| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Curcuma amada Roxb. |
English
Name |
: |
Amada, Mango ginger |
Family |
: |
Zingiberaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A rhizomatus aromatic herb having height upto 90 cm. Leaves long, petiolate, oblong-lanceolate, tapering at both ends, glabrous. Flowers white or pale yellow in spikes in the centre of the tuft of leaves. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Potentiation of amphetamine toxicity, stimulates the central nervous system, hypothermic and carminative (rhizome); fights the microorganism (Vibrio) that causes cholera and acts as a trypsin inhibitor (tuber); sweet, bitter, appetizer, alexiteric, antipyretic, aphrodisiac, laxative. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Alpha-pinene, camphor, alpha and beta- cucumene, cuminyl alcohol, turmerone and myristic acid (essential plant oil). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| alpha-Pinene |
80-56-8 |
2,7,7-trimethylbicyc
lo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene |
C10H16 |
|
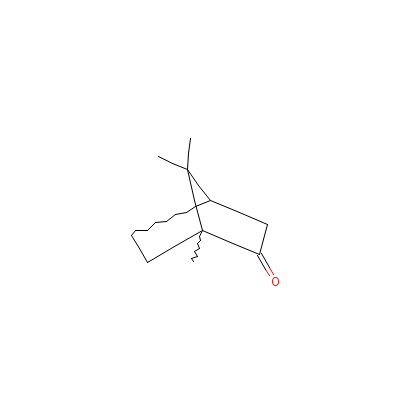
| Camphor |
8022-77-3 |
1,7,7-trimethylnorbo
rnan-2-one |
C10H16O |
|
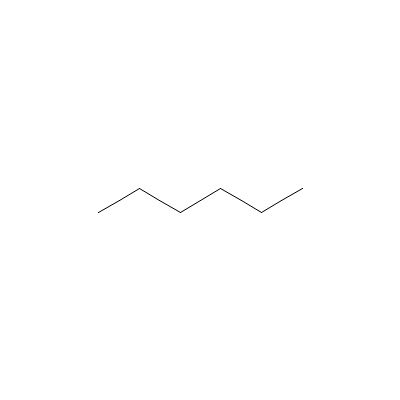
| Myristic Acid |
Not Available |
Hexane |
C6H14 |
|
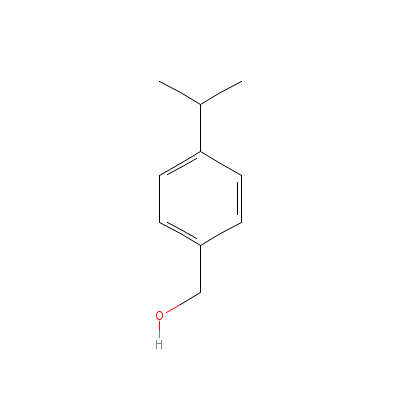
| Cuminyl alcohol |
536-60-7 |
(4-propan-2-ylphenyl
)methanol |
C10H14O |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
As a carminative, increasing the secretion of gastric juices, bruises and sprains (rhizome); biliousness, various skin related ailments, bronchitis, asthma, hiccup, inflammations etc (plant) |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|