| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Plantago ovata Forseek |
English
Name |
: |
Isphagul seeds, Psyllium |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Plantago ispaghula, Plantago decumbens |
Family |
: |
Plantaginaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A stemless or sub-caulescent soft, hairy annual. Leaves are narrowly linear or filiform, entire or distantly toothed; flowers are in cylindrical or ovoid spikes; capsules are ellipsoid, 8 mm. long, obtuse, the upper half coming off as a blunt conical lid, membranous, glabrous; seeds are ovoid-oblong, 3 mm long boat-shaped, smooth, yellowish brown. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Anticholesterolemic, demulcent, laxative, emollient. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Aucubin, fructose, linoleic acid, myristic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, tyrosine, xylose (seed); tannin (plant) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Xylose |
25990-60-7 |
oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol |
C5H10O5 |
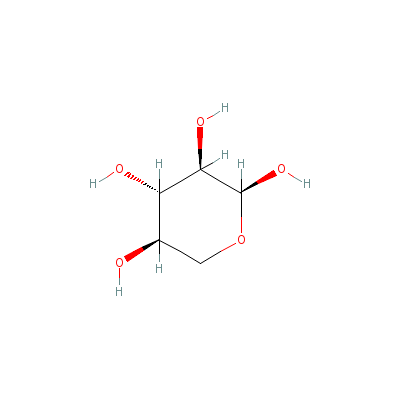
|
| Aucubin |
479-98-1 |
2-[[9-hydroxy-7-(hyd
roxymethyl)-4-oxabic
yclo[4.3.0]nona-2,7-
dien-5-yl]
oxy]-6-(
hydroxymethyl)oxane-
3,4,5-triol |
C15H22O9 |
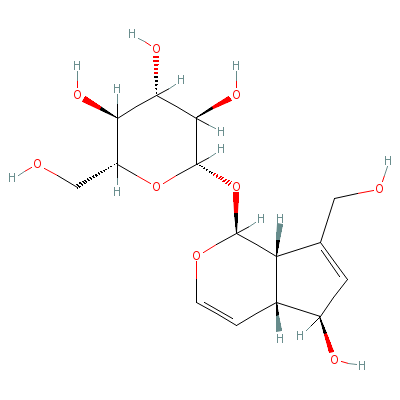
|
| Tannin |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
C27H22O18 |
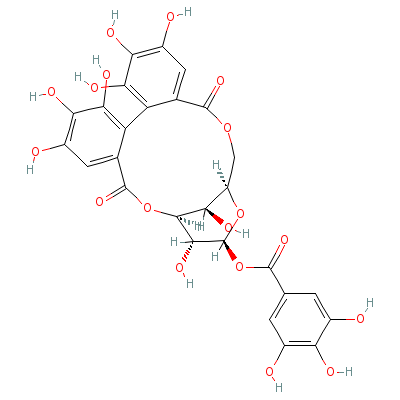
|
| Fructose |
30237-26-4 |
2,5-bis(hydroxymethy
l)oxolane-2,3,4-trio
l |
C6H12O6 |
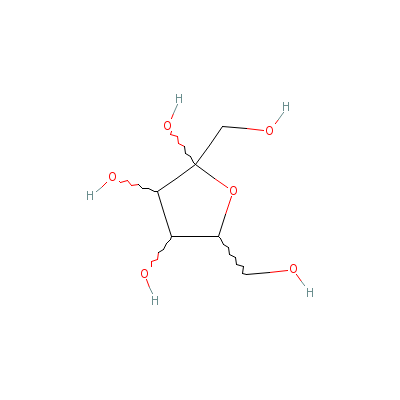
|
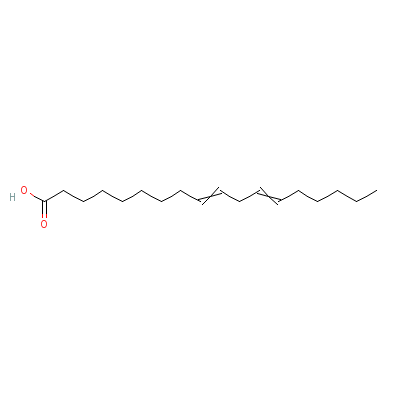
| Linoleic acid |
8024-22-4 |
Octadeca-9,12-dienoi
c acid |
C18H32O2 |
|
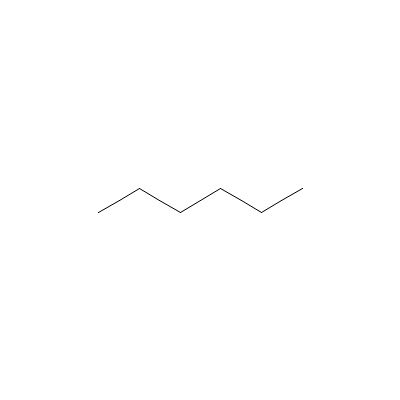
| Myristic Acid |
Not Available |
Hexane |
C6H14 |
|
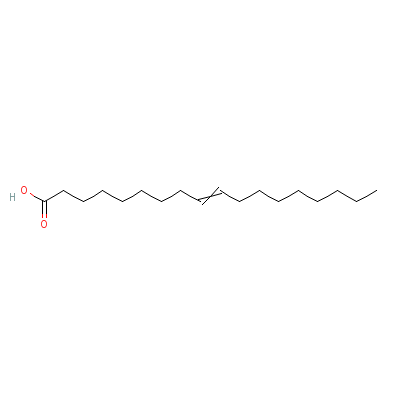
