Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. |
English
Name |
: |
Chinese asparagus, Chinese climbing asparagus fern |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Asparagus falcatus Benth., Asparagus insularis Hance., Asparagus lucidus Lindl., Melanthium cochinchinense Lour. |
Family |
: |
Asparagaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Perennial scandent shrub with tuberous roots. Stems glabrous, spinous. Branchlets reduced to leaves (cladophylls), falciform, angular. Flowers white, small, arising in the leaf-axils. Berry globose, pale-green at first, finally white. Seeds black. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antiseptic, antitussive, diuretic, expectorant, nervine, sialagogue, stomachic, nervous stimulant and tonic (root); refrigerant (a drink made from plant). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Asparagine (root) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
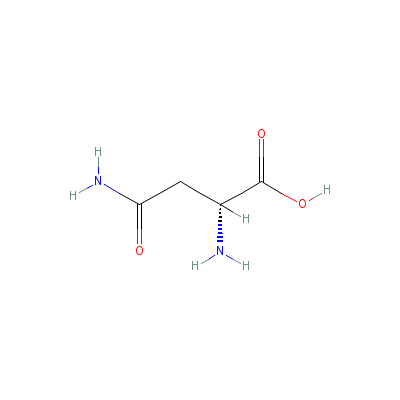
| Asparagine |
2058-58-4 |
2,4-diamino-4-oxo-bu
tanoic acid |
C4H8N2O3 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
The root is taken internally in the treatment of persistent cough, haemoptysis, sore throat, fever, dysuria, constipation and neurasthenia and often decocted with other herbs and used in the treatment of a wide range of ailments including diabetes mellitus; prolonged usage is recommended for the treatment of impotence. The plant has been used to control coughs, clear bronchial congestion, soothe inflammation, increase the flow of urine and taken internally for fevers, debility, sore throats, coughs, rhinitis, diptheria, tuberculosis and bronchitis. It is also used as a tonic for females, to treat a hacking cough, for the spitting of blood, constipation arising after fever. The leaves and flowers are crushed and left exposed to air overnight; then the juice is expressed and mixed with honey; taken for diarrhea and dysentery. |
Dealers
Products
|
|
|
|
|