| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Hamamelis virginiana L. |
English
Name |
: |
Witchhazel, American witchhazel, Virginian witch hazel, Spotted alder, Striped alder, Tobacco wood, Winterbloom, Snapping hazelnut |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Hamamelis macrophylla Pursh, Hamamelis virginiana L. var. henryi Jenne, Hamamelis virginiana L. var. macrophylla (Pursh) Nutt., Hamamelis virginiana L. var. parvifolia Nutt. |
Family |
: |
Hamamelidaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A large deciduous shrub that usually reaches a height of 15 feet, although it can sometimes grow to 30 feet. Leaves are toothed or lobed, and about 3 to 6 inches long. Flowers are bright yellow, grow in clusters, have four parts, and have ribbon-shaped petals about one inch long. Fruit is a hard woody capsule about ½ an inch long, which explodes and launches two shiny black seeds up to 30 feet when it is mature. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Astringent, haemostatic, sedative and tonic (bark). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Acetaldehyde, afzelin, alpha-ionone, astragalin, beta ionone, choline, gallic acid, gallotannin, isoquercitrin, kaempferol, leucocyanidin, leucodelphinidin, myricetin, quercetin, quercitrin, quinic acid, safrole, saponin, spiraeoside (leaf); ellagitannin, hamamelitannin, phenol (bark). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Acetaldehyde |
108-62-3 |
2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-
1,3,5,7-tetraoxocane |
C8H16O4 |
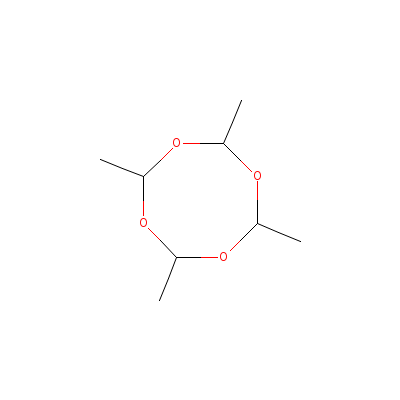
|
| Afzelin |
Not Available |
5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-3-[(2S
,3R,4R,5S,6S)-3,4,5-
trihydroxy
-6-methy
l-oxan-2-yl]oxy-chro
men-4-one |
C21H20O10 |

|
| alpha-Ionone |
31798-11-5 |
(E)-4-(2,6,6-trimeth
yl-1-cyclohex-2-enyl
)but-3-en-2-one |
C13H20O |
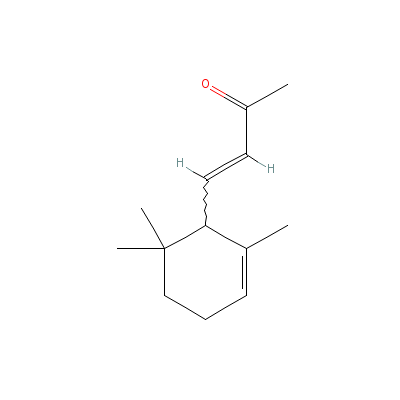
|
| Astragalin |
480-10-4 |
4,5-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-3-[3,4
,5-trihydroxy-6-(hyd
roxymethyl
)oxan-2-
yl]oxy-chromen-7-one |
C21H20O11 |
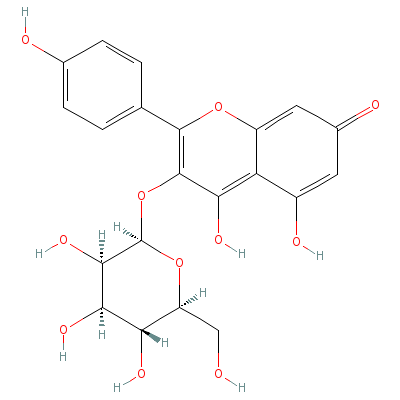
