Aegle marmelos (L.) Corrêa |
| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Aegle marmelos (L.) Corrêa |
English
Name |
: |
Bael Tree, Wood apple, Bengal Quince |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Belou marmelos (L.) A. Lyons, Crataeva marmelos L., Crateva marmelos L., Cydonia indica Spach., Feronia pellucida Roth |
Family |
: |
Rutaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
Deciduous, 6–8 meters in height with trifoliate aromatic leaves. The branches sometimes bear long straight spines. The bark is shallowly furrowed and corky. The bisexual flowers are nearly 2 cm wide, borne in clusters, sweet scented and greenish white. The shallow calyx has 5 short sepals and is pubescent on the outside. The 5 petals are oblong ovoid, blunt, thick, pale greenish white and dotted with oil glands. Stamens are numerous, sometimes coherent in bundles. Ovary are oblong ovoid, slightly tapering, axis wide, cells numerous (8–20), small arranged in a circle with numerous ovules in each cell. Fruits are 5–7.5 cm in diameter, globose, oblong pyriform, rind gray or yellow, pulp sweet, thick yellow, orange to brown in color. Seeds are numerous and arranged in the cells surrounded by a slimy transparent mucilage. Seeds have wooly hairs. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Hypoglycemic (root bark); anthelmintic and antifungal (seed); antiviral, astringent, laxative, carminative, hypothermic, hemostatic and arrests secretions, antiinflammatory and antimicrobial (against Salmonella and Vibrio cholera) (fruit); antibiotic activity (fruit, leaves and roots); sweet, aromatic, cooling, alterative and nutritive (ripe fruit); laxative (fresh fruit); astringent, digestive, stomachic, and constipative (unripe fruit); stimulant, antipyretic and antiscorbutic (pulp). |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Skimmianine, umbelliferone, coumarins, aegelin, lupeol and alkaloids (leaf); gamma and beta-sitosterol (bark and root); psoralin, xanthotoxin, scopoletin and tembamide (root); marmarin (fruit). |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Skimmianine |
