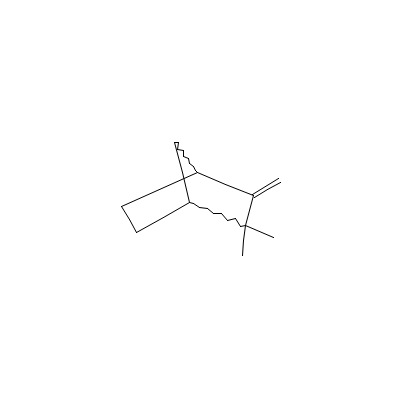
| Camphene |
5794-04-7 |
2,2-dimethyl-3-methy
lidene-norbornane |
C10H16 |
|
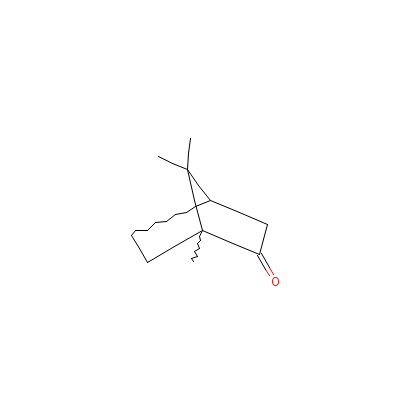
| Camphor |
8022-77-3 |
1,7,7-trimethylnorbo
rnan-2-one |
C10H16O |
|
| Formic acid |
992-98-3 |
formic acid |
CH2O2 |

|
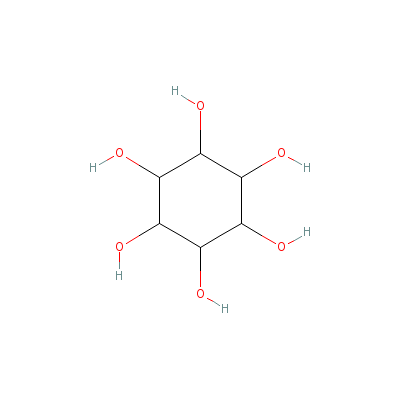
| Inositol |
551-72-4 |
cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,
5,6-hexol |
C6H12O6 |
|
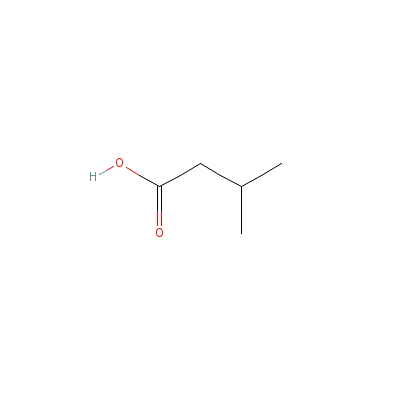
| Isovaleric acid |
503-74-2 |
3-methylbutanoic
acid |
C5H10O2 |
|
| Kaempferol 3-rhamnoside |
482-39-3 |
5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-3-[(2S
,3R,4R,5S,6S)-3,4,5-
trihydroxy-6-methyl-
oxan-2-yl]oxy-chrome
n-4-one |
C21H20O10 |
|
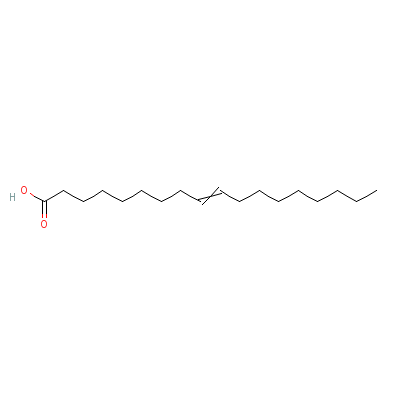
| Oleic acid |
8046-01-3 |
octadec-9-enoic acid |
C18H34O2 |
|
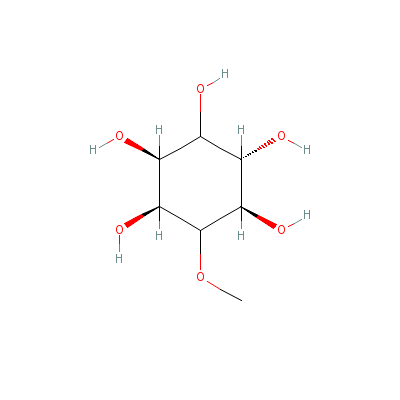
| Pinitol |
Not Available |
6-methoxycyclohexane
-1,2,3,4,5-pentol |
C7H14O6 |
|
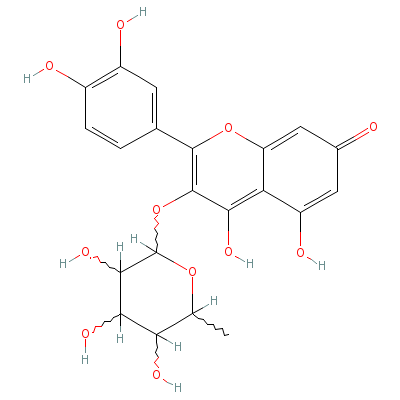
| Quercitrin |
6151-25-3 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-
(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
methyl-oxa
n-2-yl)o
xy-chromen-7-one |
C21H20O11 |
|
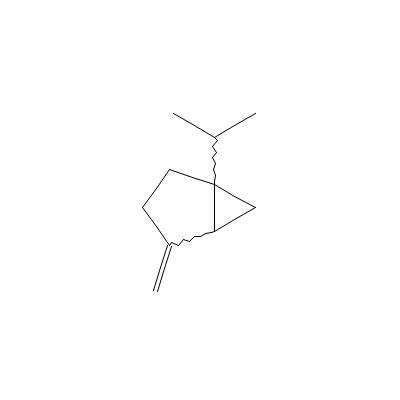
| Sabinene |
3387-41-5 |
4-methylidene-1-prop
an-2-yl-bicyclo[3.1.
