Aristolochia manshuriensis Kom. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Aristolochia manshuriensis Kom. |
English
Name |
: |
Chinese aristolochia |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Hocquartia manshuriensis (Komarov) Nakai, Isotrema manshuriense (Komarov) H. Huber. |
Family |
: |
Aristolochiaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Shrubs climbing. Stems terete, striate, densely white villous. Leaves big; petiole 6-8 cm, villous; leaf blade cordate to orbicular, 15-29 × 13-28 cm, leathery, both surfaces white villous, adaxially glabrescent, veins palmate, 2-3 pairs from base, base cordate, sinus 1-4.5 cm deep, apex obtuse or acute. Flowers axillary, solitary or paired; peduncle pendulous, 1.5-3 cm, glabrous; bractlets ovate-cordate or cordate, ca. 1 cm, inserted below middle of peduncle. Calyx limb purple, 4.5-5.5 cm; tube horseshoe-shaped, abaxially white hirsute; basal portion of tube 20-25 × 10-12 mm; limb discoid, 4-6 cm in diam., 3-lobed; lobes broadly deltoid. Anthers oblong, 2-3 mm; gynostemium 3-lobed. Capsule narrowly cylindric, 9-11 × 3-4 cm, dehiscing basipetally. Seeds deltoid-cordiform or cordiform, 6-7 × 6-7 mm, both surfaces slightly plano-convex, verrucose. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Lactagogue (decoction of stem); a circulatory stimulant (inner bark of the stem); diuretic and febrifuge (stem and shoots). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Aristolochic acid, hederagenin, and oleanolic acid (stem) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Aristolochic acid |
61117-05-3 |
Not Available |
C17H11NO7 |
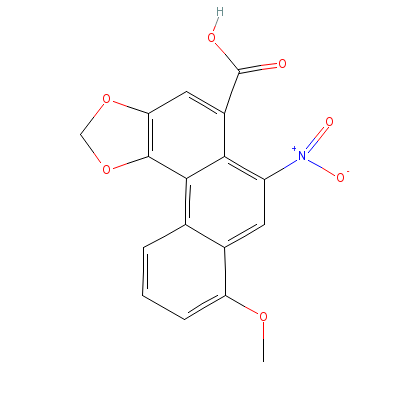
|
| Hederagenin |
465-99-6 |
10-hydroxy-9-(hydrox
ymethyl)-2,2,6a,6b,9
,12a-hexamethyl-1,3,
4,5,6,6a,7
,8,8a,10
,11,12,13,14b-tetrad
ecahydropicene-4a-ca
rboxylic acid |
C30H48O4 |
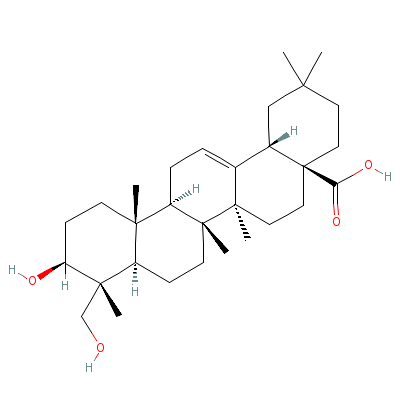
|
| Oleanolic acid |
508-02-1 |
10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b
,9,9,12a-heptamethyl
-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a
,10,11,12,
13,14b-t
etradecahydropicene-
4a-carboxylic acid |
C30H48O3 |
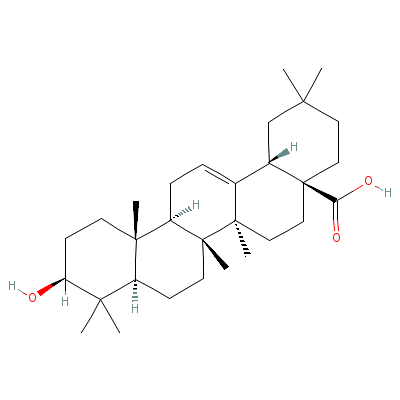
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The stem is used in decoction for the treatment of gonorrhea and rheumatic or rheumatoid arthritis. The woody, inner bark of the stem is dried in the sun and has been used to treat diabetes, dropsy, fever, increase urine flow, induce menstruation. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Use with caution in pregnant women. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 100, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005. Jing-Nuan Wu. An Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. P: 100, Oxford University Press, Inc.2005.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|