|
| Beta-ionone |
14901-07-6 |
4-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1
-cyclohexenyl)but-3-
en-2-one |
C13H20O |
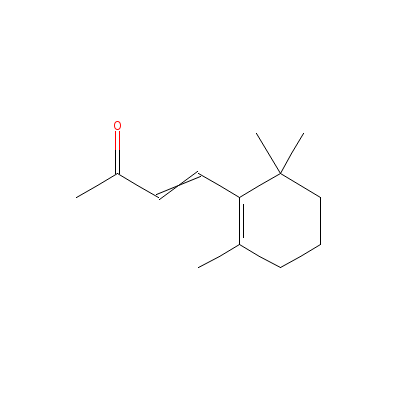
|
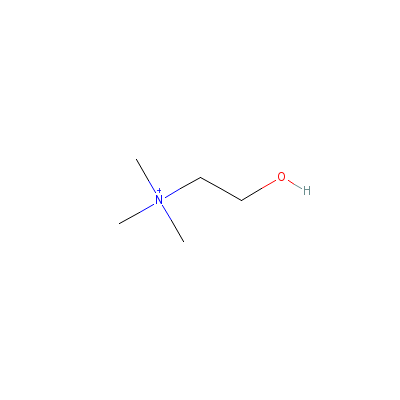
| Choline |
67-48-1 |
2-hydroxyethyl-trime
thyl-ammonium |
C5H14NO+ |
|
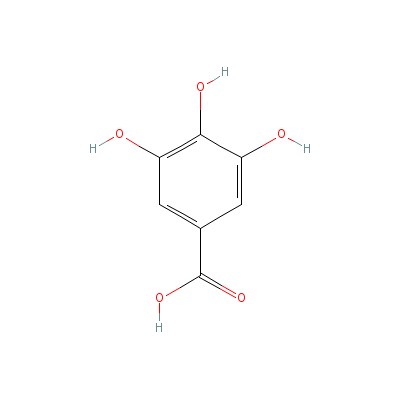
| Gallic acid |
149-91-7 |
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oic acid |
C7H6O5 |
|
| Gallotannin |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
C27H22O18 |
|
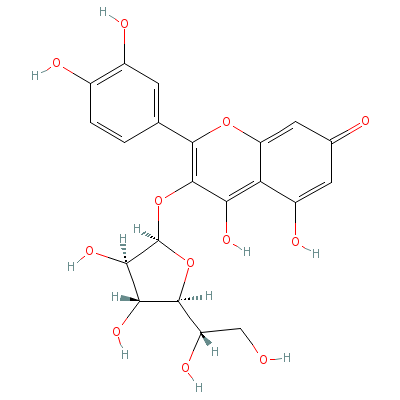
| Isoquercitrin |
21637-25-2 |
3-[5-(1,2-dihydroxye
thyl)-3,4-dihydroxy-
oxolan-2-yl]oxy-2-(3
,4-dihydro
xyphenyl
)-4,5-dihydroxy-chro
men-7-one |
C21H20O12 |
|
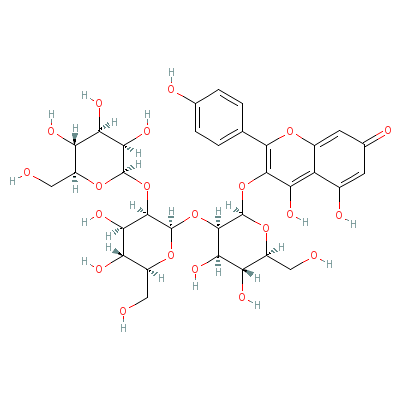
| Kaempferol |
80714-53-0 |
3-[3-[4,5-dihydroxy-
6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)oxa
n-2-yl]oxy-oxan-2-yl
]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6
-(hydroxymethyl)oxan
-2
-yl]oxy-4,5-dihy
droxy-2-(4-hydroxyph
enyl)-chromen-7-one |
C33H40O21 |
|
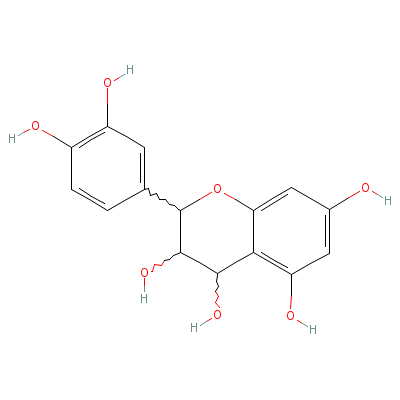
| Leucocyanidin |
480-17-1 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)chroman-3,4,5,7-t
etrol |
C15H14O7 |
|
| Leucodelphinidin |
55068-67-2 |
2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyp
henyl)chroman-3,4,5,
7-tetrol |
C15H14O8 |

|
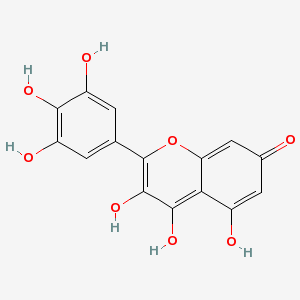
| Myricetin |
529-44-2 |
3,4,5-trihydroxy-2-(
3,4,5-trihydroxyphen
yl)-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O8 |
|
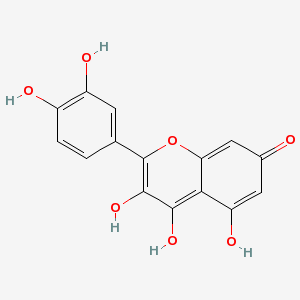
| Quercetin |
Not Available |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-3,4,5-trihydroxy
-chromen-7-one |
C15H10O7 |
|
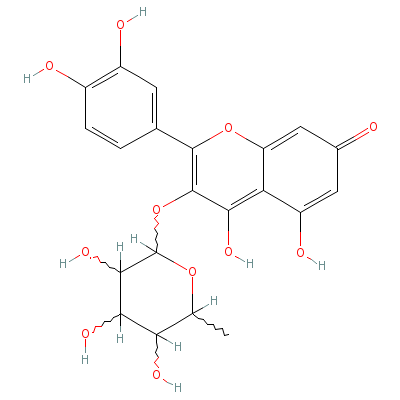
| Quercitrin |
6151-25-3 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-
(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
methyl-oxa
n-2-yl)o
xy-chromen-7-one |
C21H20O11 |
|
| Quinic acid |
36413-60-2 |
(3R,5R)-1,3,4,5-tetr
ahydroxycyclohexane-
1-carboxylic acid |
C7H12O6 |
|
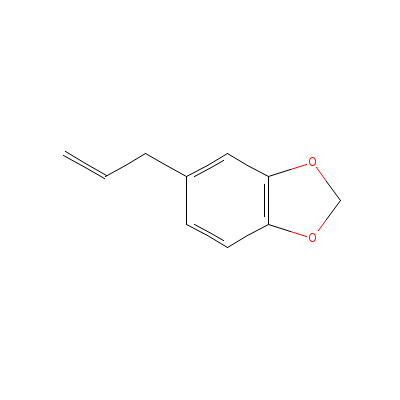
| Safrole |
Not Available |
5-prop-2-enylbenzo[1
,3]dioxole |