0]hexane |
C10H16 |
|
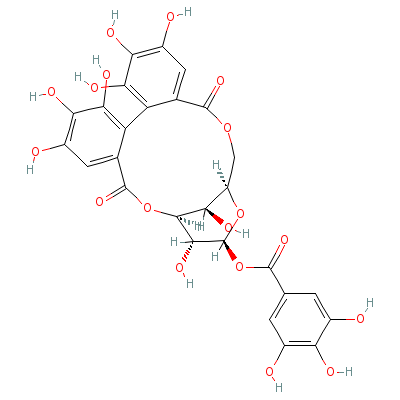
| Tannin |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
C27H22O18 |
|
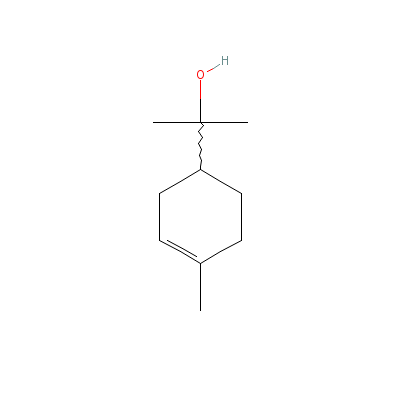
| Terpineol |
8006-39-1 |
2-(4-methyl-1-cycloh
ex-3-enyl)propan-2-o
l |
C10H18O |
|
| Valerianic acid |
70268-41-6 |
pentanoic acid |
C5H10O2 |

|
| alpha-Thujaplicin |
Not Available |
2-hydroxy-5-propan-2
-yl-cyclohepta-2,4,6
-trien-1-one |
C10H12O2 |
|
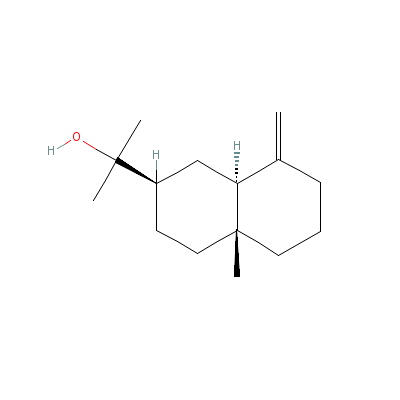
| beta-Eudesmol |
473-15-4 |
2-(4a-methyl-8-methy
lidene-decalin-2-yl)
propan-2-ol |
C15H26O |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The plant is used as a medicine to treat fevers, coughs, headaches, swollen hands, warts and polyps, scanty menstruation, acute cystitis and bed-wetting in children, cancer and rheumatic problems. A tea made from the leaves is used in the treatment for bronchitis and other respiratory problems, colds, headaches and as a cough syrup. The leaves are used in steam baths in the treatment of rheumatism, arthritis, colds etc. Externally, the leaves are used as a wash for swollen feet and burns. Extracts of the leaves can be painted on painful joints or muscles as a counter0irritant, improving local blood supply and thus facilitating the removal of toxins, easing pain and stiffness. A tincture of the leaves has been used in the treatment of warts, piles, bed sores and fungal infections. The essential oil obtained from leaves are used internally to promote menstruation and relieve rheumatism. A tea of the inner bark is used to promote menstruation and in the treatment of consumption and coughs. A homeopathic remedy is made from the leaves and twigs is used as a treatment against warts. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Should not be used by pregnant women. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 James A Duke and Maryl Fulton. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs - 2nd Edition, P: 729, CRC Press July 2002. James A Duke and Maryl Fulton. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs - 2nd Edition, P: 729, CRC Press July 2002.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|