| Oleic acid |
8046-01-3 |
octadec-9-enoic acid |
C18H34O2 |
|
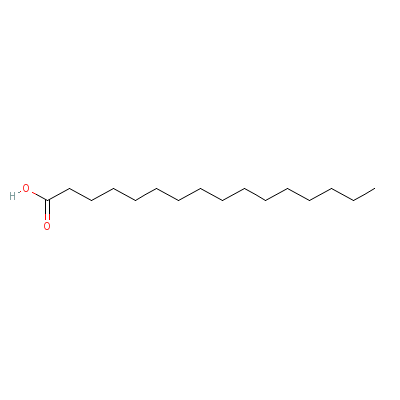
| Palmitic acid |
66321-94-6 |
Hexadecanoic acid |
C16H32O2 |
|
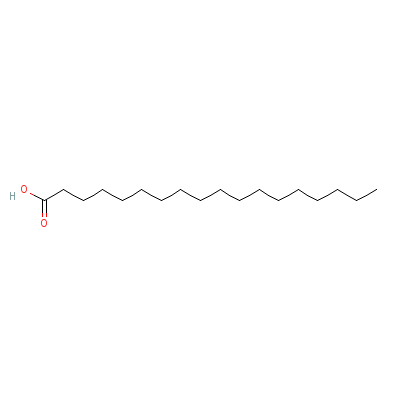
| Stearic acid |
82497-27-6 |
octadecanoic acid |
C18H36O2 |
|
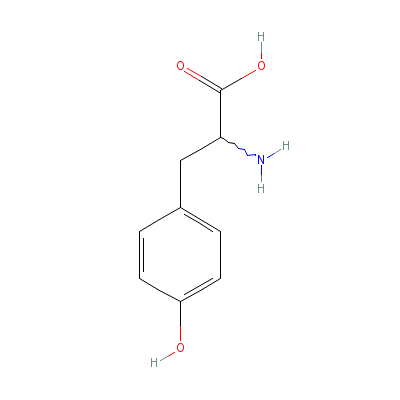
| Tyrosine |
556-02-5 |
2-amino-3-(4-hydroxy
phenyl)-propanoic
acid |
C9H11NO3 |
|
| Xylose |
25990-60-7 |
Oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol |
C5H10O5 |

|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
In the treatment of dysentery, catarrhal conditions of the genito-urinary tract, inflamed membranes of the intestinal canal etc.A decoction of seeds is prescribed in cough and cold, and the crushed seeds made into a poultice are applied to rheumatic and glandular swelling. |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Stenosis of the gastrointestinal tract. Obstruction or threatening obstruction of the bowel. Difficulties in regulating diabetes mellitus. Diabetics who are insulin-dependent may need to reduce their insulin dosage while using psyllium seeds. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Voderholzer et al., Am J Gastroenterol, 1997 92(1), 95. Voderholzer et al., Am J Gastroenterol, 1997 92(1), 95.
Anderson JW, Allgood LD, Turner J, et al. Effects of psyllium on glucose and serum lipid
responses in men with type 2 diabetes and hypercholesterolemia. Am J Clin Nutr
1999;70:466-473.
Bliss DZ, Jung HJ, Savik K, et al. Supplementation
with dietary fiber improves fecal incontinence. Nurs Res 2001;50:203-213.
Voderholzer WA, Schatke W, Muhldorfer BE,et al. Clinical response to dietary fiber treatment of chronic constipation. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92:95-98.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|