C10H10O2 |
|
| Saponin |
8047-15-2 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
|
| Spiraeoside |
Not Available |
3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-[
3-hydroxy-4-[(2R,3R,
4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trih
ydroxy-6-(
hydroxym
ethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-
phenyl]chromen-4-one |
C21H20O12 |
|
| Ellagitannin |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
|
| Hamamelitannin |
469-32-9 |
[2-formyl-2,3,4-trih
ydroxy-5-(3,4,5-trih
ydroxybenzoyl)oxy-pe
ntyl]
3,4,5-trihydroxybenz
oate |
C20H20O14 |
|
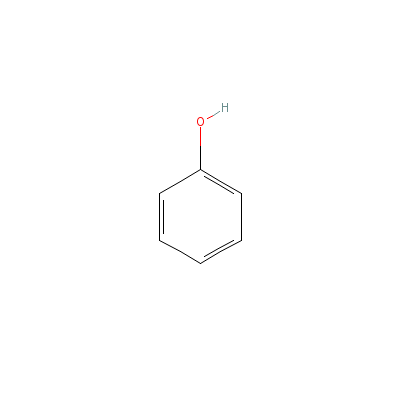
| Phenol |
8002-07-1 |
phenol |
C6H6O |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The herb is widely used as an external application to bruises, sore muscles, varicose veins, haemorrhoids, sore nipples, inflammations etc. The bark is used internally in the treatment of diarrhoea, colitis, dysentery, haemorrhoids, vaginal discharge, excessive menstruation, internal bleeding and prolapsed organs. The decoction of the bark is very useful in hemoptysis, hematemesis, and other hemorrhages, as well as in diarrhoea, dysentery, and excessive mucous discharges, with full, pale, and relaxed tissues. It may also be used as a wash or injection for sore mouth, painful tumors, external inflammations, bowel complaints, prolapsus ani and uteri, leucorrhoea, gleet, and ophthalmia. A homeopathic remedy is made from fresh bark for treating nosebleeds, piles and varicose veins. An infusion of the leaves is used to reduce inflammations, treat piles, internal haemorrhages and eye inflammations. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Excessive use, especially during lactation and pregnancy, should be avoided. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 James A Duke and Maryl Fulton. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs - 2nd Edition, P: 790-791, CRC Press July 2002. James A Duke and Maryl Fulton. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs - 2nd Edition, P: 790-791, CRC Press July 2002.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|