Leonotis leonurus (L.) R. Br. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Leonotis leonurus (L.) R. Br. |
English
Name |
: |
Wild dagga, Lion's tail, Lion's ear |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Phlomis leonurus L. |
Family |
: |
Lamiaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A shrub 2-5 m tall, branching from a thick woody base; stem pale brown and densely pubescent. Leaves simple, opposite, petiolate, coriaceous, 50-100 ´ 10-20 mm, linear, acute at apex and base, serrate in the distal half; upper surface bright green, lower surface densely pubescent. Inflorescence of 3-11 compact verticils; calyx 12-16 mm long, 4 mm in diameter, calyx teeth 10, subequal, spreading; corolla tubular, bright orange, 40-49 mm long, covered with orange hairs. Fruit a nutlet 5-6´ 1.5-2 mm, brown. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Euphoric, purgative and vermifuge (plant) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Marrubiin (plant) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Marrubiin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C20H28O4 |
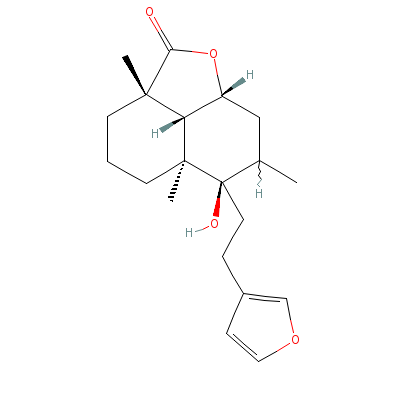
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Leaves or roots are widely used as a remedy for snakebite and also to relieve other bites and stings. Decoctions of dried leaves or roots have been applied externally to treat boils, eczema, skin diseases and itching, and muscular cramps. Leaf infusions have been used to treat asthma and viral hepatitis. The plant extracts are also used to relieve coughs, cold and influenza, as well as bronchitis, high blood pressure and headaches. Leaf tea is used to treat headache, bronchitis, high blood pressure and the common cold. The dried aerial parts are traditionally used internally for or the treatment of cough, cold, influenza, chest infections, diabetes, hypertension, eczema, epilepsy, delayed menstruation, intestinal worms, constipation, spider bites and scorpion stings and as an antidote for snakebite, and externally the relief of haemorrhoids, eczema, skin rashes and boils. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Not recommended for use by pregnant women. |
Dealers
Products
|
|
|
|
|