83-95-4 |
Not available |
C14H13NO4 |
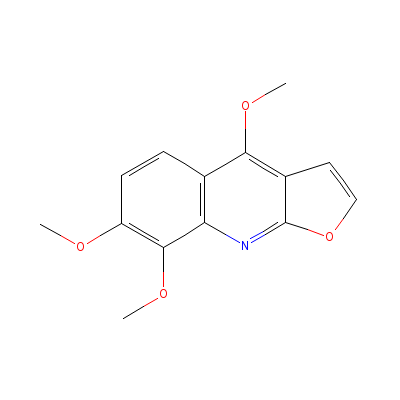
|
| Umbelliferone |
93-35-6 |
2-hydroxychromen-7-o
ne |
C9H6O3 |
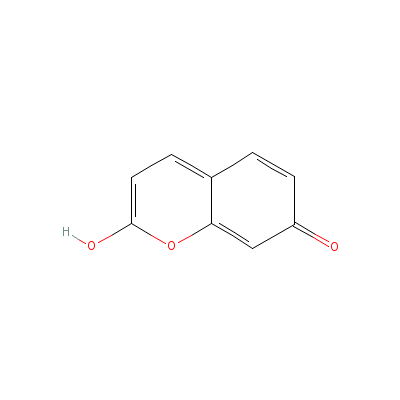
|
| Coumarins |
81-81-2 |
2-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1
-phenyl-butyl)-chrom
en-4-one |
C19H16O4 |
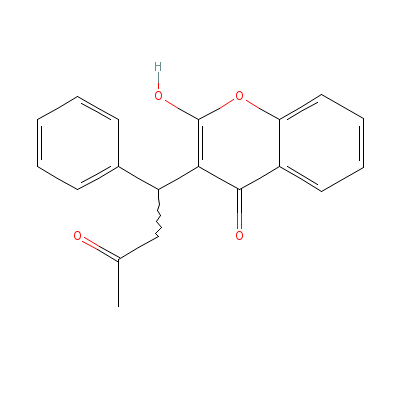
|
| Lupeol |
Not Available |
Not Available |
C30H50O |
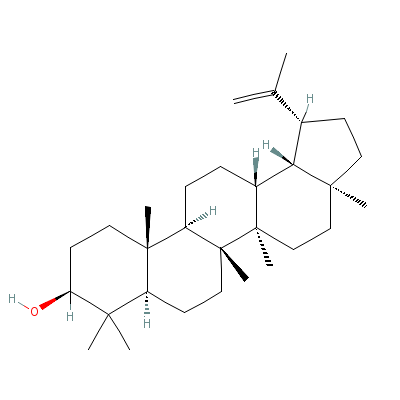
|
| Xanthotoxin |
298-81-7 |
Not Availbale |
C12H8O4 |
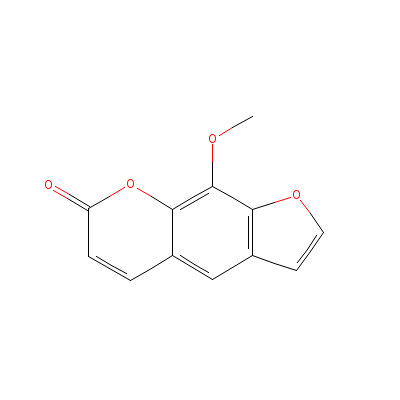
|
| Scopoletin |
92-61-5 |
2-hydroxy-6-methoxy-
chromen-7-one |
C10H8O4 |
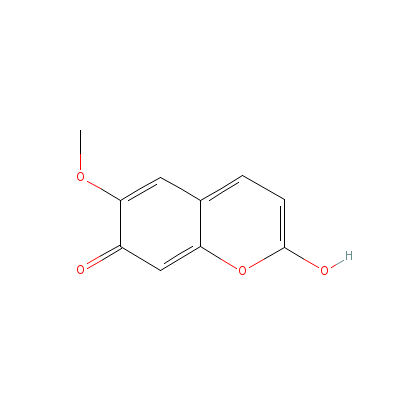
|
| Tembamide |
50802-66-9 |
N-[2-hydroxy-2-(4-me
thoxyphenyl)-ethyl]b
enzamide |
C16H17NO3 |
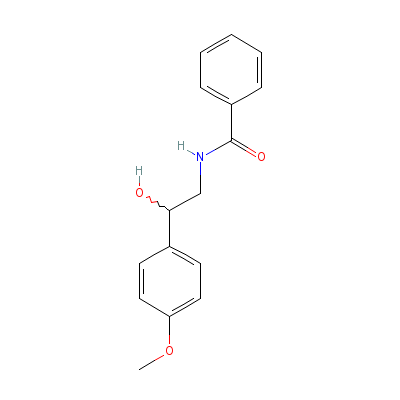
|
| Beta-Sitosterol |
5779-62-4 |
17-(5-ethyl-6-methyl
-heptan-2-yl)-10,13-
dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9
,11,12,14,
15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cycl
openta[a]phenanthren
-3-ol |
C29H50O |
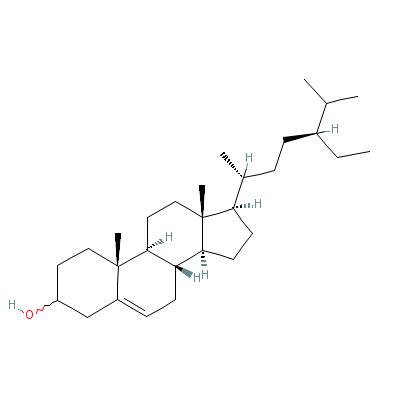
|
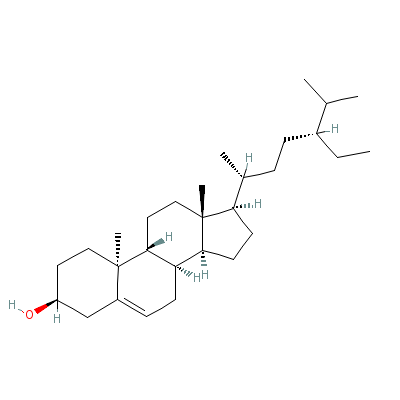
| gamma-Sitosterol |
83-46-5 |
17-(4-ethyl-1,5-dime
thyl-hexyl)-10,13-di
methyl-2,3,4,7,8,9,1
0,11,12,13
,14,15,1
6,17-tetradecahydro-
1H-cyclopenta[a]phen
anthren-3-ol |
C29H50O |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
In ophthalmia and jaundice (leaf); in constipation, cholera, dysentery, diarrhea and intestinal ulcers (fruit); leucoderma, to alleviate asthma (leaf decoction); in diabetes (root bark); in scurvy (fruit pulp). |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
The leaves are said to cause abortion and sterility in women. The bark is used as a fish poison in the Celebes. Tannin, ingested frequently and in quantity over a long period of time, is antinutrient and carcinogenic. |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Uniyal et al., Medicinal Flora of Garhwal Himalayas.
|
Dealers
Products
|
|