| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Coix lachryma-jobi L. |
English
Name |
: |
Job's Tears |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Coix agrestis Lour., Coix lachryma L. |
Family |
: |
Poaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
An annual, 1 to 2 m tall, stem erect, with brace-roots from the lower nodes. Inflorescences prolific; the first glume of the male spikelet narrowly winged, the wings not covering the raceme. Seeds yellow, purple, white or brown. The grass is monoecious with separate male and female flowers. There are soft-shelled forms for eating and hard-shelled ones for ornamentation. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
The seed, with the husk removed, is antirheumatic, diuretic, pectoral, refrigerant and tonic; astringent and irritant (plant); anticancer (grain); anodyne, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antiseptic, antispasmodic, hypoglycaemic, hypotensive, sedative, vermifuge (fruits) |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
3.4-dihydroxy-benzyaldehyde glucoside (plant) and coixenolide (grain) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
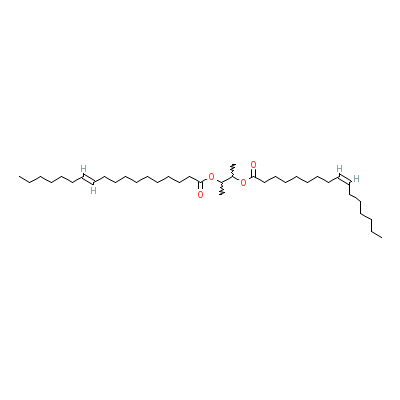
| Coixenolide |
Not Available |
3-[(Z)-hexadec-9-eno
yl]oxybutan-2-yl
(E)-octadec-11-enoat
e |
C38H70O4 |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
Menstrual problems (root); as a diuretic and tonic (seed); for abdominal tumours, oesophageal, gastrointestinal, and lung cancers, various tumours, as well as excrescences, warts, in the treatment of lung abscess, lobar pneumonia,appendicitis, rheumatoid arthritis, beriberi, diarrhoea, oedema and difficult urination (fruits); in influenza (root or young leaves). |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Coix should not be used by pregnant women. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Sharma,Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants. Sharma,Classical Uses of Medicinal Plants.
Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. |
Dealers
Products
|
|