| |
|
|
Botanical Name |
: |
Tamarindus indica L. |
English
Name |
: |
Tamarind Tree |
Synonym(s) |
: |
Tamarindus officinalis (Hook), Tamarindus occidentalis, Gaertn. |
Family |
: |
Caesalpiniaceae |
| |
General Info
| Description |
 |
|
A large handsome tree with spreading branches and a thick straight trunk, ash-grey bark, height up to 40 feet. Leaves alternate, abruptly pinnated; leaflets light green and a little hairy, in twelve to fifteen pairs. In cold damp weather and after sunset the leaflets close. Flowers fragrant, yellow-veined, red and purple filaments, in terminal and lateral racemes. Legume oblong, pendulous, nearly linear, curved, somewhat compressed, filled with a firm acid pulp. Bark hard and scabrous, never separates into valves; inside the bark are three fibres, one down, on the upper concave margin, the other two at equal distances from the convex edge. Seeds six to twelve, covered with a shiny smooth brown shell, and inserted into the convex side of the pericarp. |
| Herb Effects |
 |
|
Antiviral (flower); laxative and reduces fever (fruit pulp); astringent (seed); refrigerants in fevers and as laxatives and carminatives. |
Chemistry
| Active Ingredients |
 |
|
Tartaric and malic acids (fruit and leaf); orientin, iso-orientin, vitexin and iso-vitexin (leaf); tannic acid (seed); acetic acid, alpha-terpineol, citric acid, limonene, safrole (fruit); ascorbic acid, beta-carotene, cinnamaldehyde (flower) |
| Chemistry
of Active Ingredients |
 |
|
|
 |
Name |
CAS# |
IUPAC Name |
Formula |
Structure |
 |
|
| Tartaric acid |
526-83-0 |
2,3-dihydroxybutaned
ioic acid |
C4H6O6 |
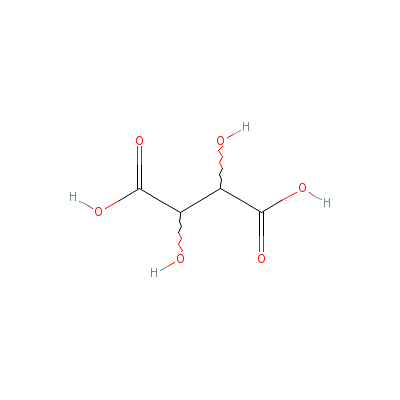
|
| Malic acid |
Not Available |
2-hydroxybutanedioic
acid |
C4H6O5 |
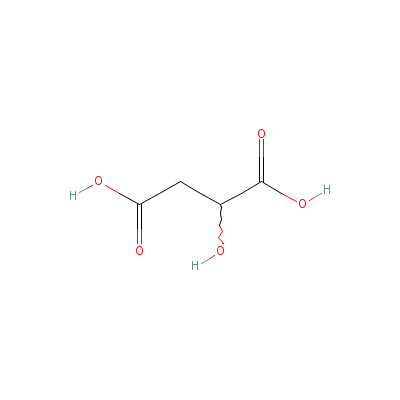
|
| Orientin |
28608-75-5 |
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphen
yl)-4,7-dihydroxy-8-
[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-
(hydroxyme
thyl)oxa
n-2-yl]-chromen-5-on
e |
C21H20O11 |
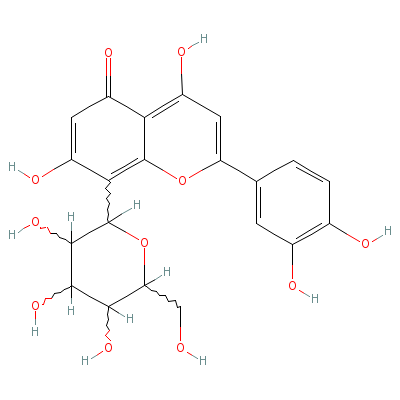
|
| Vitexin |
521-33-5 |
4,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-h
ydroxyphenyl)-8-[3,4
,5-trihydroxy-6-(hyd
roxymethyl
)oxan-2-
yl]-chromen-5-one |
C21H20O10 |
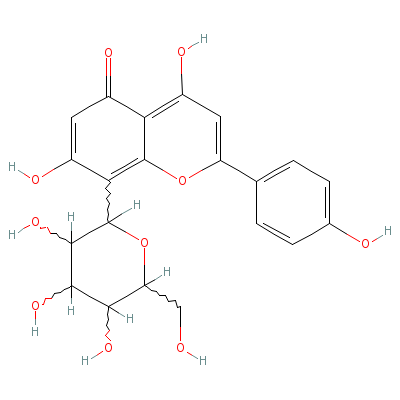
|
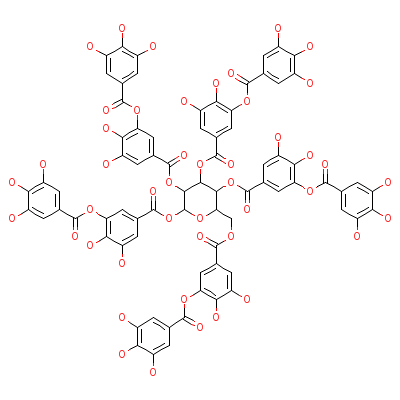
| Tannic acid |
1401-55-4 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
|
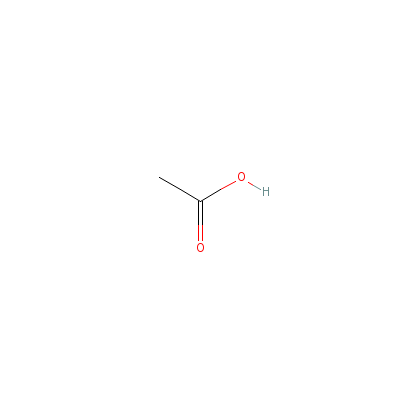
| Acetic acid |
77671-22-8 |
acetic acid |
C2H4O2 |
|
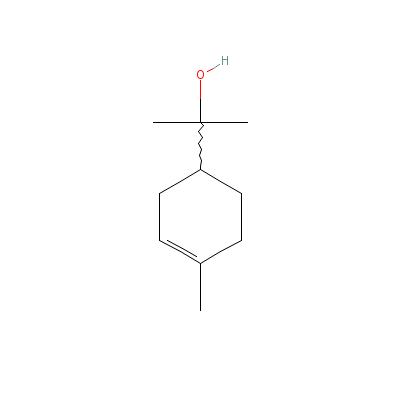
| alpha-Terpineol |
10482-56-1 |
2-(4-methyl-1-cycloh
ex-3-enyl)propan-2-o
l |
C10H18O |
|
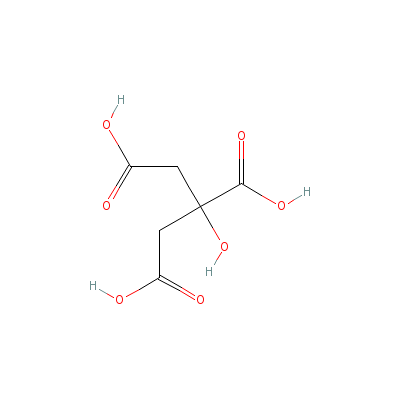
| Citric acid |
Not Available |
2-hydroxypropane-1,2
,3-tricarboxylic
acid |
C6H8O7 |
|
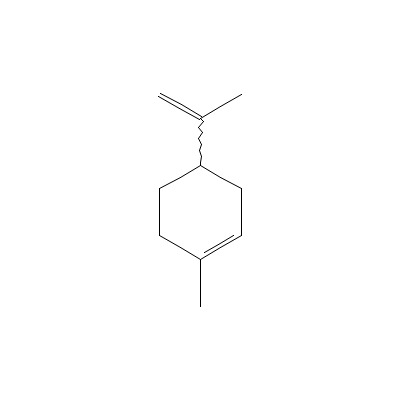
| Limonene |
9003-73-0 |
1-methyl-4-prop-1-en
-2-yl-cyclohexene |
C10H16 |
|
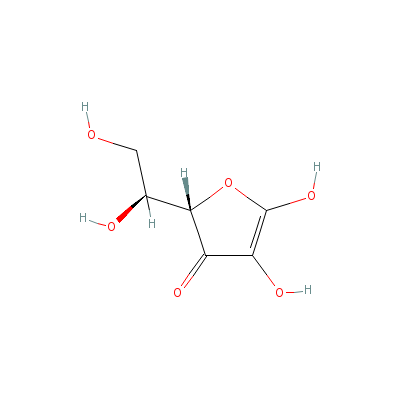
| Ascorbic acid |
Not Available |
2-(1,2-dihydroxyethy
l)-4,5-dihydroxy-fur
an-3-one |
C6H8O6 |
|
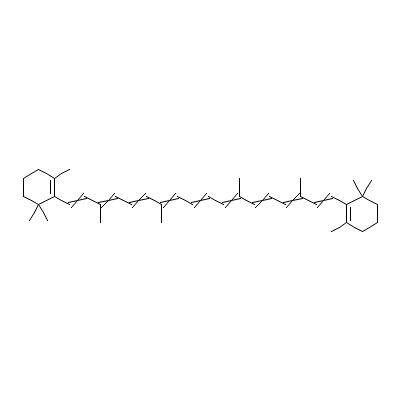
| beta-Carotene |
Not Available |
3,7,12,16-tetramethy
l-1,18-bis(2,6,6-tri
methyl-1-cyclohexeny
l)-octadec
a-1,3,5,
7,9,11,13,15,17-nona
ene |
C40H56 |
|
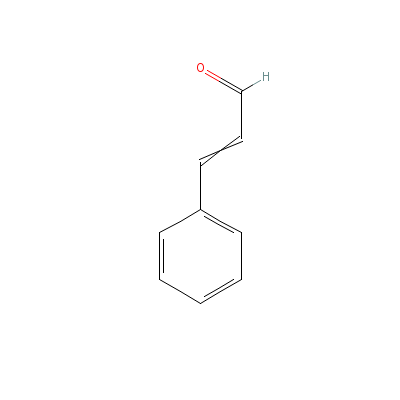
| Cinnamaldehyde |
Not Available |
3-phenylprop-2-enal |
C9H8O |
|
|
Pharmacology
| Medicinal Use |
 |
|
As an astringent in bowel complaints, to weaken the action of resinous cathartics (pulp); in correcting bilious disorders, for rheumatism (plant); used in subacid infusions, and a decoction is said to destroy worms in children, and is also useful for jaundice, and externally as a wash for sore eyes and ulcers (leaves)In some forms of sore throat the fruit has been found of service; for asthma (bark). |
| Contraindication |
 |
|
Chloroquine bioavailability in healthy men is lowered by Aradaib (Tamarindus indica), Karkadi (Hibiscus sabdarifa) & Lemon (Citrus limetta) compared with water. AUC=2.6, 2.2 & 2.4 & 7.5 mg.h/L; Tmax=3.2, 2.6, 2.5 & 3.0 h (Mahmoud et al., 1994). |
| Reference |
 |
|
 Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India. Chandel et al., Biodiversity in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in India.
Bentley and Trimen, Medicinal Plants
Johnson T. CRC Ethnobotany Desk Reference (www.herbweb.com/herbage). |
Dealers
Products
|
|